本节内容:
- Python 运算符(算术运算、比较运算、赋值运算、逻辑运算、成员运算)
- 基本数据类型(数字、布尔值、字符串、列表、元组、字典)
- 其他(编码,range,for,while)
Python 运算符
1、算术运算:
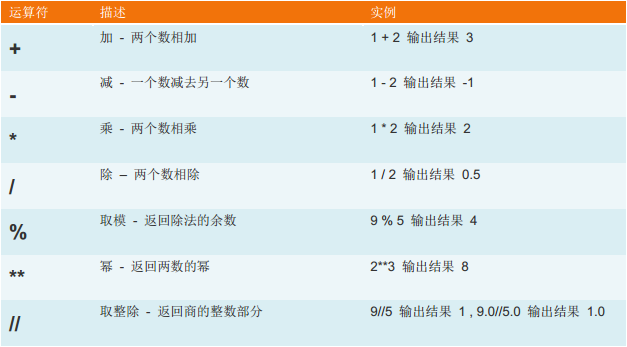
2、比较运算:
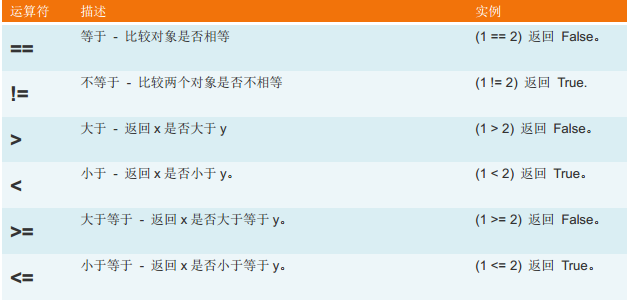
3、赋值运算:
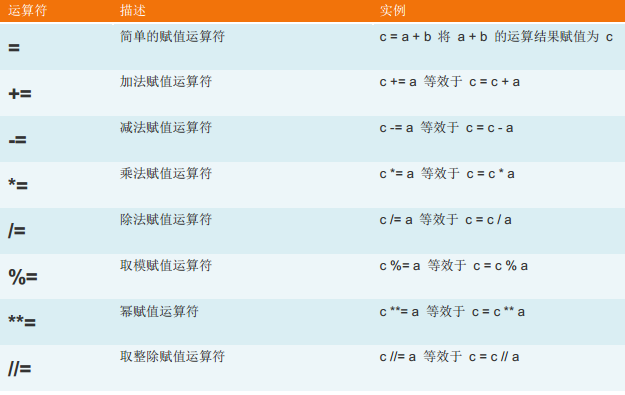
4、逻辑运算:
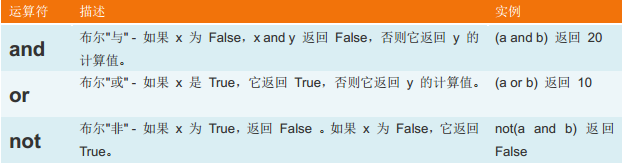
5、成员运算:

基本数据类型
1、数字
int(整型)

1 数字 int ,所有的功能,都放在int里 2 a1 = 123 3 a1 = 456 4 5 - int 6 将字符串转换为数字 7 a = "123" 8 print(type(a),a) 9 b = int(a) 10 print(type(b),b) 11 12 进制转换,例子为转换为16进制 13 num = "0011" 14 v = int(num, base=16) 15 print(v) 16 - bit_lenght 17 当前数字的二进制,至少用n位表示 18 r = age.bit_length()

1 class int(object): 2 """ 3 int(x=0) -> integer 4 int(x, base=10) -> integer 5 6 Convert a number or string to an integer, or return 0 if no arguments 7 are given. If x is a number, return x.__int__(). For floating point 8 numbers, this truncates towards zero. 9 10 If x is not a number or if base is given, then x must be a string, 11 bytes, or bytearray instance representing an integer literal in the 12 given base. The literal can be preceded by '+' or '-' and be surrounded 13 by whitespace. The base defaults to 10. Valid bases are 0 and 2-36. 14 Base 0 means to interpret the base from the string as an integer literal. 15 >>> int('0b100', base=0) 16 """ 17 def bit_length(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 18 """ 19 int.bit_length() -> int 20 21 Number of bits necessary to represent self in binary. 22 """ 23 """ 24 表示该数字返回时占用的最少位数 25 26 >>> (951).bit_length() 27 """ 28 return 0 29 30 def conjugate(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 31 """ Returns self, the complex conjugate of any int.""" 32 33 """ 34 返回该复数的共轭复数 35 36 #返回复数的共轭复数 37 >>> (95 + 11j).conjugate() 38 (95-11j) 39 #返回复数的实数部分 40 >>> (95 + 11j).real 41 95.0 42 #返回复数的虚数部分 43 >>> (95 + 11j).imag 44 11.0 45 """ 46 pass 47 48 @classmethod # known case 49 def from_bytes(cls, bytes, byteorder, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown; NOTE: unreliably restored from __doc__ 50 """ 51 int.from_bytes(bytes, byteorder, *, signed=False) -> int 52 53 Return the integer represented by the given array of bytes. 54 55 The bytes argument must be a bytes-like object (e.g. bytes or bytearray). 56 57 The byteorder argument determines the byte order used to represent the 58 integer. If byteorder is 'big', the most significant byte is at the 59 beginning of the byte array. If byteorder is 'little', the most 60 significant byte is at the end of the byte array. To request the native 61 byte order of the host system, use `sys.byteorder' as the byte order value. 62 63 The signed keyword-only argument indicates whether two's complement is 64 used to represent the integer. 65 """ 66 """ 67 这个方法是在Python3.2的时候加入的,python官方给出了下面几个例子: 68 >>> int.from_bytes(b'x00x10', byteorder='big') 69 >>> int.from_bytes(b'x00x10', byteorder='little') 70 >>> int.from_bytes(b'xfcx00', byteorder='big', signed=True) 71 -1024 72 >>> int.from_bytes(b'xfcx00', byteorder='big', signed=False) 73 >>> int.from_bytes([255, 0, 0], byteorder='big') 74 """ 75 pass 76 77 def to_bytes(self, length, byteorder, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown; NOTE: unreliably restored from __doc__ 78 """ 79 int.to_bytes(length, byteorder, *, signed=False) -> bytes 80 81 Return an array of bytes representing an integer. 82 83 The integer is represented using length bytes. An OverflowError is 84 raised if the integer is not representable with the given number of 85 bytes. 86 87 The byteorder argument determines the byte order used to represent the 88 integer. If byteorder is 'big', the most significant byte is at the 89 beginning of the byte array. If byteorder is 'little', the most 90 significant byte is at the end of the byte array. To request the native 91 byte order of the host system, use `sys.byteorder' as the byte order value. 92 93 The signed keyword-only argument determines whether two's complement is 94 used to represent the integer. If signed is False and a negative integer 95 is given, an OverflowError is raised. 