前言
有书这么说过,C++设计的最大目的在于允许程序员定义自己的类型,并使它们用起来跟内置类型一样容易和直观。就目前看来,要实现这一点,最核心的莫过于操作符的重载。科学的重载可以让类的使用最大程度地接近内置类型。本文将讨论类操作符重载涉及到的一些原则和具体做法。
实现类操作符重载的两种思路
1. 友元函数法: 将待重载操作符视作非成员函数( 它声明为操作数类型的友元函数 )
应当采用这种机制重载的运算符有:IO操作符,算数操作符,关系操作符。
2. 成员函数法: 将待重载操作符视作特殊的成员函数。
应当采用这种机制重载的运算符有:赋值操作符,下标操作符,箭头操作符,自增自减操作符。
对于其他的操作符,两种机制均可。至于为什么这么规定,请参阅相关C++教材,本文不详述。
示例一:输出操作符的重载( 友元函数法 )
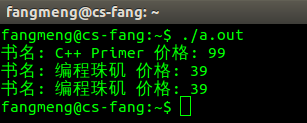
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <string> 3 4 using namespace std; 5 6 /* 7 * 定义一个简单的书类 8 */ 9 class Book { 10 public: 11 // 将输出操作符函数设定为书类的友元函数 12 friend ostream & operator<< (ostream & out,const Book &b ); 13 Book(string bookName, double price) { 14 this->bookName = bookName; 15 this->price = price; 16 } 17 string getName() const { 18 return bookName; 19 } 20 double getPrice() const { 21 return price; 22 } 23 private: 24 string bookName; 25 double price; 26 }; 27 28 /* 29 * 下为输出操作符重载函数 30 * 对象设置为引用类型的目的仅仅是为了避免复制,故加上const声明。 31 */ 32 ostream & 33 operator<< (ostream & out, const Book &b) { 34 out << "书名: " << b.getName() << " 价格: " << b.getPrice(); 35 36 return out; 37 } 38 39 int main() 40 { 41 Book book1("C++ Primer", 99.0); 42 Book book2("编程珠矶", 39.0); 43 44 /* 45 * 像使用内置类型一样使用对象 46 */ 47 cout << book1 << endl; 48 cout << book2 << endl; 49 50 return 0; 51 }
运行结果:
小结1
1. 输出操作符的格式化操作应当尽量少
2. 为什么说IO操作符重载不能够用成员函数法重载?请查阅C++相关教材。
示例二:赋值操作符的重载( 成员函数法 )
接上例:
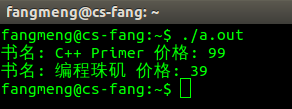
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <string> 3 4 using namespace std; 5 6 /* 7 * 定义一个简单的书类 8 */ 9 class Book { 10 public: 11 // 将输出操作符函数设定为书类的友元函数 12 friend ostream & operator<< (ostream & out,const Book &b ); 13 /* 14 * 下为输出操作符重载函数 15 * 对象设置为引用类型的目的仅仅是为了避免复制,故加上const声明。 16 */ 17 Book & operator= (const Book &b) { 18 bookName = b.getName(); 19 price = b.getPrice(); 20 21 return *this; 22 } 23 Book(string bookName, double price) { 24 this->bookName = bookName; 25 this->price = price; 26 } 27 string getName() const { 28 return bookName; 29 } 30 double getPrice() const { 31 return price; 32 } 33 private: 34 string bookName; 35 double price; 36 }; 37 38 /* 39 * 下为输出操作符重载函数 40 * 对象设置为引用类型的目的仅仅是为了避免复制,故加上const声明。 41 */ 42 ostream & 43 operator << (ostream & out, const Book &b) { 44 out << "书名: " << b.getName() << " 价格: " << b.getPrice(); 45 46 return out; 47 } 48 49 int main() 50 { 51 Book book1("C++ Primer", 99.0); 52 Book book2("编程珠矶", 39.0); 53 54 /* 55 * 像使用内置类型一样使用对象 56 */ 57 cout << book1 << endl; 58 cout << book2 << endl; 59 60 // 将book2赋值给book1后输出 61 book1 = book2; 62 cout << book1 << endl; 63 64 return 0; 65 }
运行结果