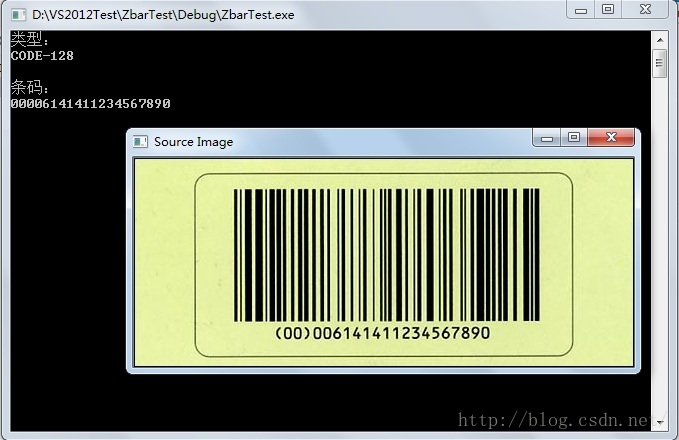
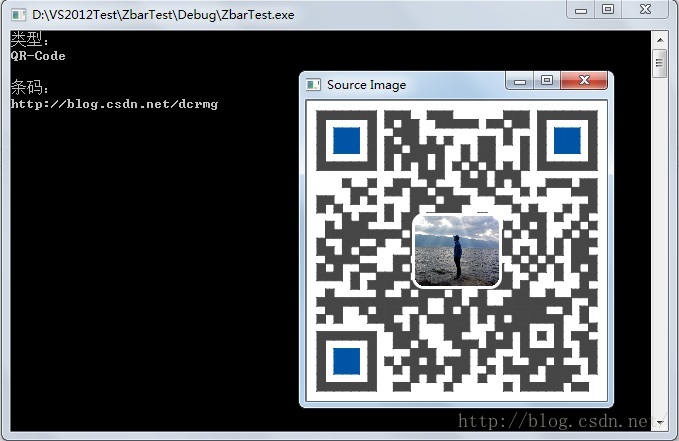
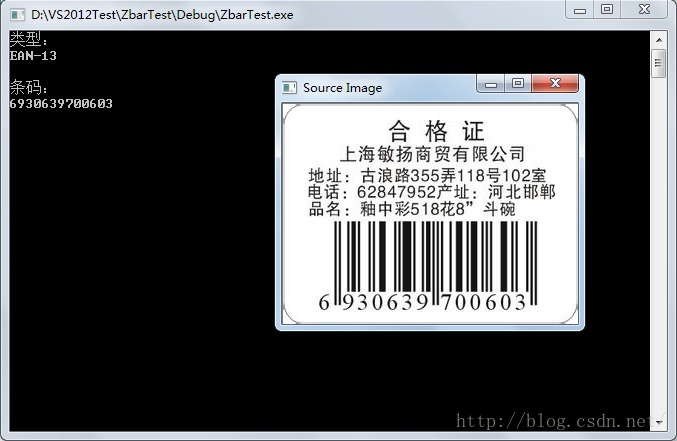
使用Opencv+Zbar组合可以很容易的识别图片中的二维码,特别是标准的二维码,这里标准指的是二维码成像清晰,图片中二维码的空间占比在40%~100%之间,这样标准的图片,Zbar识别起来很容易,不需要Opencv额外的处理。
下边这个例程演示两者配合对条形码和二维码的识别:
#include "zbar.h"
#include "cv.h"
#include "highgui.h"
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
using namespace zbar; //添加zbar名称空间
using namespace cv;
int main(int argc,char*argv[])
{
ImageScanner scanner;
scanner.set_config(ZBAR_NONE, ZBAR_CFG_ENABLE, 1);
Mat image = imread(argv[1]);
Mat imageGray;
cvtColor(image,imageGray,CV_RGB2GRAY);
int width = imageGray.cols;
int height = imageGray.rows;
uchar *raw = (uchar *)imageGray.data;
Image imageZbar(width, height, "Y800", raw, width * height);
scanner.scan(imageZbar); //扫描条码
Image::SymbolIterator symbol = imageZbar.symbol_begin();
if(imageZbar.symbol_begin()==imageZbar.symbol_end())
{
cout<<"查询条码失败,请检查图片!"<<endl;
}
for(;symbol != imageZbar.symbol_end();++symbol)
{
cout<<"类型:"<<endl<<symbol->get_type_name()<<endl<<endl;
cout<<"条码:"<<endl<<symbol->get_data()<<endl<<endl;
}
imshow("Source Image",image);
waitKey();
imageZbar.set_data(NULL,0);
return 0;
} 二维码:
这样“标准的”二维码是Zbar非常拿手的,能准确快速的检测出来,包括在条形码外有部分其他信息的,也是小菜一碟:
Zbar很省心,我们还是可以为它做点什么的,比如在一些情况下,需要把条形码裁剪出来,这就涉及到条形码位置的定位,这篇文章准备记录一下如何定位条形码,在定位之后再把裁剪出来的条形码区域丢给Zbar识别读码。
方法一. 水平、垂直方向投影
#include "zbar.h"
#include "cv.h"
#include "highgui.h"
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
using namespace zbar; //添加zbar名称空间
using namespace cv;
//***********************************************
// 函数通过水平和垂直方向投影,找到两个方向上投影的交叉矩形,定位到条形码/二维码
// int threshodValue 投影的最少像素单位
// int binaryzationValue 原图像阈值分割值