96 """ 97 """ 98 python官方给出了下面几个例子: 99 >>> (1024).to_bytes(2, byteorder='big') 100 b'x04x00' 101 >>> (1024).to_bytes(10, byteorder='big') 102 b'x00x00x00x00x00x00x00x00x04x00' 103 >>> (-1024).to_bytes(10, byteorder='big', signed=True) 104 b'xffxffxffxffxffxffxffxffxfcx00' 105 >>> x = 1000 106 >>> x.to_bytes((x.bit_length() // 8) + 1, byteorder='little') 107 b'xe8x03' 108 """ 109 pass 110 111 def __abs__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 112 """ abs(self)""" 113 114 """ 115 返回一个绝对值 116 117 >>> (95).__abs__() 118 -95 119 >>> (-95).__abs__() 120 """ 121 pass 122 123 124 def __add__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 125 """ Return self+value.""" 126 127 """ 128 加法,也可区分数字和字符串 129 130 >>> (95).__add__(1) 131 >>> (95).__add__("1") 132 NotImplemented 133 >>> 134 """ 135 pass 136 137 def __and__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 138 """ Return self&value.""" 139 pass 140 141 def __bool__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 142 """ self != 0 """ 143 144 """ 145 判断一个整数对象是否为0,如果为0,则返回False,如果不为0,则返回True 146 147 >>> (95).__bool__() 148 True 149 >>> (0).__bool__() 150 False 151 """ 152 pass 153 154 def __ceil__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 155 """ Ceiling of an Integral returns itself. """ 156 pass 157 158 def __divmod__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 159 """ Return divmod(self, value). """ 160 """ 161 返回一个元组,第一个元素为商,第二个元素为余数 162 163 >>> (9).__divmod__(5) 164 (1, 4) 165 """ 166 pass 167 168 def __eq__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 169 """ Return self==value. """ 170 """ 171 判断两个值是否相等 172 173 >>> (95).__eq__(95) 174 True 175 >>> (95).__eq__(9) 176 False 177 """ 178 pass 179 180 def __float__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 181 """ float(self) """ 182 """ 183 将一个整数转换成浮点型 184 185 >>> (95).__float__() 186 95.0 187 """ 188 pass 189 190 def __floordiv__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 191 """ Return self//value. """ 192 """ 193 整除,保留结果的整数部分 194 195 >>> (95).__floordiv__(9) 196 """ 197 pass 198 199 def __floor__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 200 """ Flooring an Integral returns itself. """ 201 """ 202 返回本身 203 204 >>> (95).__floor__() 205 """ 206 pass 207 208 def __format__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 209 """ 210 转换对象的类型 211 212 >>> (95).__format__('f') 213 '95.000000' 214 >>> (95).__format__('b') 215 '1011111' 216 """ 217 pass 218 219 220 def __getattribute__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 221 """ Return getattr(self, name). """ 222 """ 223 判断这个类中是否包含这个属性,如果包含则打印出值,如果不包含,就报错了 224 225 >>> (95).__getattribute__('__abs__') 226 <method-wrapper '__abs__' of int object at 0x9f93c0> 227 >>> (95).__getattribute__('__aaa__') 228 Traceback (most recent call last): 229 File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module> 230 AttributeError: 'int' object has no attribute '__aaa__' 231 """ 232 pass 233 234 def __getnewargs__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 235 pass 236 237 def __ge__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 238 """ Return self>=value. """ 239 """ 240 判断是否大于等于 241 242 >>> (95).__ge__(9) 243 True 244 >>> (95).__ge__(99) 245 False 246 """ 247 pass 248 249 def __gt__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 250 """ Return self>value. """ 251 """ 252 判断是否大于 253 254 >>> (95).__gt__(9) 255 True 256 >>> (95).__gt__(99) 257 False 258 """ 259 pass 260 261 def __hash__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 262 """ Return hash(self). """ 263 """ 264 计算哈希值,整数返回本身 265 266 >>> (95).__hash__() 267 >>> (95.95).__hash__() 268 """ 269 pass 270 271 def __index__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 272 """ Return self converted to an integer, if self is suitable for use as an index into a list. """ 273 pass 274 275 def __init__(self, x, base=10): # known special case of int.__init__ 276 """ 277 这个是一个类的初始化方法,当int类被实例化的时候,这个方法默认就会被执行 278 """ 279 """ 280 int(x=0) -> integer 281 int(x, base=10) -> integer 282 283 Convert a number or string to an integer, or return 0 if no arguments 284 are given. If x is a number, return x.