chapter 20 注解
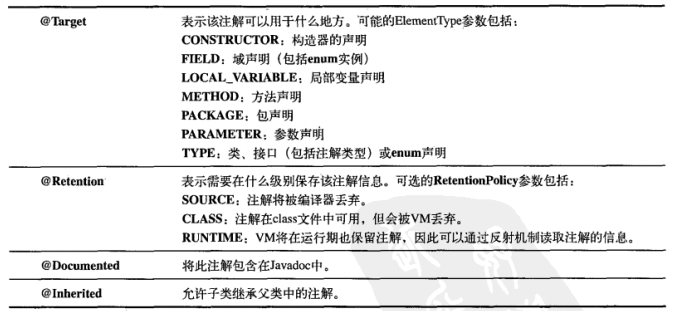
三种标准注解和四种元注解:

编写注解处理器
chapter 21 并发
基本的线程机制
定义任务
package cn.test; public class LiftOff implements Runnable { protected int countDown = 10; private static int taskCount=0; private final int id= taskCount++; public LiftOff() {} public LiftOff(int countDown) { this.countDown=countDown; } public String status() { return "#"+id+"("+ (countDown > 0 ? countDown:"Liftoff!")+"),"; } @Override public void run() { while(countDown-->0) { System.out.print(status()); Thread.yield();//线程重新抢占 } } }
public class MainThread {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LiftOff launch=new LiftOff();
launch.run();
}
}
Thread类
public class BasicThreads { public static void main(String[] args) { for(int i=0;i<5;i++) { new Thread(new LiftOff()).start(); } System.out.println("Waiting for LiftOff"); } }
使用Executor
public class CachedThreadPool { public static void main(String[] args) { // ExecutorService exec=Executors.newCachedThreadPool(); ExecutorService exec=Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5);
// ExecutorService exec=Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor(); for(int i=0;i<5;i++) { exec.execute(new LiftOff()); } exec.shutdown(); } }
从任务中产生返回值
Runnable 不会返回任何值。使用Callable接口能够返回一个值。
package cn.test; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.concurrent.Callable; import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException; import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService; import java.util.concurrent.Executors; import java.util.concurrent.Future; class TaskWithResult implements Callable<String> { private int id; public TaskWithResult(int id) { this.id=id; } @Override public String call() throws Exception { return "result of TaskWithResult "+ id; } } public class CallableDemo{ public static void main(String[] args) { ExecutorService exec=Executors.newCachedThreadPool(); ArrayList<Future<String>> results=new ArrayList<Future<String>>(); for(int i=0;i<10;i++) { results.add(exec.submit(new TaskWithResult(i))); } for(Future<String> fs:results) { try { System.out.println(fs.get()); } catch (InterruptedException e) { System.out.println(e); return; } catch (ExecutionException e) { System.out.println(e); } finally { exec.shutdown(); } } } }

