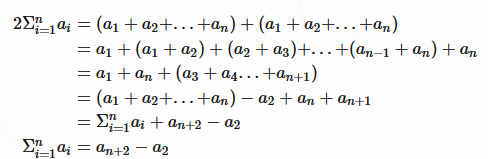当一个数列满足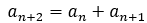 ,但它的1,2项不是1,1时,
,但它的1,2项不是1,1时,
称它为类斐波那契数列。
它满足以下性质:
若有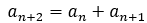 :
:
1.设 ,则
,则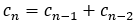
2.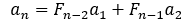
证明:
设
,则
3.前缀和公式: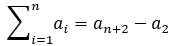
证明:
通过以上性质,发现它可以用线段树维护。
对于每个节点,$sum$表示区间和;
$c1$,$c2$表示这段区间被加上了前两项分别为$c1$,$c2$的类斐波那契数列。
因为初始的数列不一定满足类斐波那契数列的性质,所以把它储存在线段树之外的一个数组里,求值时直接用前缀和求出即可。
注意数据范围!
代码如下

#include<cstdio> #include<iostream> #include<cmath> #include<cstring> #define MogeKo qwq using namespace std; #define ls (now<<1) #define rs (now<<1|1) const int maxn = 2e6+10; const int mod = 1e9+9; long long n,m,x,y,op; long long a[maxn],f[maxn]; struct tree { long long sum,c1,c2; } t[maxn]; int read() { int x = 0,f = 1; char ch = getchar(); while(ch < '0' || ch > '9') { if(ch == '-') f = -1; ch = getchar(); } while('0' <= ch && ch <= '9') { x = (x<<3)+(x<<1) + ch-'0'; ch = getchar(); } return x * f; } long long getx(long long a1,long long a2,long long x) { if(x == 1) return a1; if(x == 2) return a2; return ( a1*f[x-2] + a2*f[x-1] ) % mod; } long long getsum(long long a1,long long a2,long long x) { if(x == 1) return a1; if(x == 2) return (a1+a2) % mod; return ( getx(a1,a2,x+2) - a2 + mod ) % mod; } void pushup(int now) { t[now].sum = (t[ls].sum + t[rs].sum) % mod; } void pushdown(int l,int r,int now) { if(!t[now].c1) return; int mid = (l+r)>>1; long long a1,a2; a1 = t[now].c1; a2 = t[now].c2; t[ls].c1 = (t[ls].c1 + a1) % mod; t[ls].c2 = (t[ls].c2 + a2) % mod; t[ls].sum = (t[ls].sum + getsum(a1,a2,mid-l+1)) % mod; a1 = getx(t[now].c1,t[now].c2,mid-l+2); a2 = getx(t[now].c1,t[now].c2,mid-l+3); t[rs].c1 = (t[rs].c1 + a1) % mod; t[rs].c2 = (t[rs].c2 + a2) % mod; t[rs].sum = (t[rs].sum + getsum(a1,a2,r-mid)) % mod; t[now].c1 = t[now].c2 = 0; } void modify(int L,int R,int l,int r,int now) { if(L <= l && r <= R) { t[now].c1 = (t[now].c1 + f[l-L+1]) % mod; t[now].c2 = (t[now].c2 + f[l-L+2]) % mod; t[now].sum = (t[now].sum + getsum(f[l-L+1],f[l-L+2],r-l+1)) % mod; return; } pushdown(l,r,now); int mid = (l+r)>>1; if(L <= mid) modify(L,R,l,mid,ls); if(R > mid) modify(L,R,mid+1,r,rs); pushup(now); } long long query(int L,int R,int l,int r,int now) { long long ans = 0; if(L <= l && r <= R) { ans = t[now].sum; return (ans + mod) % mod; } pushdown(l,r,now); int mid = (l+r)>>1; if(L <= mid) ans = (ans + query(L,R,l,mid,ls)) % mod; if(R > mid) ans = (ans + query(L,R,mid+1,r,rs)) % mod; return (ans+mod)%mod; } void init() { f[1] = f[2] = 1; for(int i = 3; i <= n+2; i++) f[i] = (f[i-1] + f[i-2]) %mod; } int main() { n = read(),m = read(); for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { x = read(); a[i] = (a[i-1] + x) % mod; } init(); while(m--) { op = read(); x = read(), y = read(); if(op == 1) modify(x,y,1,n,1); if(op == 2) printf("%lld ",((a[y]-a[x-1]+query(x,y,1,n,1))%mod+mod)%mod); } return 0; }