__int__(). For floating point 285 numbers, this truncates towards zero. 286 287 If x is not a number or if base is given, then x must be a string, 288 bytes, or bytearray instance representing an integer literal in the 289 given base. The literal can be preceded by '+' or '-' and be surrounded 290 by whitespace. The base defaults to 10. Valid bases are 0 and 2-36. 291 Base 0 means to interpret the base from the string as an integer literal. 292 >>> int('0b100', base=0) 293 # (copied from class doc) 294 """ 295 pass 296 297 def __int__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 298 """ int(self) """ 299 """ 300 转换为整型 301 302 >>> (9.5).__int__() 303 """ 304 pass 305 306 307 def __invert__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 308 """ ~self """ 309 310 pass 311 312 def __le__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 313 """ Return self<=value. """ 314 """ 315 判断是否小于等于 316 317 >>> (95).__le__(99) 318 True 319 >>> (95).__le__(9) 320 False 321 """ 322 pass 323 324 def __lshift__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 325 """ Return self<<value. """ 326 """ 327 用于二进制位移,这个是向左移动 328 329 >>> bin(95) 330 '0b1011111' 331 >>> a = (95).__lshift__(2) 332 >>> bin(a) 333 '0b101111100' 334 >>> 335 """ 336 pass 337 338 def __lt__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 339 """ Return self<value. """ 340 """ 341 判断是否小于 342 343 >>> (95).__lt__(9) 344 False 345 >>> (95).__lt__(99) 346 True 347 """ 348 pass 349 350 def __mod__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 351 """ Return self%value. """ 352 """ 353 取模 % 354 355 >>> (95).__mod__(9) 356 """ 357 pass 358 359 def __mul__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 360 """ Return self*value. """ 361 """ 362 乘法 * 363 364 >>> (95).__mul__(10) 365 """ 366 pass 367 368 def __neg__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 369 """ -self """ 370 """ 371 将正数变为负数,将负数变为正数 372 373 >>> (95).__neg__() 374 -95 375 >>> (-95).__neg__() 376 """ 377 pass 378 379 @staticmethod # known case of __new__ 380 def __new__(*args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 381 """ Create and return a new object. See help(type) for accurate signature. """ 382 pass 383 384 def __ne__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 385 """ Return self!=value. """ 386 """ 387 不等于 388 389 >>> (95).__ne__(9) 390 True 391 >>> (95).__ne__(95) 392 False 393 """ 394 pass 395 396 def __or__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 397 """ Return self|value. """ 398 """ 399 二进制或的关系,只要有一个为真,就为真 400 401 >>> a = 4 402 >>> b = 0 403 >>> a.__or__(b) # a --> 00000100 b --> 00000000 404 >>> b = 1 # b --> 00000001 405 >>> a.__or__(b) 406 """ 407 pass 408 409 def __pos__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 410 """ +self """ 411 pass 412 413 def __pow__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 414 """ Return pow(self, value, mod). """ 415 """ 416 幂 417 418 >>> (2).__pow__(10) 419 """ 420 pass 421 422 def __radd__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signatre unknown 423 """ Return value+self. """ 424 """ 425 加法,将value放在前面 426 427 >>> a.__radd__(b) # 相当于 b+a 428 """ 429 pass 430 431 def __rand__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 432 """ Return value&self. """ 433 """ 434 二进制与的关系,两个都为真,才为真,有一个为假,就为假 435 """ 436 pass 437 438 def __rdivmod__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 439 """ Return divmod(value, self). """ 440 pass 441 442 def __repr__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 443 """ Return repr(self). """ 444 pass 445 446 def __rfloordiv__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 447 """ Return value//self. """ 448 pass 449 450 def __rlshift__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 451 """ Return value<<self. """ 452 pass 453 454 def __rmod__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 455 """ Return value%self. """ 456 pass 457 458 def __rmul__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 459 """ Return value*self. """ 460 pass 461 462 def __ror__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 463 """ Return value|self. """ 464 pass 465 466 def __round__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 467 """ 468 Rounding an Integral returns itself. 