1. Thread类
C#多线程编程中Thread类需要包含名称空间System.Threading。
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Thread thread01 = new Thread(ThreadTask01);
thread01.Start();
// thread01.Join();
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine("Thread Main is working !");
Thread.Sleep(20);
}
Console.ReadKey();
}
static void ThreadTask01()
{
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine("Thread task one is working !");
Thread.Sleep(20);
}
}
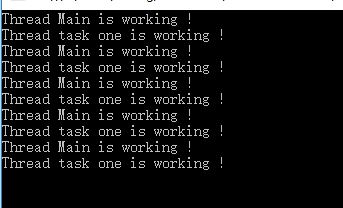
}输出:
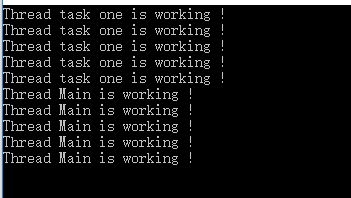
Start不会阻塞主线程,如果加入Join,则会阻塞主线程的执行,直到子线程执行完成才把控制权交还给主流程,但是各个子线程之间的并行执行不受Join影响。上例中加入Join的输出:
多个线程同时访问一个公共字段时,容易引起线程安全问题,C#中使用关键字lock保证数据的安全性和同步:
class Program
{
//static readonly object locker = new object();
static int TotalNum = 100;
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Thread thread01 = new Thread(ThreadTask01);
Thread thread02 = new Thread(ThreadTask02);
thread01.Start();
thread02.Start();
Console.ReadKey();
}
static void ThreadTask01()
{
while (TotalNum > 0)
{
Console.WriteLine(TotalNum);
TotalNum--;
Thread.Sleep(10);
}
}
static void ThreadTask02()
{
while (TotalNum > 0)
{
Console.WriteLine(TotalNum);
TotalNum--;
Thread.Sleep(10);
}
}
}输出异常,中间有重复输出的数字:
添加lock:
class Program
{
static readonly object locker = new object();
static int TotalNum = 100;
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Thread thread01 = new Thread(ThreadTask01);
Thread thread02 = new Thread(ThreadTask02);
thread01.Start();
thread02.Start();
Console.ReadKey();
}
static void ThreadTask01()
{
while (TotalNum > 0)
{
lock (locker)
{
Console.WriteLine(TotalNum);
TotalNum--;
}
Thread.Sleep(10);
}
}
static void ThreadTask02()
{
while (TotalNum > 0)
{
lock (locker)
{
Console.WriteLine(TotalNum);
TotalNum--;
}
Thread.Sleep(10);
}
}
}输出正常:
2. ParameterThreadStart委托
ParameterThreadStart委托定义为 void ParameterizedThreadStart(Object state)。
class Program
{
static int totalNum = 10;
static void Main(string[] args)
{
ParameterizedThreadStart thread01 = new ParameterizedThreadStart(ThreadTask01);
Thread thread = new Thread(thread01);
thread.Start(totalNum);
Console.ReadKey();
}
static void ThreadTask01(object obj)
{
for (int i = 0; i < Convert.ToInt32(obj); i++)
{
Console.WriteLine(i);
Thread.Sleep(10);
}
}
}3. 匿名方法
匿名方法启动多线程是使用Thread类的另一种更加灵活的方法。
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
ThreadStart threadStart = new ThreadStart(delegate ()
{
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine("Thread one is working!");
}
});
Thread thread = new Thread(threadStart);
thread.Start();//多线程启动匿名方法
//等待线程结束
while (thread.ThreadState != ThreadState.Stopped)
{
Thread.Sleep(10);
}
Console.ReadKey();
}
}4. Delegate委托
委托是一种比较高级的多线程方法,可以传入参数和获取返回值,还可以查询异步操作是否完成。
class Program
{
private delegate int NewTaskDelegate(int ms);
private static int newTask(int ms)
{
Console.WriteLine("任务开始");
Thread.Sleep(ms);
Random random = new Random();
int n = random.Next(10000);
Console.WriteLine("任务完成");
return n;
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
NewTaskDelegate task = newTask;
IAsyncResult asyncResult = task.BeginInvoke(2000, null, null);
//EndInvoke方法将被阻塞2秒
//使用WaitOne阻塞主线程,直到子线程完成操作
while (!asyncResult.AsyncWaitHandle.WaitOne(100, false))
{
Console.Write("-");
}
while (!asyncResult.IsCompleted) //查询线程是否完成
{
Console.Write("*");
Thread.Sleep(100);
}
int result = task.EndInvoke(asyncResult);
Console.WriteLine(result);
Console.Read();
}
}