题目:ironic学习笔记day1
日期:2018.7.9
参考官方文档:https://docs.openstack.org/ironic/latest/user/index.html
一.絮絮叨叨
今年刚毕业,作为应届生入职了一家云计算公司,开发基于openstack的产品.
openstack真的是个很大分布式系统,通过网络将用户和网络背后丰富的硬件资源分离开.
而我进入的是计算组,主要需要掌握Nova的知识,目前除了了解一些Nova表面上的对虚机的运维操作,很多很深入的知识还是两眼一摸黑,不过功夫不负有心人嘛,好的开始是成功的一半,工作生活都是一步一步来的,现在只能给自己打气啦嘿嘿~
加油加油~
二.内容概述
现在掌握的情报:对Nova而言,Nova是用于管理虚机的生命周期;而ironic是用于管理物理机的生命周期.
在网上讲ironic的文章很多,但是对于小白的我来说还是感到很苦手,因为内容真的太多了,感到有点无力,我只能很笨的从官方的文档进行一个大致的浏览.
看到了整个ironic与Nova交互的一个部署过程官方文档,通过谷歌翻译了一下,进行了如下的摘录:
三.ironic简介
Ironic is an OpenStack project which provisions bare metal (as opposed to virtual) machines. It may be used independently or as part of an OpenStack Cloud, and integrates with the OpenStack Identity (keystone), Compute (nova), Network (neutron), Image (glance) and Object (swift) services
Ironic是一个OpenStack项目,为裸机(而不是虚拟)机器提供服务。 它可以单独使用,也可以作为OpenStack Cloud的一部分使用,并与OpenStack Identity(keystone),Compute(nova),Network(neutron),Image(glance)和Object(swift)服务集成。
四.ironic节点部署过程图示
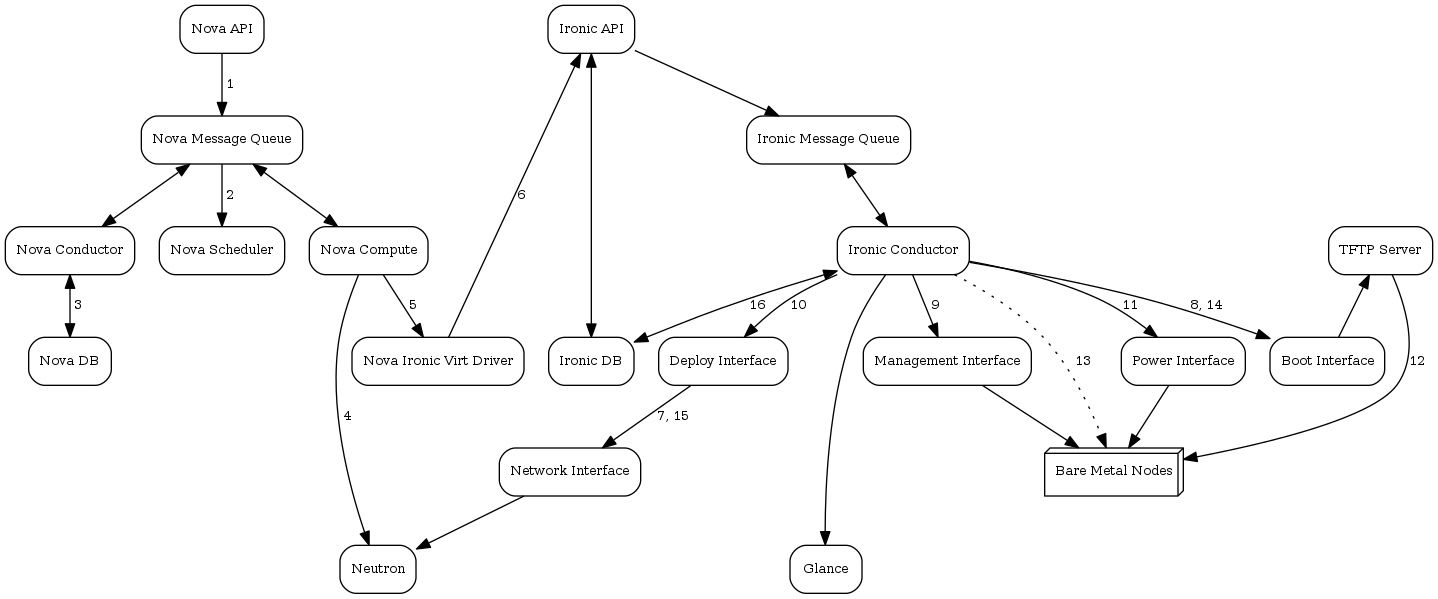
五.部署过程(Deploy Process)
This describes a typical ironic node deployment using PXE and the Ironic Python Agent (IPA). Depending on the ironic driver interfaces used, some of the steps might be marginally different, however the majority of them will remain the same.
- A boot instance request comes in via the Nova API, through the message queue to the Nova scheduler.
