结对项目完成WordCount
合作者:201631062507 201631062526(学号)
代码地址:https://gitee.com/WordCountMC/WordCountTeam
本次作业链接:https://edu.cnblogs.com/campus/xnsy/2018Systemanalysisanddesign/homework/2188
1.结对项目PSP编写
我们的项目于10月11日正式开始,在开始编写代码之前,我们先对我们如何完成项目以及对老师布置的作业等进行再一次的商定和讨论。并结合我们平时上课的时间以及项目外等因素,约定了我们一起进行结对编程的时间和地点。最后一起完成了PSP表格的填写:
PSP2.1 |
PSP阶段 |
预估耗时(分钟) |
实际耗时(分钟) |
| Planning | 计划 | 30 | 30 |
| · Estimate | · 估计这个任务需要多少时间 | 30 | 30 |
| Development | 开发 | 620 | 945 |
| · Analysis | · 需求分析 (包括学习新技术) | 30 | 40 |
| · Design Spec | · 生成设计文档 | 20 | 30 |
| · Design Review | · 设计复审 (和同事审核设计文档) | 30 | 60 |
| · Coding Standard | · 代码规范 (为目前的开发制定合适的规范) | 30 | 40 |
| · Design | · 具体设计 | 40 | 45 |
| · Coding | · 具体编码 | 350 | 500 |
| · Code Review | · 代码复审 | 60 | 100 |
| · Test | · 测试(自我测试,修改代码,提交修改) | 60 | 130 |
| Reporting | 报告 | 80 | 80 |
| · Test Report | · 测试报告 | 30 | 30 |
| · Size Measurement | · 计算工作量 | 20 | 10 |
| · Postmortem & Process Improvement Plan | .事后总结并提出改进计划 | 30 | 40 |
| 合计 | 730 | 1055 |
总结分析:这次在项目完成后,发现预估时间和实际耗时相差比较大,其主要表现在开发阶段。由于我们在代码自审和互审阶段,都发现了编码所存在的不规范,所以花了更多的时间去修改代码。还有就是在编码的时候,我们要完成的内容比我们想象得要困难一点,所以在编码的时候花了更多的时间。最后就是测试,这次项目开发采用了TDD,我们要先编写测试代码,再实现接口,这与我们之间采用的方式也不同,所以也花了更多的时间。
2.代码互审
2.1总体情况分析
在审查之后发现,队友的代码已经根据了我们一起编写的小组编程规范进行了修改。修改后的代码风格简洁明了,非常容易理解和阅读。但是仍需注意的地方是,方法里的代码注释要写在对应代码的上面而不是后面,这样会使代码阅读更加清晰。除此之外,在互审之后,发现代码存在一个小bug需要进行改正。
2.2 问题
出现问题的模块在CountUtil类中的returnWords方法。
问题是在测试时发现:当一个文件为空的时候,它会返回单词数为1,而且当有两个文件同时测试时,如果第一个文件的单词数比第二个文件的单词数多的话,只显示第一个的单词数。
2.3 解决方法
在问题提出后,我和队友一起解决了问题,发现问题出在每次统计单词数目所要用的StringBuffer没有进行清空的操作。
3.设计
3.1 结构设计
功能类:主函数类(WordCount类) 接口类(CountUtil类)
WordCount类:

CountUtil类:

3.2 类间关系

3.3 WordCount类的流程图

4.代码说明
4.1扩展功能:
(1)当输入-e时,后面跟停用词表stoplist.txt
首先解析停用词表中的单词:
/**
* 用来解析停用词表中单词
* **/
public String[] stoplistWord(String stopList)
{
String lineString = null;
String[] stopListBuffer = null;
File sl = new File(stopList);
try {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(sl));
while((lineString = br.readLine())!=null) {
//当遇到空格的时候,就为一个单词
stopListBuffer = lineString.split("\s+");
}
br.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
return stopListBuffer;
}
然后判断文件中的单词是否是停用词表中的单词:
/*** * * 判断该词是否存在于停用词表内 * */ public static boolean inStop(String str, String[] fileBuffer) { int count = 0; for(int i = 0;i<fileBuffer.length;i++) {
//将获得的单词,与停用词表中的单词一个一个的与进行比较 if(str.equals(fileBuffer[i])) { count++; } } if(count > 0) { return true; }else return false; }
(2)当输入-a时,查询文件中的代码行数、注释行数、空行数
getCodeLines() 函数:
/**
* 查询文件的代码行数
* @param filePaths 所有有效文件的集合
* @return String类型 查询结果
*/
public String getCodeLines(Set<String> filePaths) {
// 结果字符串
String result = "";
// 缓存变量
String tmp = "";
// 统计次数
int count = 0;
// 得到输入流
FileInputStream is = null;
InputStreamReader ist = null;
BufferedReader br = null;
try {
for (String filePath : filePaths) {
is = new FileInputStream(filePath);
ist = new InputStreamReader(is);
br = new BufferedReader(ist);
while((tmp = br.readLine())!=null) {
// 去除读取的空格,方便识别内容类型
tmp = tmp.replace(" ", "");
// 改行不为空,则计数+1
if (!"".equals(tmp)&&!tmp.startsWith("//")&&tmp.indexOf("//")!=1) {
count++;
}
}
// 拼接结果字符串
result+=filePath+CODE_LINES+count+SPACE;
// 重置count计数变量
count = 0;
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try {
// 关闭输入流
is.close();
ist.close();
br.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return result;
}
getEmptyLines() 函数:
/**
* 查询文件的空行数
* @param filePaths 所有有效文件的集合
* @return String类型 查询结果
*/
public String getEmptyLines(Set<String> filePaths) {
// 结果字符串
String result = "";
// 缓存变量
String tmp = "";
// 统计次数
int count = 0;
// 得到输入流
FileInputStream is = null;
InputStreamReader ist = null;
BufferedReader br = null;
try {
for (String filePath : filePaths) {
is = new FileInputStream(filePath);
ist = new InputStreamReader(is);
br = new BufferedReader(ist);
while((tmp = br.readLine())!=null) {
// 改行不为空,则计数+1
if ("".equals(tmp)) {
count++;
}
}
// 拼接结果字符串
result+=filePath+EMPTY_LINES+count+SPACE;
// 重置count计数变量
count = 0;
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try {
// 关闭输入流
is.close();
ist.close();
br.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return result;
}
getNoteLines() 函数:
/**
* 查询文件的注释行数
* @param filePaths 所有有效文件的集合
* @return String类型 查询结果
*/
public String getNoteLines(Set<String> filePaths) {
// 结果字符串
String result = "";
// 缓存变量
String tmp = "";
// 统计次数
int count = 0;
// 得到输入流
FileInputStream is = null;
InputStreamReader ist = null;
BufferedReader br = null;
try {
for (String filePath : filePaths) {
is = new FileInputStream(filePath);
ist = new InputStreamReader(is);
br = new BufferedReader(ist);
while((tmp = br.readLine())!=null) {
// 去除读取的空格,方便识别内容类型
tmp = tmp.replace(" ", "");
// 改行不为空,则计数+1
if (!"".equals(tmp)&&tmp.startsWith("//")||tmp.indexOf("//")==1) {
count++;
}
}
// 拼接结果字符串
result+=filePath+NOTE_LINES+count+SPACE;
// 重置count计数变量
count = 0;
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try {
// 关闭输入流
is.close();
ist.close();
br.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return result;
}
(3)当输入-s时,递归处理目录下符合条件的文件
/** * 得到输入文件中指定文件和指定文件夹下符合条件的文件 * @param names 输入文件的集合 * @param condition 文件夹下的筛选条件 * @return Set<String>类型 所有指定文件和指定文件夹下符合条件的文件 */ public Set<String> getAllFileWithCondition(Set<String> names,String condition) { // 存储输入文件和输入文件夹下符合指定条件的文件的集合 Set<String> filePaths = new HashSet<String>(); for (String name : names) { File file = new File(name); if (file.isFile()) { filePaths.add(name); }else if (file.isDirectory()) { // 调用处理文件夹下查询符合指定条件的文件 filePaths.addAll(getDirectoryFilesWithCondition(file, condition)); } } return filePaths; }
4.2高级功能:
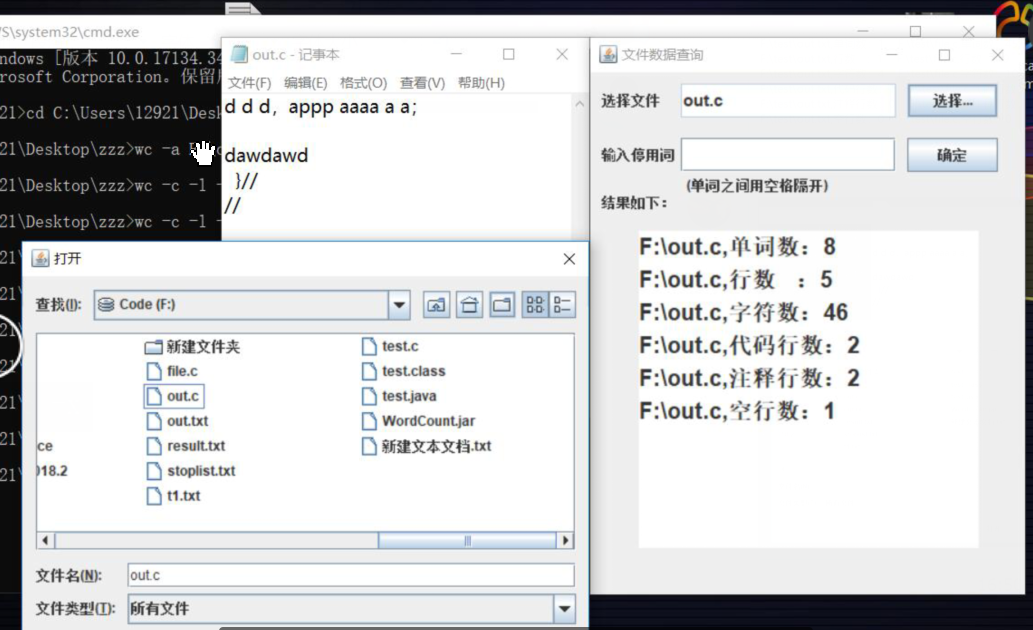
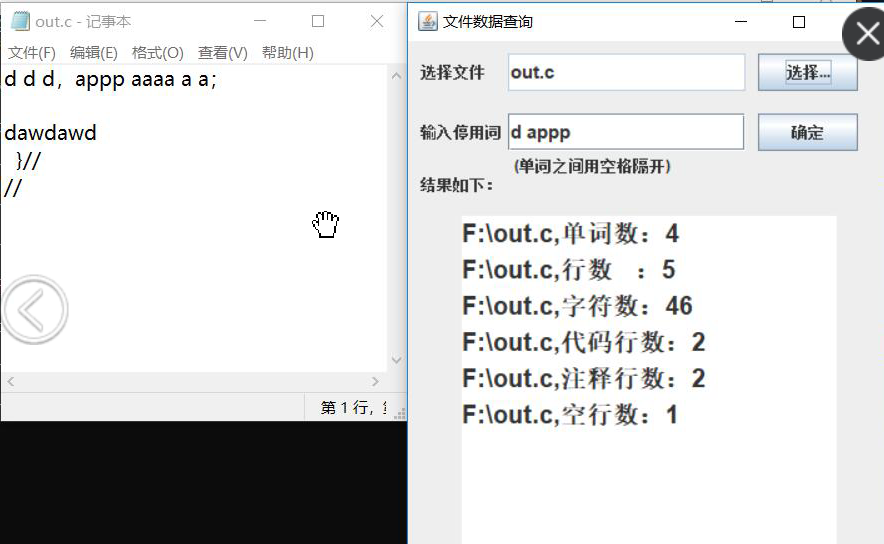
当输入-x的时候,打开图形化界面操作,调用getUI()方法