休眠
Thread.sleep();
优先级
package cn.test; import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService; import java.util.concurrent.Executors; public class SimplePriorities implements Runnable{ private int countDown=5; private volatile double d; private int priority; public SimplePriorities(int priority) { this.priority=priority; } public String toString() { return Thread.currentThread()+":"+countDown; } @Override public void run() { Thread.currentThread().setPriority(priority); while(true) { for(int i=1;i<100000;i++) { d+=(Math.PI+Math.E)/(double)i; if(i%1000 == 0) Thread.yield(); } System.out.println(this); if(--countDown == 0) return; } } public static void main(String[] args) { ExecutorService exec=Executors.newCachedThreadPool(); for(int i=0;i<5;i++) exec.execute(new SimplePriorities(Thread.MIN_PRIORITY)); exec.execute(new SimplePriorities(Thread.MAX_PRIORITY)); exec.shutdown(); } }
让步
Thread.yield();
后台线程
daemon线程。
package cn.test; public class SimpleDaemons implements Runnable{ public void run() { try { while(true) { Thread.sleep(100); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" "+this); } } catch (Exception e) { System.out.println("sleep() interrupted"); e.printStackTrace(); } } public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { for(int i=0;i<10;i++) { Thread daemon=new Thread(new SimpleDaemons()); daemon.setDaemon(true); daemon.start(); } System.out.println("All daemons started"); Thread.sleep(100); } }
使用isDaemon()方法来确定线程是否是一个后台线程。
package cn.test; import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; class Daemon implements Runnable{ private Thread[] t=new Thread[10]; public void run() { for(int i=0;i<t.length;i++) { t[i]=new Thread(new DaemonSpawn()); t[i].start(); System.out.println("DaemonSpawn "+i+" started,"); } for(int i=0;i<t.length;i++) System.out.println("t["+i+"].siDaemon()="+ t[i].isDaemon()+","); while(true) { Thread.yield(); } } class DaemonSpawn implements Runnable{ public void run() { while(true) Thread.yield(); } } } public class Daemons { public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { Thread d=new Thread(new Daemon()); d.setDaemon(true); d.start(); System.out.println("d.isDaemon()="+d.isDaemon()+","); TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1); } }
一旦main()退出,JVM就会立即关闭所有的后台进程。
package cn.test; import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; class ADaemon implements Runnable{ public void run() { try { System.out.println("Starting ADaemon"); TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1); }catch(Exception e) { System.out.println("Exiting via InterruptedException"); }finally { System.out.println("This should always run?"); } } } public class DaemonsDontRunFinally { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { Thread t= new Thread(new ADaemon()); t.setDaemon(true); t.start(); // TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1); } }
编码的变体
package cn.test; import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; class ADaemon implements Runnable{ public void run() { try { System.out.println("Starting ADaemon"); TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1); }catch(Exception e) { System.out.println("Exiting via InterruptedException"); }finally { System.out.println("This should always run?"); } } } public class DaemonsDontRunFinally { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { Thread t= new Thread(new ADaemon()); t.setDaemon(true); t.start(); // TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1); } }
加入一个线程【】
package cn.test; class Sleeper extends Thread{ private int duration; public Sleeper(String name,int sleepTime) { super(name); duration=sleepTime; start(); } public void run() { try { sleep(duration); } catch(InterruptedException e) { System.out.println(getName()+" was interrupted ."+ "isInterrupted():"+isInterrupted()); return; } System.out.println(getName()+" has awakened"); } } class Joiner extends Thread{ private Sleeper sleeper; public Joiner(String name,Sleeper sleeper) { super(name); this.sleeper=sleeper; start(); } public void run() { try { sleeper.join(); }catch (InterruptedException e) { System.out.println("Interrupted"); } System.out.println(getName()+" join completed"); } } public class Joining { public static void main(String[] args) { Sleeper sleepy=new Sleeper("Sleeper",1500), grumpy=new Sleeper("Grumpy",1500); Joiner dopey=new Joiner("Dopey",sleepy), doc=new Joiner("Doc",grumpy); grumpy.interrupt(); } }
创建有响应的用户界面
使用线程的动机之一就是建立有响应的用户界面。
package cn.test; import java.io.IOException; class UnresponsiveUI{ private volatile double d=1; public UnresponsiveUI() throws IOException { while(d>0) d=d+(Math.PI+Math.E)/d; System.in.read(); } } public class ResponsiveUI extends Thread{ private static volatile double d=1; public ResponsiveUI() { setDaemon(true); start(); } @Override public void run() { while(true) d=d+(Math.PI+Math.E)/d; } public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { // new UnresponsiveUI(); new ResponsiveUI(); System.in.read(); System.out.println(d); } }

线程组
捕获异常

package cn.test; import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService; import java.util.concurrent.Executors; public class ExceptionThread implements Runnable{ public void run() { throw new RuntimeException(); } public static void main(String[] args) { try { ExecutorService exec = Executors.newCachedThreadPool(); exec.execute(new ExceptionThread()); }catch(RuntimeException ue) { //无法捕获异常 System.out.println("Exception has been handled!"); } } }
package cn.test; import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService; import java.util.concurrent.Executors; import java.util.concurrent.ThreadFactory; class ExceptionThread2 implements Runnable{ public void run() { Thread t=Thread.currentThread(); System.out.println("run() by "+t); System.out.println("eh = "+t.getUncaughtExceptionHandler()); throw new RuntimeException(); } } class MyUncaughtExceptionHandler implements Thread.UncaughtExceptionHandler{ @Override public void uncaughtException(Thread t, Throwable e) { System.out.println("caught "+e); } } class HandlerThreadFactory implements ThreadFactory{ public Thread newThread(Runnable r) { System.out.println(this+" creating new Thread"); Thread t=new Thread(); System.out.println("created "+t); t.setUncaughtExceptionHandler(new MyUncaughtExceptionHandler()); System.out.println("eh="+t.getUncaughtExceptionHandler()); return t; } } public class CaptureUncaughtException { public static void main(String[] args) { ExecutorService exec=Executors.newCachedThreadPool(new HandlerThreadFactory()); exec.execute(new ExceptionThread2()); } }