- Nova scheduler applies filters and finds the eligible hypervisor. The nova scheduler also uses the flavor’s extra_specs, such as cpu_arch, to match the target physical node.
- Nova compute manager claims the resources of the selected hypervisor.
- Nova compute manager creates (unbound) tenant virtual interfaces (VIFs) in the Networking service according to the network interfaces requested in the nova boot request. A caveat here is, the MACs of the ports are going to be randomly generated, and will be updated when the VIF is attached to some node to correspond to the node network interface card’s (or bond’s) MAC.Nova计算管理器根据nova引导请求中请求的网络接口在Networking服务中创建(未绑定)租户虚拟接口(VIF)。 这里需要注意的是,端口的MAC将随机生成,并且当VIF连接到某个节点以对应于节点网络接口卡(或债券)MAC时将更新。
- A spawn task is created by the nova compute which contains all the information such as which image to boot from etc. It invokes the driver.spawn from the virt layer of Nova compute. During the spawn process, the virt driver does the following:产生的任务由nova计算机创建,它包含所有信息,例如从哪个图像引导等。它从Nova计算的virt层调用driver.spawn。 在spawn过程中,virt驱动程序执行以下操作:
- Updates the target ironic node with the information about deploy image, instance UUID, requested capabilities and various flavor properties.
- Validates node’s power and deploy interfaces, by calling the ironic API.
- Attaches the previously created VIFs to the node. Each neutron port can be attached to any ironic port or port group, with port groups having higher priority than ports. On ironic side, this work is done by the network interface. Attachment here means saving the VIF identifier into ironic port or port group and updating VIF MAC to match the port’s or port group’s MAC, as described in bullet point 4..将先前创建的VIF附加到节点。 每个neutron端口可以连接到任何ironic的端口或端口组,端口组的优先级高于端口。 在ironic这一边,这项工作是通过网络接口完成的。 此处的附件意味着将VIF标识符保存到ironic端口或端口组中,并更新VIF MAC以匹配端口或端口组的MAC,如第4点中所述。
- Generates config drive, if requested.
- Nova’s ironic virt driver issues a deploy request via the Ironic API to the Ironic conductor servicing the bare metal node.
- Virtual interfaces are plugged in and Neutron API updates DHCP port to set PXE/TFTP options. In case of using neutron network interface, ironic creates separate provisioning ports in the Networking service, while in case of flat network interface, the ports created by nova are used both for provisioning and for deployed instance networking.插入虚拟接口,Neutron API更新DHCP端口以设置PXE / TFTP选项。 在使用neutron网络接口的情况下,ironic在网络服务中创建单独的配置端口,而在扁平网络接口的情况下,nova创建的端口用于配置和部署的实例网络。
- The ironic node’s boot interface prepares (i)PXE configuration and caches deploy kernel and ramdisk.
- The ironic node’s management interface issues commands to enable network boot of a node.
- The ironic node’s deploy interface caches the instance image (in case of iscsi deploy interface or most pxe_* classic drivers), and kernel and ramdisk if needed (it is needed in case of netboot for example).ironic节点的部署接口缓存实例映像(在iscsi部署接口或大多数pxe_ *经典驱动程序的情况下),以及内核和ramdisk(如果需要)(例如在netboot的情况下需要)。
- The ironic node’s power interface instructs the node to power on.
- The node boots the deploy ramdisk.
- Depending on the exact driver used, either the conductor copies the image over iSCSI to the physical node (iSCSI deploy) or the deploy ramdisk downloads the image from a temporary URL (Direct deploy). The temporary URL can be generated by Swift API-compatible object stores, for example Swift itself or RadosGW.根据所使用的确切驱动程序,导体将图像通过iSCSI复制到物理节点(iSCSI部署),或者部署ramdisk从临时URL下载映像(直接部署)。 临时URL可以由Swift API兼容的对象存储生成,例如Swift本身或RadosGW。The image deployment is done.
- The node’s boot interface switches pxe config to refer to instance images (or, in case of local boot, sets boot device to disk), and asks the ramdisk agent to soft power off the node. If the soft power off by the ramdisk agent fails, the bare metal node is powered off via IPMI/BMC call.节点的引导接口将pxe config切换为引用实例映像(或者,如果是本地引导,则将引导设备设置为磁盘),并要求ramdisk代理软关闭节点电源。 如果ramdisk代理关闭软电源失败,则通过IPMI / BMC呼叫关闭裸机节点电源。
- The deploy interface triggers the network interface to remove provisioning ports if they were created, and binds the tenant ports to the node if not already bound. Then the node is powered on.部署接口会触发网络接口,以便在创建时删除配置端口,并将租户端口绑定到节点(如果尚未绑定)。 然后节点上电。Note:There are 2 power cycles during bare metal deployment; the first time the node is powered-on when ramdisk is booted, the second time after the image is deployed.注意:裸机部署期间有2个电源循环; 第一次启动ramdisk时启动节点,第二次部署映像后。
- The bare metal node’s provisioning state(配置状态) is updated to active.