/** * 获得图形界面 */ public void getUI() { JFileChooser jFileChooser = new JFileChooser(); JFrame jFrame = new JFrame("文件数据查询"); Container container = jFrame.getContentPane(); container.setLayout(null); JLabel hint = new JLabel("选择文件",Label.RIGHT); hint.setBounds(10,10,100,30); JTextField name = new JTextField(); name.setBounds(80,10,190, 30); name.setEditable(false); name.setFont(new Font("dialog", 1, 15)); name.setBackground(Color.WHITE); JLabel hint1 = new JLabel("输入停用词",Label.RIGHT); hint1.setBounds(10,58,100,30); JTextField wordList = new JTextField(); wordList.setBounds(80,58,190, 30); wordList.setFont(new Font("dialog", 1, 15)); wordList.setBackground(Color.white); JLabel hint3 = new JLabel("(单词之间用空格隔开)"); hint3.setBounds(85,85,150,30); JButton confirm = new JButton("确定"); confirm.setBounds(280,58,80,30); JButton choose = new JButton("选择..."); choose.setBounds(280,10,80,30); JLabel hint2 = new JLabel("结果如下:"); hint2.setBounds(10,100,190,30); JTextArea contents = new JTextArea(); contents.setBounds(43,140,300,280); choose.addActionListener(new ActionListener() { @Override public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) { int returnVal = jFileChooser.showOpenDialog(null); if(JFileChooser.APPROVE_OPTION == returnVal) { filePaths.add(jFileChooser.getSelectedFile().getAbsolutePath()); name.setText(jFileChooser.getSelectedFile().getName()); contents.setText(performOperation()); } } }); confirm.addActionListener(new ActionListener() { @Override public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) { CountUtil.USE_STOP = true; CountUtil.putInFile(wordList.getText()+" ", stopListPath); STOPLIST_FILE = stopListPath; } }); container.add(hint); container.add(name); container.add(choose); container.add(contents); container.add(wordList); container.add(hint1); container.add(confirm); container.add(hint2); container.add(hint3); jFrame.setSize(400, 500); jFrame.setVisible(true); }
5.测试过程
5.1测试模块建立

