类的加载分为三个阶段,加载--->链接--->初始化
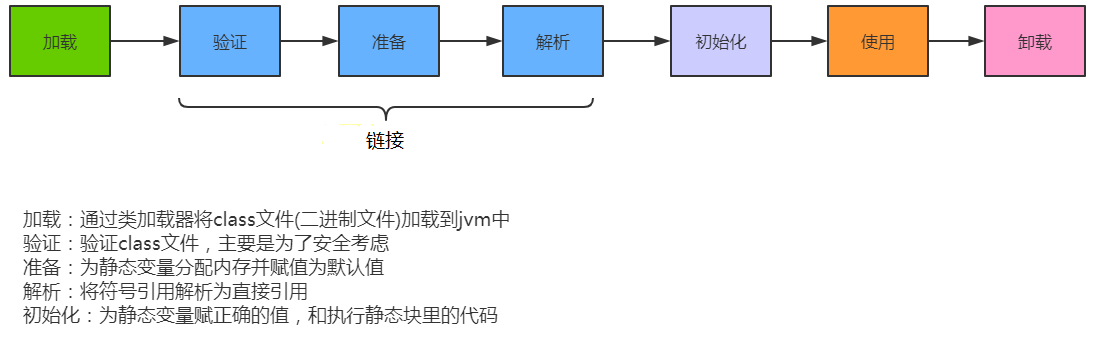
类加载的过程
将class表示的二进制文件加载到内存,放在方法区中,并在堆中创建一个java.lang.Class对象(封装的是class的数据结构)
类的主动使用,会加载类
1 new Test()
2 对类中的静态变量进行读写,对接口中的静态变量进行读取
3 反射某个类 , Class.forName()
4 调用静态方法
5 初始化子类时,父类将被初始化
6 启动类 ,采用java命令执行某个类
类的被动使用,不会加载类
1 子类引用父类的静态变量 ,父类会被初始化,子类不会被初始化
public class Parent { public static int a = 123; static { System.out.println("Parent init"); } } public class Child extends Parent { static { System.out.println("Child init"); } } public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { // 这里是访问的父类的静态变量 System.out.println(Child.a); } }
只初始化了父类

2 通过引用类型定义数组,不会触发此类的初始化
3 final修饰的常量,不会触发此类的初始化,因为在编译期间就放入了常量池
4 final修饰的复杂类型,会触发此类的初始化,因为在编译期间不能计算得出其值
4 JVM最先初始化的总是java.lang.Object类
类初始化要注意的地方
/** * * 在static块里,不能对在它后面的静态变量进行读取的操作,但可以写入 * 在对它前面定义的静态变量,可以读取和写入 */ public class MyObject { private static String x = "abc"; static { x= "edf"; b =12; //这里会提示错误,can not reference a field before define it //System.out.println(b); } private static int b = 10; }
/** * * 在初始化类Foo时候,会执行类的static块。这时候开启两个线程进行new对象,JVM保证了只能有一个线程执行类的初始化 * */ public class ClinitTest { public static void main(String[] args) { new Thread(()-> {new Foo();}).start(); new Thread(()-> {new Foo();}).start(); } } class Foo{ private static AtomicBoolean init = new AtomicBoolean(true); static { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " will be inint"); while (init.get()) { } System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " have done inint"); } }
对象实例化

类的初始化和对象实例化有时是同时进行的
class Price { static Price P = new Price(2.7); static double apple = 20; double price; public Price(double orange) { price = apple - orange; } } public class PriceTest { public static void main(String[] args) { //Price.P访问了类的静态变量,会触发类的初始化,即(加载,连接,初始化),当执行构造函数时 //apple还没有初始化完成,处于连接阶段的准备阶段,其值为默认值0,这时构造函数计算的price为-2.7 System.out.println(Price.P.price);// 结果为-2.7 } }
class Price { static Price P = new Price(2.7); final static double apple = 20; double price; public Price(double orange) { price = apple - orange; } } public class PriceTest { public static void main(String[] args) { //apple在编译阶段就完成赋值了,其值为20,这时构造函数计算的price为17.3 System.out.println(Price.P.price);// 结果为17.3 } }
class Price { static double apple = 20; static Price P = new Price(2.7); double price; public Price(double orange) { price = apple - orange; } } public class PriceTest { public static void main(String[] args) { //Price.P访问了类的静态变量,会触发类的初始化,即(加载,连接,初始化),当执行构造函数时 //apple已经完成了初始化,其值为20了,这时构造函数计算的price为17.3 System.out.println(Price.P.price);// 结果为17.3 } }