469 Rounding with an ndigits argument also returns an integer. 470 """ 471 pass 472 473 def __rpow__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 474 """ Return pow(value, self, mod). """ 475 pass 476 477 def __rrshift__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 478 """ Return value>>self. """ 479 pass 480 481 def __rshift__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 482 """ Return self>>value. """ 483 pass 484 485 def __rsub__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 486 """ Return value-self. """ 487 pass 488 489 def __rtruediv__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 490 """ Return value/self. """ 491 pass 492 493 def __rxor__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 494 """ Return value^self. """ 495 pass 496 497 def __sizeof__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 498 """ Returns size in memory, in bytes """ 499 """ 500 在内存中占多少个字节 501 502 >>> a = 95 503 >>> a.__sizeof__() 504 """ 505 pass 506 507 def __str__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 508 """ Return str(self). """ 509 """ 510 将一个正数转为字符串 511 512 >>> a = 95 513 >>> a = a.__str__() 514 >>> print(type(a)) 515 <class 'str'> 516 """ 517 pass 518 519 def __sub__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 520 """ Return self-value. """ 521 """ 522 减法运算 523 524 >>> (95).__sub__(5) 525 """ 526 pass 527 528 def __truediv__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 529 """ Return self/value. """ 530 """ 531 除法运算 532 533 >>> (95).__truediv__(5) 534 19.0 535 """ 536 pass 537 538 def __trunc__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 539 """ Truncating an Integral returns itself. """ 540 """ 541 返回一个对象的整数部分 542 543 >>> (95.95).__trunc__() 544 """ 545 pass 546 def __xor__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 547 """ Return self^value. """ 548 """ 549 将对象与值进行二进制的或运算,一个为真,就为真 550 551 >>> a = 4 552 >>> b = 1 553 >>> a.__xor__(b) 554 >>> c = 0 555 >>> a.__xor__(c) 556 """ 557 558 pass 559 560 denominator = property(lambda self: object(), lambda self, v: None, lambda self: None) # default 561 """ 分母 = 1 """ 562 """the denominator of a rational number in lowest terms""" 563 564 imag = property(lambda self: object(), lambda self, v: None, lambda self: None) # default 565 """ 虚数 """ 566 """the imaginary part of a complex number""" 567 568 numerator = property(lambda self: object(), lambda self, v: None, lambda self: None) # default 569 """ 分子 = 数字大小 """ 570 """the numerator of a rational number in lowest terms""" 571 572 real = property(lambda self: object(), lambda self, v: None, lambda self: None) # default 573 """ 实属 """ 574 """the real part of a complex number""" 575 576 int
2、布尔值
真或假
1 或 0
一下情况一般为False
None "" () [] {} 0 ==> False
其余情况一般为真
3、字符串

1 test = "来啊相互伤害啊" 2 3 # 一、for循环 4 # for 变量名 in 字符串: 5 # 变量名 6 # break 7 # continue 8 9 index = 0 10 while index < len(test): 11 v = test[index] 12 print(v) 13 index += 1 14 print('=======') 15 16 for in test: 17 print() 18 19 test = "来啊相互伤害啊" 20 for item in test: 21 print(item) 22 break 23 24 for item in test: 25 continue 26 print(item) 27 28 # 二、索引,下标,获取字符串中的某一个字符 29 v = test[3] 30 print(v) 31 32 # 三、切片 33 v = test[0:-1] # 0=< <1 34 print(v) 35 36 # 四、获取长度 37 # Python3: len获取当前字符串中由几个字符组成 38 v = len(test) 39 print(v) 40 41 # 注意: 42 # len("asdf") 43 # for循环 44 # 索引 45 # 切片 46 47 # 五、获取连续或不连续的数字,range用法 48 # Python2中直接创建在内容中 49 # python3中只有for循环时,才一个一个创建 50 r1 = range(10) 51 r2 = range(1,10) 52 r3 = range(1,10,2) 53 # 帮助创建连续的数字,通过设置步长来指定不连续 54 v = range(0, 100, 5) 55 for item in v: 56 print(item)