此次测试使用的是java提供的单元测试工具进行测试,新建了一个CountUtilTest类,对CountUtil中的接口方法进行测试。在此次单元测试的设计中,我们所设计的测试用例包括了没有内容的.c文间,只有一个单词的.c文件等比较典型的测试用例。

private CountUtil countUtil = new CountUtil(); @org.junit.Test public void testReturnCharacters() { Set<String> filePaths = new HashSet<String>(); String File1 = "F:\out.c"; filePaths.add(File1); filePaths =countUtil.getAllFilePaths(filePaths); String result = "F:\out.c,字符数:46 "; assertTrue("字符数错误",result.equals(countUtil.returnCharacters(filePaths))); } @org.junit.Test public void testReturnWords() { Set<String> filePaths = new HashSet<String>(); String File1 = "F:\test.java"; String File2 = "F:\WordCount"; String stopList = ""; filePaths.add(File2); filePaths.add(File1); filePaths =new CountUtil().getAllFilePaths(filePaths); String result = "F:\WordCount\result.txt,单词数:35 F:\WordCount\wc.exe,单词数:256100 " + "F:\WordCount\AimResult.txt,单词数:76 F:\test.java,单词数:3 " + "F:\WordCount\ddd\hello.txt,单词数:2 "; assertTrue("单词数错误", result.equals(countUtil.returnWords(filePaths, stopList))); } @org.junit.Test public void testReturnLines() { Set<String> filePaths = new HashSet<String>(); String File1 = "F:\test.java"; String File2 = "F:\WordCount"; filePaths.add(File2); filePaths.add(File1); filePaths =countUtil.getAllFilePaths(filePaths); String result = "F:\WordCount\result.txt,行数 :3 F:\WordCount\wc.exe,行数 :3042 " + "F:\WordCount\AimResult.txt,行数 :3 F:\test.java,行数 :1 " + "F:\WordCount\ddd\hello.txt,行数 :1 "; assertTrue("行数错误", result.equals(countUtil.returnLines(filePaths))); } @org.junit.Test public void testOutPutFile() { String FilePath = "result.txt"; String Content = "OutPutFile test !"; assertTrue(countUtil.outPutFile(FilePath, Content)); } @org.junit.Test public void testGetAllFilePaths() { Set<String> filePaths = new HashSet<String>(); Set<String> resultPaths = new HashSet<String>(); String File1 = "F:\WordCount"; String FIle2 = "F:\out.c"; String result1 = "F:\WordCount\result.txt"; String result2 = "F:\out.c"; String result3 = "F:\WordCount\wc.exe"; String result4 = "F:\WordCount\AimResult.txt"; String result5 = "F:\WordCount\ddd\hello.txt"; filePaths.add(File1); filePaths.add(FIle2); resultPaths.add(result1); resultPaths.add(result2); resultPaths.add(result3); resultPaths.add(result4); resultPaths.add(result5); filePaths = countUtil.getAllFilePaths(filePaths); assertTrue("得到的文件错误", resultPaths.equals(filePaths)); } @org.junit.Test public void testGetDirectoryFiles() { Set<String> filePaths = new HashSet<String>(); Set<String> resultPaths = new HashSet<String>(); File File1 = new File("F:\WordCount"); String file1 = "F:\WordCount\result.txt"; String file2 = "F:\WordCount\wc.exe"; String file3 = "F:\WordCount\AimResult.txt"; String file4 = "F:\WordCount\ddd\hello.txt"; resultPaths.add(file1); resultPaths.add(file2); resultPaths.add(file3); resultPaths.add(file4); filePaths = CountUtil.getDirectoryFiles(File1); assertTrue("得到的文件错误", resultPaths.equals(filePaths)); } @org.junit.Test public void testGetAllFileWithCondition() { Set<String> filePaths = new HashSet<String>(); Set<String> resultPaths = new HashSet<String>(); Set<String> Files = new HashSet<String>(); String File1 = "F:\WordCount"; String FIle2 = "F:\out.c"; Files.add(FIle2); Files.add(File1); String condition = ".c"; String result = "F:\out.c"; resultPaths.add(result); filePaths = new CountUtil().getAllFileWithCondition(Files, condition); assertTrue("得到的文件错误", resultPaths.equals(filePaths)); } @org.junit.Test public void testGetDirectoryFilesWithCondition() { Set<String> filePaths = new HashSet<String>(); Set<String> resultPaths = new HashSet<String>(); File File1 = new File("F:\WordCount"); String condition = ".c"; filePaths = CountUtil.getDirectoryFilesWithCondition(File1, condition); assertTrue("得到的文件错误", resultPaths.equals(filePaths)); } @org.junit.Test public void testGetCodeLines() { Set<String> filePaths = new HashSet<String>(); filePaths.add("F:\out.c"); String result = "F:\out.c,代码行数:2 "; assertTrue("代码行错误", result.equals(countUtil.getCodeLines(filePaths))); } @org.junit.Test public void testGetEmptyLines() { Set<String> filePaths = new HashSet<String>(); filePaths.add("F:\out.c"); String result = "F:\out.c,空行数:1 "; assertTrue("空行数错误", result.equals(countUtil.getEmptyLines(filePaths))); } @org.junit.Test public void testGetNoteLines() { Set<String> filePaths = new HashSet<String>(); filePaths.add("F:\out.c"); String result = "F:\out.c,注释行数:2 "; assertTrue("注释行错误", result.equals(countUtil.getNoteLines(filePaths))); }
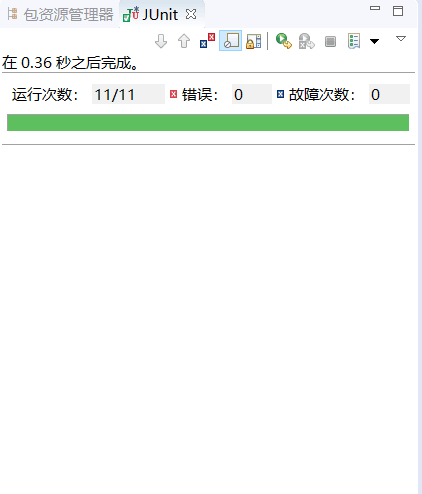
5.2 单元测试结果
5.3 exe文件测试结果
所有的文件:
out.c用例:

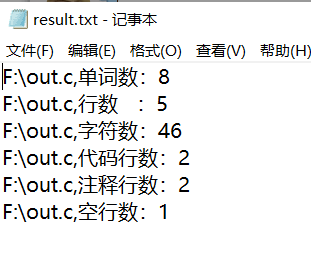
(1)代码行数、注释行数、空行数测试:


(2)单词数、行数、字符数测试


(3)字符数、行数、单词数和代码数、注释行数、空行数测试:
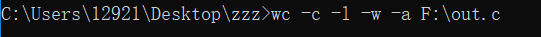
(4)基础功能和扩展功能测试
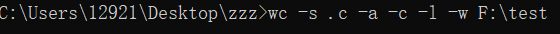
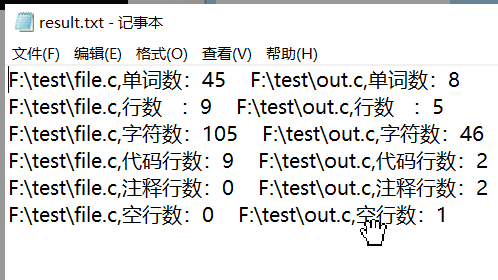
(5)停用词表测试
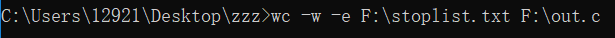
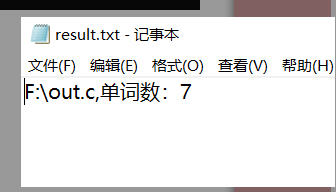
(6)UI界面

6.总结
在这次结对项目实践完成之后,我发现1+1是大于2的。我们项目完成的效率远比当时我一个人完成的时候要高出很多,而且我们一起编程可以及时解决所遇到的问题和避免一些不必要的问题。避免走了很多的弯路。除此之外,我还学习到了我队员的编程思想和他的学习方式,这些东西都给我带来了很多的启发和新的思路。总得来说,整个项目的完成也比之前的更加顺利和充满动力。提高了我对完成项目的积极性。
