PriorityQueue是一个优先级队列,底层是小顶堆实现
概念
- 优先级队列
通常的队列是先进先出,那有一种特殊的队列并不是先进先出,而是根据优先级的顺序出队
- 二叉堆
二叉堆是一种数据结构,堆是一种特殊的二叉树,满足一下条件的二叉树
1.该二叉树必须是一个完全二叉树。
2.子节点的值总是单调的。这里又分为两种情况,如果子节点总是小于等于父节点,那么整体的树顶元素就越大,那么我们叫它大顶堆,反过来子节点总是大于等于父节点,那么我们叫它小顶堆
- 完全二叉树
元素是按照从上到下层级,从左到右的顺序排列的树形结构
- 堆
上面我们说了二叉堆,那么其实堆也可以是多叉堆,多叉堆同理也有上面两个类似性质。1.完全多叉树 2.父子节点单调性
二叉堆
虽说这里的数据结构是二叉树,但实际装数据的容器,或者说底层还是使用的数组,PriorityQueue中源码:
transient Object[] queue; // non-private to simplify nested class access
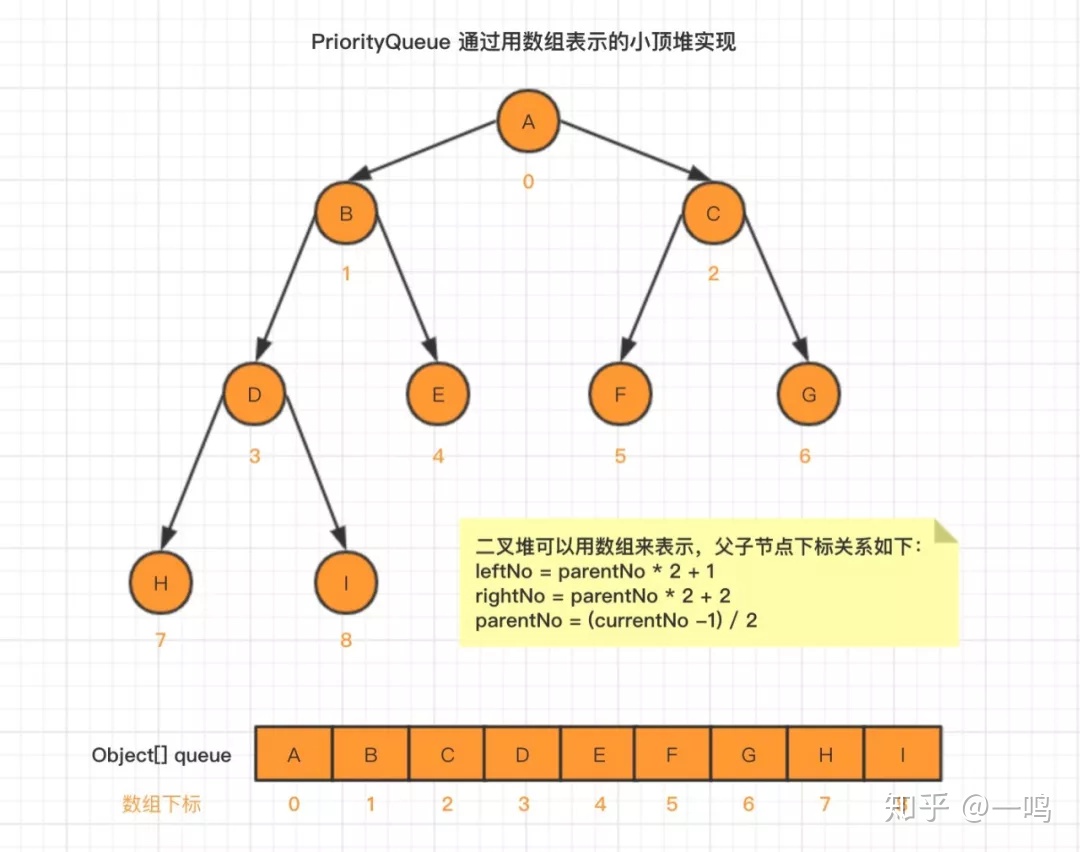
在上图中,我们给每个元素的下标做了标注,足够细心的你会发现,数组下标,存在以下关系:
leftNo = parentNo * 2 + 1
rightNo = parentNo * 2 + 2
parentNo = (currentNo -1) / 2
这样一来,我们在得到任意节点的情况下,就能通过该公式找到它的父节点和子节点
入堆
当有了基础的概念和理论之后,我们来构建堆,像堆中加入元素就是构建堆的一个过程。
/**
* Inserts the specified element into this priority queue.