package cn.test; import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService; import java.util.concurrent.Executors; public class SettingDefaultHandler { public static void main(String[] args) { Thread.setDefaultUncaughtExceptionHandler( new MyUncaughtExceptionHandler()); ExecutorService exec = Executors.newCachedThreadPool(); exec.execute(new ExceptionThread()); } }
共享受限资源
不正确地访问资源
package cn.test; import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService; import java.util.concurrent.Executors; abstract class IntGenerator{ private volatile boolean canceled=false; public abstract int next(); public void cancel() {canceled=true;} public boolean isCanceled() {return canceled;} } public class EvenChecker implements Runnable{ private IntGenerator generator; private final int id; public EvenChecker (IntGenerator g,int ident) { generator = g; id = ident; } public void run() { while(!generator.isCanceled()) { int val=generator.next(); if(val%2!=0) { System.out.println(val+" not even!"); generator.cancel(); } } } public static void test(IntGenerator gp,int count) { System.out.println("Press Control-C to exit"); ExecutorService exec=Executors.newCachedThreadPool(); for(int i=0;i<count;i++) exec.execute(new EvenChecker(gp,i)); exec.shutdown(); } public static void test(IntGenerator gp) { test(gp,10); } } package cn.test; public class EvenGenerator extends IntGenerator { private int currentEvenValue=0; public int next() { ++currentEvenValue; ++currentEvenValue; return currentEvenValue; } public static void main(String[] args) { EvenChecker.test(new EvenGenerator()); } }
在java中,递增不是原子性的操作。因此,如果不保护任务,即使单一的递增也是不安全的。
解决共享资源竞争
序列化访问共享资源方法。
互斥量。

(该类的其他对象调用synchronized任务的操作被锁定,只有已经进入被锁任务的那个对象完成任务后才可竞权)


package cn.test; public class EvenGenerator extends IntGenerator { private int currentEvenValue=0; public synchronized int next() { ++currentEvenValue; Thread.yield(); ++currentEvenValue; return currentEvenValue; } public static void main(String[] args) { EvenChecker.test(new EvenGenerator()); } }
使用显式的Lock对象
java.util.concurrent.locks
package cn.test; import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock; import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock; public class MutexEvenGenerator extends IntGenerator{ private int currentEvenValue=0; private Lock lock=new ReentrantLock(); public int next() { lock.lock(); try { ++currentEvenValue; Thread.yield(); ++currentEvenValue; return currentEvenValue; } finally { lock.unlock(); } } public static void main(String[] args) { EvenChecker.test(new MutexEvenGenerator()); } }
package cn.test; import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock; public class AttemptLocking { private ReentrantLock lock=new ReentrantLock(); public void untimed() { boolean captured=lock.tryLock(); try { System.out.println("untimed tryLock(): "+captured); }finally { if(captured) lock.unlock(); } } public void timed() { boolean captured = false; try { captured = lock.tryLock(2, TimeUnit.SECONDS); }catch(InterruptedException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } try { System.out.println("timed tryLock(2,TimeUnit.SECONDS): " +captured); }finally { if(captured) lock.unlock(); } } public static void main(String[] args) { final AttemptLocking al=new AttemptLocking(); al.untimed(); al.timed(); new Thread() { {setDaemon(true);} public void run() { al.lock.lock(); System.out.println("acquired"); } }.start(); Thread.yield(); al.untimed(); al.timed(); } }
原子性与易变性
理解volatile