//***********************************************
Rect DrawXYProjection(const Mat image,Mat &imageOut,const int threshodValue,const int binaryzationValue);
int main(int argc,char*argv[])
{
Mat image = imread(argv[1]);
Mat imageCopy=image.clone();
Mat imageGray,imagOut;
cvtColor(image,imageGray,CV_RGB2GRAY);
Rect rect(0,0,0,0);
rect= DrawXYProjection(image,imagOut,image.rows/10,100);
Mat roi=image(rect);
//画出条形码的矩形框
rectangle(imageCopy,Point(rect.x,rect.y),Point(rect.x+rect.width,rect.y+rect.height),Scalar(0,0,255),2);
imshow("Source Image",image);
imshow("水平垂直投影",imagOut);
imshow("Output Image",roi);
imshow("Source Image Rect",imageCopy);
waitKey();
return 0;
}
Rect DrawXYProjection(const Mat image,Mat &imageOut,const int threshodValue,const int binaryzationValue)
{
Mat img=image.clone();
if(img.channels()>1)
{
cvtColor(img,img,CV_RGB2GRAY);
}
Mat out(img.size(),img.type(),Scalar(255));
imageOut=out;
//对每一个传入的图片做灰度归一化,以便使用同一套阈值参数
normalize(img,img,0,255,NORM_MINMAX);
vector<int> vectorVertical(img.cols,0);
for(int i=0;i<img.cols;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<img.rows;j++)
{
if(img.at<uchar>(j,i)<binaryzationValue)
{
vectorVertical[i]++;
}
}
}
//列值归一化
int high=img.rows/6;
normalize(vectorVertical,vectorVertical,0,high,NORM_MINMAX);
for(int i=0;i<img.cols;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<img.rows;j++)
{
if(vectorVertical[i]>threshodValue)
{
line(imageOut,Point(i,img.rows),Point(i,img.rows-vectorVertical[i]),Scalar(0));
}
}
}
//水平投影
vector<int> vectorHorizontal(img.rows,0);
for(int i=0;i<img.rows;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<img.cols;j++)
{
if(img.at<uchar>(i,j)<binaryzationValue)
