本章内容:
- 学习使用心得数据结构-图,来创建网络模型
- 学习广度优先搜索,使用图这种算法回答“到X的最短路径是什么的问题”
- 学习有向图和无向图
- 学习拓扑排序,这种排序算法指出了节点之间的依赖关系
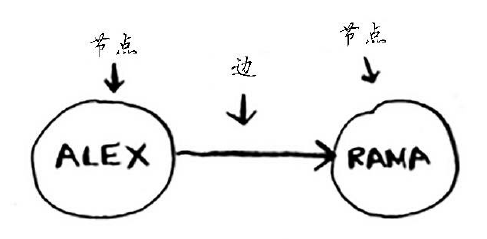
6.1图简介
图有节点和边组成。如下图:
6.3广度优先算法
6.3.1查找最短路径
广度优先算法回答两类问题:
1、从节点A出发,有前往节点B的路径么?(在你的朋友中找芒果销售商)
2、从节点A出发,前往节点B的那条路径最短?(哪个销售商与你的关系最近)
注意:只有按条件顺序查找时,才能实现这样的目的。否则,查找到的结果并非是最近的。队列(queue)就是这样的数据结构。
6.3.2队列
队列只支持两种操作:入队和出队。
6.4实现图
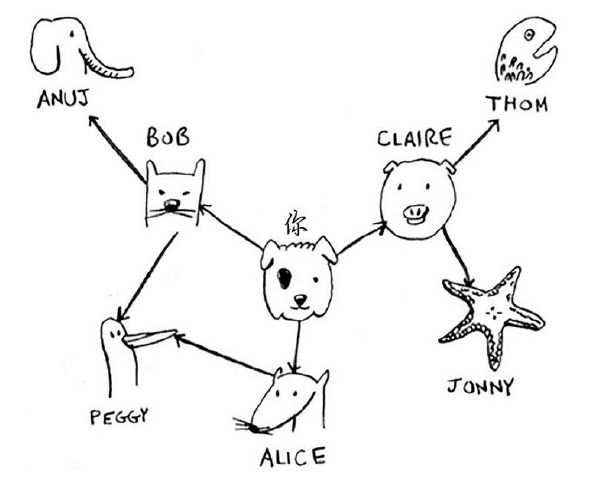
graph = {} graph["you"] = ["alice", "bob", "claire"] graph["bob"] = ["anuj", "peggy"] graph["alice"] = ["peggy"] graph["claire"] = ["thom", "jonny"] graph["anuj"] = [] graph["peggy"] = [] graph["thom"] = [] graph["jonny"] = []
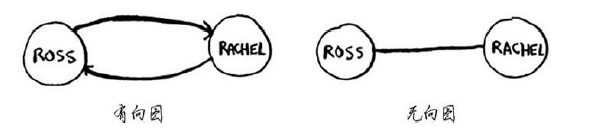
有向图(directed graph):有箭头,关系是单向的
无向图(undirected graph):无箭头,直接相连的节点互为邻居
如下二图是等价的:
6.5实现算法

from collections import deque def person_is_seller(name): return name[-1] == 'm' #last element is m. graph = {} graph["you"] = ["alice", "bob", "claire"] graph["bob"] = ["anuj", "peggy"] graph["alice"] = ["peggy"] graph["claire"] = ["thom", "jonny"] graph["anuj"] = [] graph["peggy"] = [] graph["thom"] = [] graph["jonny"] = [] def search(name): search_queue = deque() search_queue += graph[name] # This array is how you keep track of which people you've searched before. searched = [] while search_queue: person = search_queue.popleft() print person # Only search this person if you haven't already searched them. if not person in searched: if person_is_seller(person): print person + " is a mango seller!" return True else: search_queue += graph[person] # Marks this person as searched searched.append(person) else: print "skip repeatedly " + person #peggy is repeatedly return False search("you")
运行时间:广度优先搜索的运行时间为O(V+E),其中V为定点(vertice)数,E为边数。
另,树是一种特殊的图,其边是单向的。
6.6小结
- 广度优先算法之处是否有从A到B的路径
- 如果有,广度优先搜索将找出最短路径
- 如果面临类似于寻找最短路径的问题,可尝试用图来创建模型,再用广度优先搜索来解决问题
- 有向图的边为箭头,箭头的方向制定了关系的方向,如,你->我,代表你欠我钱。
- 无向图的边有箭头,关系是双向的,如你和我约会,等同我和你约会
- 队列是FIFO
- 栈是LIFO
- 搜索列表必须是有序的,否则找不到最短路径
- 检查过的,务必不要再检查,否则可能导致无限循环
广度优先算法的C语言实现:
https://blog.csdn.net/code_mlym/article/details/52435044

1 /************************************************************************* 2 > File Name: graph.c 3 > Author: jeff zhu 4 > Mail: 908190355@qq.com 5 > Created Time: 2016年09月04日 星期日 18时58分08秒 6 ************************************************************************/ 7 8 #include <stdio.h> 9 #include <malloc.h> 10 #include <limits.h> 11 12 #define MAXSIZE 100 //图的最大的顶点数量为100, 13 #define WHITE 1 //定义每个顶点的可能的颜色,白色代表没有探索,灰色代表已经探索,但是其邻接的定点没有完全探索,黑的代表其所有邻接的顶点都探索过。 