java中,对域中的值做赋值和返回操作是原子性的。
package cn.test; import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService; import java.util.concurrent.Executors; public class AtomicityTest implements Runnable{ private int i=0; public int getValue() {return i;} private synchronized void evenIncrement() {i++;i++;} public void run() { while(true) evenIncrement(); } public static void main(String[] args) { ExecutorService exec = Executors.newCachedThreadPool(); AtomicityTest at = new AtomicityTest(); exec.execute(at); while(true) { int val=at.getValue(); if(val % 2 != 0) { System.out.println(val); System.exit(0); } } } }
原子类
package cn.test; import java.util.Timer; import java.util.TimerTask; import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService; import java.util.concurrent.Executors; import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger; public class AtomicIntegerTest implements Runnable{ private AtomicInteger i=new AtomicInteger(0); public int getValue() {return i.get();} private void evenIncrement() {i.addAndGet(2);} public void run() { while(true) evenIncrement(); } public static void main(String[] args) { new Timer().schedule(new TimerTask() { public void run() { System.err.println("Aborting"); System.exit(0); } }, 5000); ExecutorService exec=Executors.newCachedThreadPool(); AtomicIntegerTest ait=new AtomicIntegerTest(); exec.execute(ait); while(true) { int val=ait.getValue(); if(val % 2 != 0) { System.out.println(val); System.exit(0); } } } }
临界区(同步控制块)【】
在其他对象上同步
package cn.test; class DualSynch{ private Object syncObject = new Object(); public synchronized void f() { for(int i=0;i<5;i++) { System.out.println("f()"); Thread.yield(); } } public void g() { synchronized(syncObject) { for(int i=0;i<5;i++) { System.out.println("g()"); Thread.yield(); } } } } public class SyncObject { public static void main(String[] args) { final DualSynch ds=new DualSynch(); new Thread() { public void run() { ds.f(); } }.start(); ds.g(); } }
线程本地存储【】
package cn.test; import java.util.Random; import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService; import java.util.concurrent.Executors; import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; class Accessor implements Runnable{ private final int id; public Accessor (int idn) {id=idn;} public void run() { while(!Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()) { ThreadLocalVariableHolder.increment(); System.out.println(this); Thread.yield(); } } public String toString() { return "#"+id+": "+ThreadLocalVariableHolder.get(); } } public class ThreadLocalVariableHolder { private static ThreadLocal<Integer> value= new ThreadLocal<Integer>() { private Random rand=new Random(47); protected synchronized Integer initialValue() { return rand.nextInt(10000); } }; public static void increment() { value.set(value.get()+1); } public static int get() {return value.get();} public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { ExecutorService exec = Executors.newCachedThreadPool(); for(int i=0;i<5;i++) exec.execute(new Accessor(i)); TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(3); exec.shutdown(); } }
package cn.test; import java.util.Random; import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService; import java.util.concurrent.Executors; import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; class Accessor implements Runnable{ private final int id; public Accessor (int idn) {id=idn;} public void run() { while(!Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()) { ThreadLocalVariableHolder.increment(); System.out.println(this); Thread.yield(); } } public String toString() { return "#"+id+": "+ThreadLocalVariableHolder.get(); } } public class ThreadLocalVariableHolder { private static ThreadLocal<Integer> value= new ThreadLocal<Integer>() { private Random rand=new Random(47); protected synchronized Integer initialValue() { return rand.nextInt(10000); } }; public static void increment() { value.set(value.get()+1); } public static int get() {return value.get();} public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { ExecutorService exec = Executors.newCachedThreadPool(); for(int i=0;i<5;i++) exec.execute(new Accessor(i)); TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(3); exec.shutdown(); } }
终结任务
装饰性花园
package cn.test; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; import java.util.Random; import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService; import java.util.concurrent.Executors; import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; class Count{ private int count=0; private Random rand=new Random(47); public synchronized int increment() { int temp=count; if(rand.nextBoolean()) Thread.yield(); return (count= ++temp); } public synchronized int value() {return count;} } class Entrance implements Runnable{ private static Count count=new Count(); private static List<Entrance> entrances= new ArrayList<Entrance>(); private int number=0; private final int id; private static volatile boolean canceled=false; public static void cancel() {canceled =true;} public Entrance(int id) { this.id=id; entrances.add(this); } public void run() { while(!canceled) { synchronized(this) { ++number; } System.out.println(this+"Total: "+count.increment()); try { TimeUnit.MICROSECONDS.sleep(100); }catch(InterruptedException e) { System.out.println("sleep interrupted"); } } System.out.println("Stopping "+this); } public synchronized int getValue() {return number;} public String toString() { return "Entrance "+id+": "+getValue(); } public static int getTotalCount() { return count.value(); } public static int sumEntrances() { int sum=0; for(Entrance entrance:entrances) sum+=entrance.getValue(); return sum; } } public class OrnamentalGarden { public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { ExecutorService exec = Executors.newCachedThreadPool(); for(int i=0;i<5;i++) exec.execute(new Entrance(i)); TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(3); Entrance.cancel(); exec.shutdown(); if(!exec.awaitTermination(250, TimeUnit.MICROSECONDS)) System.out.println("Some tasks were not terminated!"); System.out.println("Total: "+Entrance.getTotalCount()); System.out.println("Sum of Entrances: "+Entrance.sumEntrances()); } }
在阻塞时终结
线程状态:
- 新建
- 就绪
- 阻塞
- 死亡