1 #!/usr/bin/env python 2 # -*- coding:UTF-8 -*- 3 # Author:Ocean 4 class str(object): 5 6 def capitalize(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 7 8 # 首字母变大写 9 # name = "ocean" 10 # a = name.capitalize() 11 # print(a) 12 13 def casefold(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 14 15 # 首字母变小写 16 # name = "Ocean" 17 # a =name.casefold() 18 # print(a) 19 20 def center(self, width, fillchar=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 21 22 # 内容居中,width:总长度;fillchar:空白处填充内容,默认无。 23 # name = "ocean" 24 # a = name.center(60,'$') 25 # print(a) 26 27 28 def count(self, sub, start=None, end=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 29 30 # 子序列个数,0到12中a出现了几次。 31 # name = "ocean is a good man" 32 # v= name.count("a",0,12) 33 # print(v) 34 35 def encode(self, encoding='utf-8', errors='strict'): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 36 37 # 编码,针对unicode. 38 # temp = "烧饼" 39 # temp.encode("unicode") 40 41 def endswith(self, suffix, start=None, end=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 42 # 是否以XX结束,0到4是否以n结尾 43 # name = "ocean is a good man" 44 # v = name.endswith("n",0,4) 45 # print(v) 46 47 def expandtabs(self, tabsize=8): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 48 # 将tab转换成空格,默认一个tab转换成8个空格 49 # a = n.expandtabs() 50 # b = n.expandtabs(16) 51 # print(a) 52 # print(b) 53 54 def find(self, sub, start=None, end=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 55 56 # 寻找子序列位置,如果没找到,返回 -1。 57 # name = "ocean is a good man" 58 # a = name.find("good") 59 # print(a) 60 61 def format(self, *args, **kwargs): # known special case of str.format 62 # 字符串格式化,动态参数 63 # 格式化,传入的值 {"name": 'alex', "a": 19} 64 # test = 'i am {name}, age {a}' 65 # v1 = test.format(name='df',a=10) 66 # v2 = test.format_map({"name": 'alex', "a": 19}) format_map用法(一般用字典键值) 67 68 69 def index(self, sub, start=None, end=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 70 71 # 子序列位置,如果没有找到就报错 72 # name = "ocean is a good man" 73 # a = name.index("ocean") 74 # print(a) 75 76 def isalnum(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 77 78 # 是否是字母和数字 79 # name = "ocean is a good man" 80 # a = name.isalnum() 81 # print(a) 82 83 84 def isalpha(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 85 86 # 是否是字母 87 # name = "ocean is a good man" 88 # a = name.isalpha() 89 # print(a) 90 91 92 def isdecimal(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 93 94 # 检查字符串是否只包含十进制字符。这种方法只存在于unicode对象。 95 96 97 98 def isdigit(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 99 100 # 是否是数字 101 # name = "ocean is a good man" 102 # a = name.isdigit() 103 # print(a) 104 105 def isidentifier(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 106 107 # 判断字符串是否可为合法的标识符 108 109 110 def islower(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 111 112 # 是否小写 113 # name = "ocean is A good man" 114 # a = name.islower() 115 # print(a) 116 117 def isnumeric(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 118 119 # 检查是否只有数字字符组成的字符串 120 # name = "111111111111111” 121 # a = name.isnumeric() 122 # print(a) 123 124 def isprintable(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 125 126 # 判断字符串中所有字符是否都属于可见字符 127 # name = "ocean is a good man" 128 # a = name.isprintable() 129 # print(a) 130 131 def isspace(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 132 133 # 字符串是否只由空格组成 134 # name = " " 135 # a = name.isspace() 136 # print(a) 137 138 def istitle(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 139 140 141 # 检测字符串中所有的单词拼写首字母是否为大写,且其他字母为小写 142 # name = "Ocean Is A Good Man" 143 # a = name.istitle() 144 # print(a) 145 146 def isupper(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 147 148 # 检测字符串中所有的字母是否都为大写 149 # name = "OCEAN" 150 # a = name.isupper() 151 # print(a) 152 153 def join(self, iterable): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 154 155 # 连接两个字符串 156 # li = ["ocean","handsome"] 157 # a = "".join(li) 158 # b = "_".join(li) 159 # print(a) 160 # print(b) 161 162 def ljust(self, width, fillchar=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 163 164 # 向左对齐,右侧填充 165 # name = "ocean is a good man" 166 # a = name.ljust(60,$) 167 # print(a) 168 169 def lower(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 170 171 # 所有大写变小写 172 # name = "OCEan" 173 # a = name.lower() 174 # print(a) 175 176 def lstrip(self, chars=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 177 178 # 移除左侧空白 179 180 def maketrans(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 181 182 # 用于创建字符映射的转换表,对于接受两个参数的最简单的调用方式,第一个参数是字符串,表示需要转换的字符,第二个参数也是字符串表示转换的目标。 