*
* @return {@code true} (as specified by {@link Collection#add})
* @throws ClassCastException if the specified element cannot be
* compared with elements currently in this priority queue
* according to the priority queue's ordering
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified element is null
*/
public boolean add(E e) {
return offer(e);
}
/**
* Inserts the specified element into this priority queue.
*
* @return {@code true} (as specified by {@link Queue#offer})
* @throws ClassCastException if the specified element cannot be
* compared with elements currently in this priority queue
* according to the priority queue's ordering
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified element is null
*/
public boolean offer(E e) {
if (e == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
modCount++;
int i = size;
if (i >= queue.length) //如果queue数组中的数据满了,扩容
grow(i + 1);
siftUp(i, e); //siftUp,上浮元素
size = i + 1;
return true;
}
private void siftUp(int k, E x) {
if (comparator != null)//比较器优先
siftUpUsingComparator(k, x, queue, comparator);
else
siftUpComparable(k, x, queue);
}
/**
* Increases the capacity of the array.
*
* @param minCapacity the desired minimum capacity
*/
private void grow(int minCapacity) {
int oldCapacity = queue.length;
// Double size if small; else grow by 50%
int newCapacity = ArraysSupport.newLength(oldCapacity,
minCapacity - oldCapacity, /* minimum growth */
oldCapacity < 64 ? oldCapacity + 2 : oldCapacity >> 1
/* preferred growth */);
queue = Arrays.copyOf(queue, newCapacity);
}
offer方法中我们可以看到的流程
- 如果queue数组中的数据满了,扩容
- siftUp,上浮元素
- 因为元素的父子元素具有单调性,所以可以通过比较,和父节点交换位置,直到找到它合适的位置
- 这里我们看到的是 比较器(siftUpUsingComparator)优先。
- 合适的位置指的是 满足 单调性 的位置
- 因为元素的父子元素具有单调性,所以可以通过比较,和父节点交换位置,直到找到它合适的位置
出堆
/**
* Retrieves and removes the head of this queue,
* or returns {@code null} if this queue is empty.
*
* @return the head of this queue, or {@code null} if this queue is empty
*/
public E poll() {
final Object[] es;
final E result;
if ((result = (E) ((es = queue)[0])) != null) {//取出第一个元素(索引为0)
modCount++;
final int n;
final E x = (E) es[(n = --size)];//获得最后一个元素
es[n] = null;//最后一个元素置空
if (n > 0) {
final Comparator<? super E> cmp;
if ((cmp = comparator) == null) //比较器优先
siftDownComparable(0, x, es, n);//然后做下层操作
else
siftDownUsingComparator(0, x, es, n, cmp);//然后做下层操作
}
}
return result;
}
private static <T> void siftDownComparable(int k, T x, Object[] es, int n) {
// assert n > 0;
Comparable<? super T> key = (Comparable<? super T>)x;
int half = n >>> 1; // loop while a non-leaf
while (k < half) {
int child = (k << 1) + 1; // assume left child is least
Object c = es[child];
int right = child + 1;
if (right < n &&
((Comparable<? super T>) c).compareTo((T) es[right]) > 0)
c = es[child = right];
if (key.compareTo((T) c) <= 0)
break;
es[k] = c;
k = child;
}
es[k] = key;
}
private static <T> void siftDownComparable(int k, T x, Object[] es, int n) {
// assert n > 0;
Comparable<? super T> key = (Comparable<? super T>)x;
int half = n >>> 1; // loop while a non-leaf
while (k < half) {
int child = (k << 1) + 1; // assume left child is least 翻译 假设左孩子是更小的
Object c = es[child];
int right = child + 1;
if (right < n &&
((Comparable<? super T>) c).compareTo((T) es[right]) > 0)
c = es[child = right]; //得到较小的孩子
if (key.compareTo((T) c) <= 0) //用教小的孩子做比较,做交换
break;
es[k] = c;
k = child;
}
es[k] = key;
}
poll过程如下
- 首先取出索引为0的元素,堆顶元素
- 把索引最大的元素拿到堆顶做下沉操作
- 如果PriorityQueue构造的时候拥有比较器就用比较器来做下沉比较,否者使用元素继承的Comparable比较性做比较
Queue常见对外方法
- boolean add(e) 添加
- boolean offer(E e) 同add相同
- E poll() 取出堆顶元素,也就是数组索引为0的元素,size会减少。size=0时会得到 null
- E peek() 读取堆顶元素,size不会减少。size=0时会得到 null
- E remove() 和poll()功能相同,只是会@throws NoSuchElementException if this queue is empty
- E element() 和peek()功能相同,只是会@throws NoSuchElementException if this queue is empty