14 #define GRAY 2 15 #define BLACK 3 16 #define INFINITE INT_MAX //定义一个正无穷 17 18 typedef struct gra_ptr_node { //这个地方我定义了一个数据结构,这个数据结构用来实现链表(这个链表的节点的关键字是指针,所以节省了空间,在效率上也没有损耗) 19 struct gra_ptr_node *next; 20 struct graph_node *ptr; 21 }PTR_NODE; 22 typedef struct graph_node { //图的每个顶点,parent用来实现广度优先搜索树,nect用来实现来链表,key代表编号,d是距离搜索顶点的距离,f是为了深度优先搜索而准备<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>//的 23 struct graph_node *parent; 24 struct graph_node *next; 25 int key; 26 int d; 27 int f; 28 int color; 29 }NODE; 30 typedef struct graph { //图的数据结构,length代表adj实际的长度 31 PTR_NODE *adj[MAXSIZE]; 32 int length; 33 }GRAPH; 34 typedef struct stack_of_granode { //在BFS中会用到的栈 35 NODE *arr_temp[MAXSIZE]; 36 int start; 37 int end; 38 int length; 39 int count; 40 }NODEQUEUE; 41 42 NODE *arr_V[MAXSIZE]; //这个数组保存所有的顶点,可以直接在这个数组中找到想要的定点 43 void BFS (GRAPH *G , NODE *s) ; 44 45 void init_graph (GRAPH *G , int len) ; 46 NODE *create_and_init_node (int key) ; 47 void insert_to_adj (GRAPH *G , NODE *x , int key) ; 48 void init_queue (NODEQUEUE *Q , GRAPH *G) ; 49 void enqueue (NODEQUEUE *Q , NODE *x) ; 50 NODE *dequeue (NODEQUEUE *Q) ; 51 void BFS (GRAPH *G , NODE *s) ; 52 53 int main () { 54 int i; 55 int count = 0; 56 GRAPH G; 57 NODE *temp; 58 NODE *temp1; 59 PTR_NODE *ptr_temp; 60 NODEQUEUE Q; //一下两行代码放到BFS函数中更好,写注释的时候发现的懒得改了 61 init_queue (&Q , &G); 62 63 init_graph (&G , 8); //初始化图 64 65 temp = create_and_init_node (0); //一下代码都是初始化一个图,图的逻辑结构见《算法导论》图22-3 66 arr_V[count++] = temp; 67 insert_to_adj (&G , temp , 1); 68 69 temp = create_and_init_node (1); 70 arr_V[count++] = temp; 71 insert_to_adj (&G , temp , 0); 72 insert_to_adj (&G , temp , 2); 73 74 temp = create_and_init_node (2); 75 temp1 = temp; 76 arr_V[count++] = temp; 77 insert_to_adj (&G , temp , 1); 78 insert_to_adj (&G , temp , 3); 79 80 temp = create_and_init_node (3); 81 arr_V[count++] = temp; 82 insert_to_adj (&G , temp , 2); 83 insert_to_adj (&G , temp , 4); 84 insert_to_adj (&G , temp , 5); 85 86 temp = create_and_init_node (4); 87 arr_V[count++] = temp; 88 insert_to_adj (&G , temp , 3); 89 insert_to_adj (&G , temp , 5); 90 insert_to_adj (&G , temp , 6); 91 insert_to_adj (&G , temp , 7); 92 93 temp = create_and_init_node (5); 94 arr_V[count++] = temp; 95 insert_to_adj (&G , temp , 3); 96 insert_to_adj (&G , temp , 4); 97 insert_to_adj (&G , temp , 6); 98 99 temp = create_and_init_node (6); 100 arr_V[count++] = temp; 101 insert_to_adj (&G , temp , 5); 102 insert_to_adj (&G , temp , 4); 103 insert_to_adj (&G , temp , 7); 104 105 temp = create_and_init_node (7); 106 arr_V[count++] = temp; 107 insert_to_adj (&G , temp , 6); 108 insert_to_adj (&G , temp , 4); //图初始化结束 109 110 for (i = 0 ; i < 8 ; i++) { 111 ptr_temp = G.adj[i]; 112 while (ptr_temp != NULL) { 113 printf ("%d " , ptr_temp->ptr->key); 114 ptr_temp = ptr_temp->next; 115 } 116 printf (" "); 117 } //打印一下结果,看看是否和逻辑图是一样的 118 printf (" "); 119 BFS (&G , temp1); //执行BFS算法 120 121 for (i = 0 ; i < count ; i++) { 122 printf ("%d " , arr_V[i]->d); 123 } 124 printf (" "); 125 } 126 127 void init_graph (GRAPH *G , int len) { //初始化图的函数 128 int i; 129 130 G->length = len; 131 for (i = 0 ; i < len ; i++) { 132 G->adj[i] = NULL; 133 } 134 } 135 136 NODE *create_and_init_node (int key) { //创建和初始化图 137 NODE *temp = (NODE *) malloc (sizeof (NODE)); 138 139 temp->key = key; 140 temp->d = 0; 141 temp->f = 0; 142 temp->next = NULL; 143 temp->parent = NULL; 144 145 return temp; 146 } 147 148 void insert_to_adj (GRAPH *G , NODE *x , int key) { //这个函数从图论的角度来说是将边加入到一个关于顶点的便于搜索数组。 149 if (key >= G->length) { 150 printf ("the key is too big"); 151 return; 152 } 153 154 PTR_NODE *temp; 155 temp = (PTR_NODE *) malloc (sizeof (PTR_NODE)); 156 temp->next = G->adj[key]; 157 temp->ptr = x; 158 G->adj[key] = temp; 159 } 160 161 void init_queue (NODEQUEUE *Q , GRAPH *G) { //初始化BFS算法要用到的队列Q。 162 Q->start = 0; 163 Q->end = 0; 164 Q->length = G->length; 165 Q->count = 0; 166 } 167 void enqueue (NODEQUEUE *Q , NODE *x) { //将节点x加入到队列Q中。同时,Q->count加1。 168 if (((Q->end+1) % Q->length) == Q->start) 169 return; 170 else { 171 Q->arr_temp[Q->end] = x; 172 Q->end++; 173 if (Q->end == Q->length) 174 Q->end = 0; 175 Q->count++; 176 } 177 } 178 179 NODE *dequeue (NODEQUEUE *Q) { //返回Q->arr[Q->start],同时将这个数组给删除。同时,Q->count减1。 180 NODE *temp; 181 if (Q->start == Q->end) 182 return; 183 else { 184 temp = Q->arr_temp[Q->start]; 185 Q->start++; 186 if (Q->start == Q->length) 187 Q->start = 0; 188 Q->count--; 189 } 190 return temp; 191 } 192 193 void BFS (GRAPH *G , NODE *s) { //终于到了广度优先算法了,这个算法的核心思想就是,先探索和当前节点邻接的顶点,然后再探索别的定点 194 int i; 195 NODEQUEUE Q; 196 init_queue (&Q , G); 197 NODE *temp; 198 PTR_NODE *ptr_temp; 199 200 for (i = 0 ; i < G->length ; i++) { 201 if (arr_V[i] != s) { 202 arr_V[i]->color = WHITE; 203 arr_V[i]->d = INFINITE; 204 arr_V[i]->parent = NULL; 205 } 206 } 207 s->color = GRAY; 208 s->parent = NULL; 209 s->d = 0; 210 enqueue (&Q , s); 211 212 while (Q.count != 0) { 213 temp = dequeue (&Q); 214 ptr_temp = G->adj[temp->key]; 215 while (ptr_temp != NULL) { 216 if (ptr_temp->ptr->color == WHITE) { 217 ptr_temp->ptr->color = GRAY; 218 ptr_temp->ptr->d = temp->d + 1; 219 ptr_temp->ptr->parent = temp; 220 enqueue (&Q , ptr_temp->ptr); 221 } 222 ptr_temp = ptr_temp->next; 223 } 224 temp->color = BLACK; 225 } 226 }
