嘟嘟嘟
题意:用一条水平线段表示以栋房子:((x_0, y_0)(x_0', y_0))。然后有一条低于房子的水平线段(l_0),代表你可以到的位置。接下来输入一个数(n),一下(n)行每行(3)个数,用一条水平线段代表障碍物。求你在(l_0)上能看到房子的最大连续长度。(看到房子指房子完全没被挡上)
刚开始自己(yy)了一个(O(n ^ 2))的算法,结果(TLE)了……谁叫这题不告诉我数据范围的。
正解比较有意思:我们要逆向思维:对于一个障碍物,求出它能遮挡的范围,那么最后的答案就是没被遮挡的区间长度的最大值。
遮挡的范围画个图就明白了:
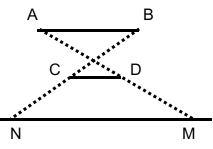
则([N, M])就是被遮挡的区间,然后用叉积求交点即可。
那么现在我们就得到了一堆区间(可能重叠),然后想括号匹配一样跑一边,如果当前栈空,就那(a _ {i + 1} - a _ i)更新答案。
需要注意的是([N, M])可能在直线(l_0)之外,这时候那(l_0)两个端点限制(N, M)即可,具体看代码。
还有一点就是区间的头和尾的地方要单独算一下,即(a _ 1 - L)和(R - a _ n)
#include<cstdio>
#include<iostream>
#include<cmath>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstring>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<cctype>
#include<vector>
#include<stack>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
#define enter puts("")
#define space putchar(' ')
#define Mem(a, x) memset(a, x, sizeof(a))
#define rg register
typedef long long ll;
typedef double db;
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const db eps = 1e-8;
const int maxn = 5e4 + 5;
inline ll read()
{
ll ans = 0;
char ch = getchar(), last = ' ';
while(!isdigit(ch)) last = ch, ch = getchar();
while(isdigit(ch)) ans = (ans << 1) + (ans << 3) + ch - '0', ch = getchar();
if(last == '-') ans = -ans;
return ans;
}
inline void write(ll x)
{
if(x < 0) x = -x, putchar('-');
if(x >= 10) write(x / 10);
putchar(x % 10 + '0');
}
int n;
struct Vec
{
db x, y;
db operator * (const Vec& oth)const
{
return x * oth.y - oth.x * y;
}
};
struct Point
{
db x, y;
Vec operator - (const Point& oth)const
{
return (Vec){x - oth.x, y - oth.y};
}
}H1, H2, L1, L2;
struct Node
{
db x; int flg;
bool operator < (const Node& oth)const
{
return x < oth.x;
}
}a[maxn];
int cnt = 0;
void solve(Point A, Point B, int flg)
{
Vec AB = B - A;
Vec CA = A - L1, CD = L2 - L1, DB = B - L2;
db s1 = CA * CD, s2 = -(DB * CD);
db ret = A.x + AB.x / (s1 + s2) * s1;
if(ret > L2.x) ret = L2.x; //限制N, M
if(ret < L1.x) ret = L1.x;
a[++cnt] = (Node){ret, flg};
}
int main()
{
while(scanf("%lf%lf%lf", &H1.x, &H2.x, &H1.y))
{
if(H1.x == 0 && H1.y == 0 && H2.x == 0) break;
cnt = 0;
H2.y = H1.y;
scanf("%lf%lf%lf", &L1.x, &L2.x, &L1.y); L2.y = L1.y;
n = read();
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)
{
db L, R, y;
scanf("%lf%lf%lf", &L, &R, &y);
if(y < L1.y || y >= H1.y) continue;
solve(H1, (Point){R, y}, -1);
solve(H2, (Point){L, y}, 1);
}
if(!n) {printf("%.2f
", L2.x - L1.x); continue;}
sort(a + 1, a + cnt + 1);
a[cnt + 1].x = L2.x;
db ans = max(0.00, a[1].x - L1.x);
int st = 0; //模仿栈操作
for(int i = 1; i <= cnt; ++i)
{
st += a[i].flg;
if(!st) ans = max(ans, a[i + 1].x - a[i].x);
}
if(ans == 0) puts("No View");
else printf("%.2f
", ans);
}
return 0;
}