183 # from string import maketrans 184 # intab = "aeiou" 185 # outtab = "12345" 186 # trantab = maketrans(intab, outtab) 187 # str = "this is string example....wow!!!" 188 # print(str.translate(trantab)) 189 190 def partition(self, sep): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 191 192 # 分割,前,中,后三部分 193 # name = "ocean is a good man" 194 # a = name.partition("good") 195 # print(a) 196 197 def replace(self, old, new, count=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 198 199 # 替换 200 # name = "ocean is a good man" 201 # a = name.replace("good","man") 202 # print(a) 203 204 205 def rfind(self, sub, start=None, end=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 206 207 # 返回字符串最后一次出现的位置,如果没有匹配项则返回-1 208 209 def rindex(self, sub, start=None, end=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 210 211 # 返回子字符串 str 在字符串中最后出现的位置,如果没有匹配的字符串会报异常 212 213 def rjust(self, width, fillchar=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 214 215 # 返回一个原字符串右对齐,并使用空格填充至长度 width 的新字符串。如果指定的长度小于字符串的长度则返回原字符串 216 # str = "this is string example....wow!!!" 217 # print(str.rjust(50, '$')) 218 219 def rpartition(self, sep): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 220 221 # 根据指定的分隔符将字符串进行分割 222 223 def rsplit(self, sep=None, maxsplit=-1): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 224 225 # 指定分隔符对字符串进行切片 226 # name = "ocean is a good man" 227 # a = name.rsplit("is") 228 # print(a) 229 230 def rstrip(self, chars=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 231 232 # 删除 string 字符串末尾的指定字符(默认为空格) 233 234 def split(self, sep=None, maxsplit=-1): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 235 236 # 通过指定分隔符对字符串进行切片 237 # str = "Line1-abcdef Line2-abc Line4-abcd"; 238 # print str.split( ); 239 # print str.split(' ', 1 ); 240 241 def splitlines(self, keepends=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 242 243 # 按照行分隔,返回一个包含各行作为元素的列表 244 245 def startswith(self, prefix, start=None, end=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 246 247 # 检查字符串是否是以指定子字符串开头,如果是则返回 True,否则返回 False 248 249 def strip(self, chars=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 250 251 # 用于移除字符串头尾指定的字符(默认为空格). 252 253 def swapcase(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 254 255 # 用于对字符串的大小写字母进行转换 256 257 def title(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 258 """ 259 S.title() -> str 260 261 Return a titlecased version of S, i.e. words start with title case 262 characters, all remaining cased characters have lower case. 263 """ 264 return "" 265 266 def translate(self, table): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 267 """ 268 S.translate(table) -> str 269 270 Return a copy of the string S in which each character has been mapped 271 through the given translation table. The table must implement 272 lookup/indexing via __getitem__, for instance a dictionary or list, 273 mapping Unicode ordinals to Unicode ordinals, strings, or None. If 274 this operation raises LookupError, the character is left untouched. 275 Characters mapped to None are deleted. 276 """ 277 return "" 278 279 def upper(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 280 281 # 将字符串中的小写字母转为大写字母 282 283 def zfill(self, width): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 284 285 # 返回指定长度的字符串,原字符串右对齐,前面填充0
4、列表