{
vectorHorizontal[i]++;
}
}
}
normalize(vectorHorizontal,vectorHorizontal,0,high,NORM_MINMAX);
for(int i=0;i<img.rows;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<img.cols;j++)
{
if(vectorHorizontal[i]>threshodValue)
{
line(imageOut,Point(img.cols-vectorHorizontal[i],i),Point(img.cols,i),Scalar(0));
}
}
}
//找到投影四个角点坐标
vector<int>::iterator beginV=vectorVertical.begin();
vector<int>::iterator beginH=vectorHorizontal.begin();
vector<int>::iterator endV=vectorVertical.end()-1;
vector<int>::iterator endH=vectorHorizontal.end()-1;
int widthV=0;
int widthH=0;
int highV=0;
int highH=0;
while(*beginV<threshodValue)
{
beginV++;
widthV++;
}
while(*endV<threshodValue)
{
endV--;
widthH++;
}
while(*beginH<threshodValue)
{
beginH++;
highV++;
}
while(*endH<threshodValue)
{
endH--;
highH++;
}
//投影矩形
Rect rect(widthV,highV,img.cols-widthH-widthV,img.rows-highH-highV);
return rect;
}
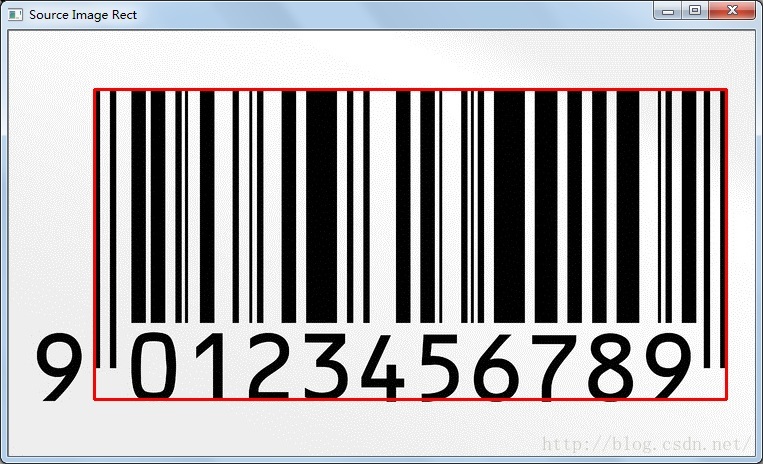
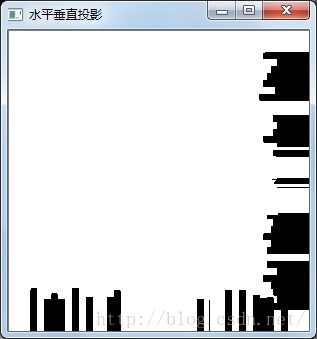
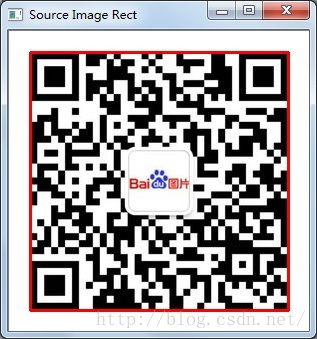
通过图像在水平和垂直方向上的投影,按照一定的阈值,找到二维码所在位置,剪切出来用于下一步Zbar条码识别。当然这个方法只能识别出背景简单的图片中的二维码。
条形码效果:
水平、垂直投影
检出条形码区域
二维码效果:
方法二.梯度运算
#include "core/core.hpp"
#include "highgui/highgui.hpp"
#include "imgproc/imgproc.hpp"
using namespace cv;
int main(int argc,char *argv[])
{
Mat image,imageGray,imageGuussian;
Mat imageSobelX,imageSobelY,imageSobelOut;
image=imread(argv[1]);
//1. 原图像大小调整,提高运算效率
resize(image,image,Size(500,300));
imshow("1.原图像",image);
//2. 转化为灰度图
cvtColor(image,imageGray,CV_RGB2GRAY);
imshow("2.灰度图",imageGray);
//3. 高斯平滑滤波
GaussianBlur(imageGray,imageGuussian,Size(3,3),0);
imshow("3.高斯平衡滤波",imageGuussian);
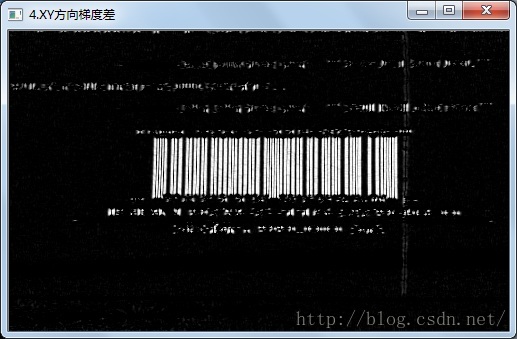
