转载自:https://blog.csdn.net/anita9999/article/details/82346552
问题
在开发的时候一段字符串的中间某一部分是需要可变的 比如一个Textview需要显示”XXX用户来自 上海 年龄 21 性别 男”
其中的 XXX 是用户名 每个用户也是不一样的
地区 上海 为可变的string数据
年龄 21 为可变的int数据
性别 男 为可变的string数据
遇到这种情况你们是怎么样解决的呢?把这段字符串保存在常量类里吗?不!我们应该遵循Google的开发模式
XML
1 <string name="user_info'> %1$s</span> 用户来自 <span class="hljs-variable">%2</span><span class="hljs-variable">$s 年龄 %3$d</span> 性别 <span class="hljs-variable">%4</span><span class="hljs-variable">$s</string>
JAVA
1 String userName="XXX"; 2 String userProvince="上海"; 3 int userAge=21; 4 String userSex="男"; 5 String string=getResources().getString(R.string.user_info); 6 String userInfo=String.format(string,userName,userProvince,userAge,userSex);
是不是觉得很方便
本来是打算当笔记记录下来备忘的,但是有朋友有朋友问到的一些相关的东西,我就完善一下吧
String.format()字符串常规类型格式化的两种重载方式
- format(String format, Object… args) 新字符串使用本地语言环境,制定字符串格式和参数生成格式化的新字符串。
- format(Locale locale, String format, Object… args) 使用指定的语言环境,制定字符串格式和参数生成格式化的字符串。
上个栗子有用到了字符类型和整数类型的格式化 下面我把常用的类型例举出来
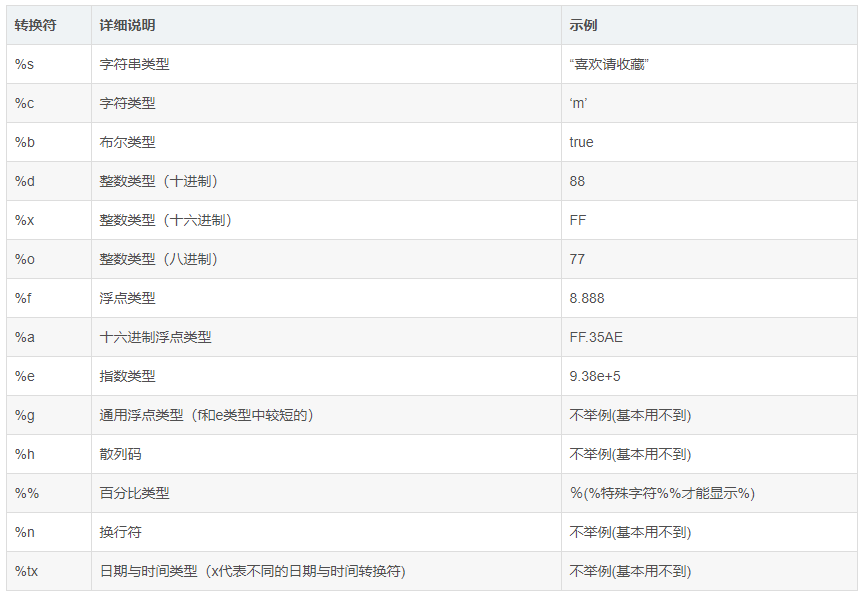
为了方便理解还是举个例子
1 String str=null; 2 str=String.format("Hi,%s", "小超"); 3 System.out.println(str); 4 str=String.format("Hi,%s %s %s", "小超","是个","大帅哥"); 5 System.out.println(str); 6 System.out.printf("字母c的大写是:%c %n", 'C'); 7 System.out.printf("布尔结果是:%b %n", "小超".equal("帅哥")); 8 System.out.printf("100的一半是:%d %n", 100/2); 9 System.out.printf("100的16进制数是:%x %n", 100); 10 System.out.printf("100的8进制数是:%o %n", 100); 11 System.out.printf("50元的书打8.5折扣是:%f 元%n", 50*0.85); 12 System.out.printf("上面价格的16进制数是:%a %n", 50*0.85); 13 System.out.printf("上面价格的指数表示:%e %n", 50*0.85); 14 System.out.printf("上面价格的指数和浮点数结果的长度较短的是:%g %n", 50*0.85); 15 System.out.printf("上面的折扣是%d%% %n", 85); 16 System.out.printf("字母A的散列码是:%h %n", 'A');
输出结果
1 Hi,小超 2 Hi,小超 是个 大帅哥 3 字母c的大写是:C 4 布尔的结果是:false 5 100的一半是:50 6 100的16进制数是:64 7 100的8进制数是:144 8 50元的书打8.5折扣是:42.500000 元 9 上面价格的16进制数是:0x1.54p5 10 上面价格的指数表示:4.250000e+01 11 上面价格的指数和浮点数结果的长度较短的是:42.5000 12 上面的折扣是85% 13 字母A的散列码是:41
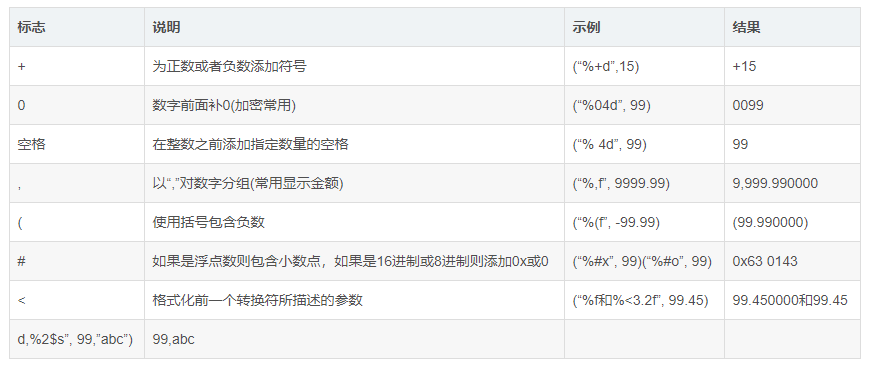
###搭配转换符还有实现高级功能 第一个例子中有用到 $
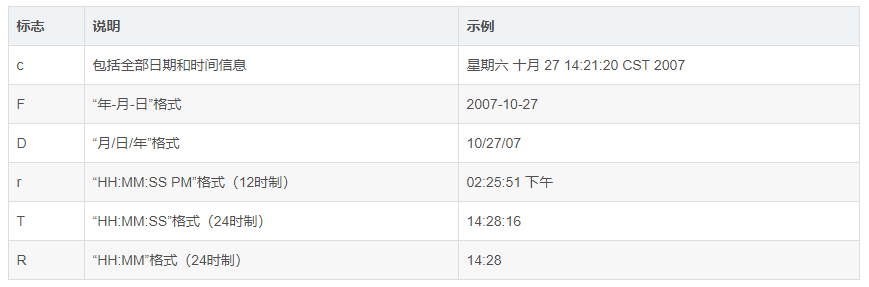
第一个例子中有说到 %tx x代表日期转换符 我也顺便列举下日期转换符
来个例子方便理解
1 Date date=new Date(); 2 //c的使用 3 System.out.printf("全部日期和时间信息:%tc%n",date); 4 //f的使用 5 System.out.printf("年-月-日格式:%tF%n",date); 6 //d的使用 7 System.out.printf("月/日/年格式:%tD%n",date); 8 //r的使用 9 System.out.printf("HH:MM:SS PM格式(12时制):%tr%n",date); 10 //t的使用 11 System.out.printf("HH:MM:SS格式(24时制):%tT%n",date); 12 //R的使用 13 System.out.printf("HH:MM格式(24时制):%tR",date);
输出结果:
1 全部日期和时间信息:星期三 九月 21 22:43:36 CST 2016 2 年-月-日格式:2016-09-21 3 月/日/年格式:16/10/21 4 HH:MM:SS PM格式(12时制):10:43:36 下午 5 HH:MM:SS格式(24时制):22:43:36 6 HH:MM格式(24时制):22:43
转载自:https://blog.csdn.net/anita9999/article/details/82346552