1 1. 列表格式 2 # 中括号括起来 3 # 用 ,分割每个元素 4 5 2. 列表中可以嵌套任何类型,列表中的元素可以是 数字,字符串,列表,布尔值..所有的都能放进去 6 7 3. 索引取值 8 print(li[3]) 9 10 4. 切片,切片结果也是列表 11 12 print(li[3:-1]) 13 14 5. 支持for循环、while循环 15 for item in li: 16 print(item) 17 18 # 列表元素,可以被修改 19 20 # li = [1, 12, 9, "age", ["aaa", ["19", 10], "bbb"], "alex", True] 21 22 6 .索引 23 # 修改 24 # li[1] = 120 25 # print(li) 26 # li[1] = [11,22,33,44] 27 # print(li) 28 29 7、删除,索引删除 30 # del li[1] 31 # print(li) 32 # 切片替换修改 33 # li[1:3] = [120,90] 34 # print(li) 35 # 切片删除 36 # del li[2:6] 37 # print(li) 38 39 8. in 操作 40 # li = [1, 12, 9, "age", ["aaa", ["19", 10], "bbb"], "alex", True] 41 # v1 = "aaa" in li 42 # print(v1) 43 # v2 = "age" in li 44 # print(v2) 45 ###### 列表中的元素, 46 47 9 .操作 48 # li = [1, 12, 9, "age", ["aaa", ["19", 10], "bbb"], "alex", True] 49 # li[4][1][0] 50 # [1] 51 52 # li = [1, 12, 9, "age", ["aaa", ["19", 10], "bbb"], "alex", True] 53 54 # s = "pouaskdfauspdfiajsdkfj" 55 # s = 123 56 # a = "123" 57 # int(a) 58 # a = 123 59 # str(a) 60 10 转换 61 # 字符串转换列表 li = list("asdfasdfasdf"), 内部使用for循环 62 # s = "pouaskdfauspdfiajsdkfj" 63 # new_li = list(s) 64 # print(new_li) 65 66 # 列表转换成字符串, 67 既有数字又有字符串:需要自己写for循环一个一个处理 68 # li = [11,22,33,"123","alex"] 69 # # r = str(li) # '[11,22,33,"123","alex"]' 70 # # print(r) 71 # s = "" 72 # for i in li: 73 # s = s + str(i) 74 # print(s) 75 直接使用字符串join方法:列表中的元素只有字符串 76 # li = ["123","alex"] 77 # v = "".join(li) 78 # print(v) 79 80 补充:字符串创建后,不可修改 81 82 # 列表,有序;元素可以被修改

1 # def append(self, p_object): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 2 # 在原来的最后追加 3 li=[1,2,3,2,34,5] 4 li.append([22,33]) 5 print(li) 6 #结果:[1, 2, 3, 2, 34, 5, [22, 33]] 7 # def clear(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 8 # 清空列表 9 li=[1,2,3,2,34,5] 10 li.clear() 11 print() 12 13 # def copy(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 14 # 复制列表,需赋值 15 li=[1,2,3,2,34,5] 16 v = li.copy() 17 print(v) 18 # def count(self, value): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 19 # 统计列表中元素的个数 20 li = [1,2,3,2,34,5] 21 v = li.count(2) 22 print(v) 23 # 结果为2,也就是有两个2 24 25 # def extend(self, iterable): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 26 # 扩展列表,参数为可迭代对象(可以for循环的对象)以for循环遍历完结果加入列表 27 # 注意区别append 28 li = [1,2,3,2,34,5] 29 li.extend(["aa",12,34]) 30 print(li) 31 # def index(self, value, start=None, stop=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 32 # 根据值获取当前索引位置(左边优先) 33 li = [1,2,3,2,34,5] 34 v = li.index(34) 35 print(v) 36 # def insert(self, index, p_object): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 37 # 在指定索引位置插入元素 38 li = [1,2,3,2,34,5] 39 li.insert(0,[1,2]) 40 print(li) 41 # def pop(self, index=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 42 # 删除指定列表索引位置元素,默认删除最后一个,并且获取删除的值 43 li = [1,2,3,2,34,5] 44 v=li.pop(0) 45 print(li) 46 print(v) 47 # def remove(self, value): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 48 # 删除列表指定值,左边优先(不可获取) 49 li = [1,2,3,2,34,5] 50 li.remove(2) 51 print(li) 52 # def reverse(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 53 # 将当前列表反转 54 li = [1,2,3,2,34,5] 55 li.reverse() 56 print(li) 57 # def sort(self, key=None, reverse=False): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 58 # 列表排序(从小到大)可以用反转来reverse()反排序 59 li = [1,2,3,2,34,5] 60 li.sort() 61 print(li) 62 li.sort(reverse=True) 63 print(li)
5、元组(不可修改)

1 # 元组,元素不可被修改,不能被增加或者删除 2 # 1. 书写格式 3 # tu = (111,"alex",(11,22),[(33,44)],True,33,44,) 4 # 一般写元组的时候,推荐在最后加入 , 5 # 元素不可被修改,不能被增加或者删除 6 # 2. 索引 7 # v = tu[0] 8 # print(v) 9 10 # 3. 切片 11 # v = tu[0:2] 12 # print(v) 13 14 # 4. 可以被for循环,可迭代对象 15 # for item in tu: 16 # print(item) 17 18 # 5. 转换 19 # s = "asdfasdf0" 20 # li = ["asdf","asdfasdf"] 21 # tu = ("asdf","asdf") 22 #遍历字符串,每个字符成为元组元素 23 # v = tuple(s) 24 # print(v) 25 #字典可以直接转换为元组 26 # v = tuple(li) 27 # print(v) 28 #元组可以直接转化成列表 29 # v = list(tu) 30 # print(v) 31 # 如果元组中都为字符串的时候可以用join粘合元组中元素,如果有数字则不可以 32 # v = "_".join(tu) 33 # print(v) 34 # 列表能够遍历加入列表中 35 # li = ["asdf","asdfasdf"] 36 # li.extend((11,22,33,)) 37 # print(li) 38 39 # 6.元组的一级元素不可修改/删除/增加 40 # tu = (111,"alex",(11,22),[(33,44)],True,33,44,) 41 # # 元组,有序。 42 # # v = tu[3][0][0] 43 # # print(v) 44 # # v=tu[3] 45 # # print(v) 46 # tu[3][0] = 567 47 # print(tu)

1 # 由于元组是不可更改的所以只有索引查询跟计数的功能 2 def count(self, value): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 3 # 获取指定元素在元组中出现的次数 4 # tu = (11,22,33,44) 5 # tu.count(22) 6 def index(self, value, start=None, stop=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 7 # 获取指定元素在元组中的位置 8 # tu = (11,22,33,44) 9 # tu.index(22)