//4.求得水平和垂直方向灰度图像的梯度差,使用Sobel算子
Mat imageX16S,imageY16S;
Sobel(imageGuussian,imageX16S,CV_16S,1,0,3,1,0,4);
Sobel(imageGuussian,imageY16S,CV_16S,0,1,3,1,0,4);
convertScaleAbs(imageX16S,imageSobelX,1,0);
convertScaleAbs(imageY16S,imageSobelY,1,0);
imageSobelOut=imageSobelX-imageSobelY;
imshow("4.X方向梯度",imageSobelX);
imshow("4.Y方向梯度",imageSobelY);
imshow("4.XY方向梯度差",imageSobelOut);
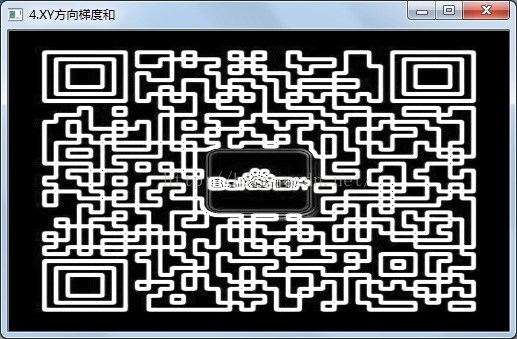
//5.均值滤波,消除高频噪声
blur(imageSobelOut,imageSobelOut,Size(3,3));
imshow("5.均值滤波",imageSobelOut);
//6.二值化
Mat imageSobleOutThreshold;
threshold(imageSobelOut,imageSobleOutThreshold,180,255,CV_THRESH_BINARY);
imshow("6.二值化",imageSobleOutThreshold);
//7.闭运算,填充条形码间隙
Mat element=getStructuringElement(0,Size(7,7));
morphologyEx(imageSobleOutThreshold,imageSobleOutThreshold,MORPH_CLOSE,element);
imshow("7.闭运算",imageSobleOutThreshold);
//8. 腐蚀,去除孤立的点
erode(imageSobleOutThreshold,imageSobleOutThreshold,element);
imshow("8.腐蚀",imageSobleOutThreshold);
//9. 膨胀,填充条形码间空隙,根据核的大小,有可能需要2~3次膨胀操作
dilate(imageSobleOutThreshold,imageSobleOutThreshold,element);
dilate(imageSobleOutThreshold,imageSobleOutThreshold,element);
dilate(imageSobleOutThreshold,imageSobleOutThreshold,element);
imshow("9.膨胀",imageSobleOutThreshold);
vector<vector<Point>> contours;
vector<Vec4i> hiera;
//10.通过findContours找到条形码区域的矩形边界
findContours(imageSobleOutThreshold,contours,hiera,CV_RETR_EXTERNAL,CV_CHAIN_APPROX_NONE);
for(int i=0;i<contours.size();i++)
{
Rect rect=boundingRect((Mat)contours[i]);
rectangle(image,rect,Scalar(255),2);
}
imshow("10.找出二维码矩形区域",image);
waitKey();
} 原图像
平滑滤波
水平和垂直方向灰度图像的梯度差
闭运算、腐蚀、膨胀后通过findContours找到条形码区域的矩形边界
二维码:
原图:
平衡滤波
梯度和
闭运算、腐蚀、膨胀后通过findContours找到条形码区域的矩形边界