进入阻塞状态
调用sleep(milliseconds)会进入休眠状态,设定的时间结束时继续运行。
调用wait()使线程挂起,直到线程被notify()或notifyAll(),线程会进入就绪状态。
当前任务的等待输入/输出。
当然任务被阻塞在锁外。
中断
cancel()是一种中断由Executor启动的单个线程的方式。
package cn.test; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStream; import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService; import java.util.concurrent.Executors; import java.util.concurrent.Future; import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; class SleepBlocked implements Runnable{ public void run() { try { TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(100); } catch(InterruptedException e) { System.out.println("InterruptedException"); } System.out.println("Exiting SleepBlocked.run() "); } } class IOBlocked implements Runnable{ private InputStream in; public IOBlocked(InputStream in) {this.in = in; } public void run() { try { System.out.println("Waiting for read():"); in.read(); } catch (IOException e) { if(Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()) System.out.println("Interrupted from blocked I/O"); else throw new RuntimeException(); } System.out.println("Exiting IOBlocked.run() "); } } class SynchronizedBlocked implements Runnable{ public synchronized void f() { while(true) Thread.yield(); } public SynchronizedBlocked() { new Thread() { public void run() { f(); } }.start(); } public void run() { System.out.println("Trying to call f()"); f(); System.out.println("Exiting SynchronizedBlocked.run()"); } } public class Interrupting { private static ExecutorService exec= Executors.newCachedThreadPool(); static void test(Runnable r) throws InterruptedException { Future<?> f= exec.submit(r); TimeUnit.MICROSECONDS.sleep(100); System.out.println("Interrupting "+r.getClass().getName()); f.cancel(true); System.out.println("Interrupt sent to "+r.getClass().getName()); } public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { test(new SleepBlocked()); test(new IOBlocked(System.in)); test(new SynchronizedBlocked()); TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(3); System.out.println("Aborting with System.exit(0)"); System.exit(0); } }
被互斥所阻塞【】
package cn.test; public class MultiLock { public synchronized void f1(int count) { if(count-- >0) { System.out.println("f1() calling f2() with count "+count); f2(count); } } public synchronized void f2(int count) { if(count-- >0) { System.out.println("f2() calling f1() with count "+count); f1(count); } } public static void main(String[] args) { final MultiLock multiLock=new MultiLock(); new Thread() { public void run() { multiLock.f1(10); } }.start(); } }
package cn.test; import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock; import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock; class BlockedMutex{ private Lock lock=new ReentrantLock(); public BlockedMutex() { lock.lock(); } public void f() { try { lock.lockInterruptibly(); System.out.println("lock acquired in f()"); } catch (InterruptedException e) { System.out.println("Interrupted from lock acquisition in f()"); } } } class Blocked2 implements Runnable { BlockedMutex blocked=new BlockedMutex(); public void run() { System.out.println("Waiting for f() in BlockedMutex"); blocked.f(); System.out.println("Broken out of blocked call"); } } public class Interrupting2 { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { Thread t= new Thread(new Blocked2()); t.start(); TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1); System.out.println("Issuing t.interrupt()"); t.interrupt(); } }
检查中断
线程之间的协作
wait()与notifyAll()
package cn.test; import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService; import java.util.concurrent.Executors; import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; class Car{ private boolean waxOn=false; public synchronized void waxed() { waxOn=true; notifyAll(); } public synchronized void buffed() { waxOn=false; notifyAll(); } public synchronized void waitForWaxing() throws InterruptedException { while(waxOn== false) wait(); } public synchronized void waitForBuffing() throws InterruptedException { while(waxOn== true) wait(); } } class WaxOn implements Runnable{ private Car car; public WaxOn(Car c) {car= c;} public void run() { try { while(!Thread.interrupted()) { System.out.println("Wax On!"); TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(200); car.waxed(); car.waitForBuffing(); } }catch(InterruptedException e) { System.out.println("Exiting via interrupt"); } System.out.println("Ending Wax On task"); } } class WaxOff implements Runnable{ private Car car; public WaxOff(Car c) {car=c;} public void run() { try { while(!Thread.interrupted()) { car.waitForWaxing(); System.out.println("Wax Off!"); TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(200); car.buffed(); } }catch(InterruptedException e) { System.out.println("Exiting via interrupt"); } System.out.println("Ending Wax Off task"); } } public class WaxOMatic { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { Car car=new Car(); ExecutorService exec = Executors.newCachedThreadPool(); exec.execute(new WaxOff(car)); exec.execute(new WaxOn(car)); TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(5); exec.shutdownNow(); } }