6、set集合

1 class set(object): 2 3 def add(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 4 """添加元素 5 >>> a = {"alex","mm","ocean"} 6 >>> a.add('ss') 7 >>> a 8 {"alex","mm","ocean","ss"} 9 10 """ 11 12 def clear(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 13 """清除内容 14 >>> a = {"alex","mm","ocean"} 15 >>> a.clear() 16 >>> a 17 set() 18 """ 19 def copy(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 20 """浅拷贝 21 >>> a = {"alex","mm","ocean"} 22 >>> b = a.copy() 23 >>> b 24 {"alex","mm","ocean"} 25 """ 26 27 def difference(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 28 """A中存在,B中不存在,差集(-) 29 >>> a = {"alex","mm","ocean"} 30 >>> b = {"ll","tt","alex"} 31 >>> a.difference(b) #或者可以为print(a-b) 32 {"mm","ocean"} 33 """ 34 35 def difference_update(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 36 """从当前集合中删除和B中相同的元素,并更新到a中 37 >>> a = {"alex","mm","ocean"} 38 >>> b = {"ll","tt","alex"} 39 >>> a.difference_update(b) 40 >>> a 41 {"mm","ocean"} 42 """ 43 44 def discard(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 45 """移除指定元素,不存在不报错 46 >>> a = {"alex","mm","ocean"} 47 >>> a.discard("aa") 48 >>> a 49 """ 50 51 def intersection(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 52 """a与b的交集(&) 53 >>> a = {"alex","mm","ocean"} 54 >>> b = {"ll","tt","alex"} 55 >>> a.intersection(b) #a&b 56 {"alex"} 57 """ 58 59 def intersection_update(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 60 """取交集并更更新到a中 61 """ 62 63 def isdisjoint(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 64 """如果没有交集,返回True,否则返回False 65 >>> a = {"alex","mm","ocean"} 66 >>> b = {"ll","tt","alex"} 67 >>> a.isdisjoint(b) 68 False 69 """ 70 71 def issubset(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 72 """是否是子序列 73 >>> a = {"alex","mm","ocean"} 74 >>> b = {"alex"} 75 >>> b.issubset(a) 76 True 77 >>> a.issubset(b) 78 False 79 """ 80 81 def issuperset(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 82 """是否是父序列 83 >>> a = {"alex","mm","ocean"} 84 >>> b = {"alex"} 85 >>> a.issuperset(b) 86 True 87 >>> b.issuperset(a) 88 False 89 """ 90 91 def pop(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 92 """移除元素 93 >>> a = {"alex","mm","ocean"} 94 >>> a.pop() 95 "alex" 96 >>> a 97 {"mm","ocean"} 98 """ 99 100 def remove(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 101 """移除指定元素,不存在报错 102 >>> a = {"alex","mm","ocean"} 103 >>> a.remove("ss") 104 Traceback (most recent call last): 105 File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module> 106 KeyError: "ss" 107 >>> 108 """ 109 110 def symmetric_difference(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 111 """交叉补集 (^) 112 >>> a = {"alex","mm","ocean"} 113 >>> b = {"ll","tt","alex"} 114 >>> a.symmetric_difference(b) #a^b 115 {"mm","ocean","ll","tt"} 116 """ 117 118 def symmetric_difference_update(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 119 """交叉补集,并更新到a中 120 >>> a = {"alex","mm","ocean"} 121 >>> b = {"ll","tt","alex"} 122 >>> a.symmetric_difference_update(b) 123 >>> a 124 {"mm","ocean","ll","tt"} 125 """ 126 127 def union(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 128 """并集,(|) 129 >>> a = {"alex","mm","ocean"} 130 >>> b = {"ll","tt","alex"} 131 >>> a.union(b) #a|b 132 {"alex","mm","ocean","ll","tt"} 133 """ 134 135 def update(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 136 """更新,添加多个元素,更新 注意区别add 137 >>> a = {"alex","mm","ocean"} 138 >>> b = {"ll","tt","alex"} 139 >>> a.update(b) #把b中的多个元素加入到a中并更新a中的内容,b并不改变 140 >>> a 141 {"alex","mm","ocean", "ll","tt"} 142 >>> b 143 {"ll","tt","alex"} 144 """
7、字典(无序)

1 # 1、基本结构 2 # info = { 3 # "k1": "v1", # 键值对 4 # "k2": "v2" 5 # } 6 #2、字典的value可以是任何值 7 # info = { 8 # "k1": 18, 9 # "k2": True, 10 # "k3": [ 11 # 11, 12 # [], 13 # (), 14 # 22, 15 # 33, 16 # { 17 # 'kk1': 'vv1', 18 # 'kk2': 'vv2', 19 # 'kk3': (11,22), 20 # } 21 # ], 22 # "k4": (11,22,33,44) 23 # } 24 # print(info) 25 26 #3、列表、字典不能作为字典的key 27 # info ={ 28 # 1: 'asdf', 29 # "k1": 'asdf', 30 # True: "123", 31 # # [11,22]: 123 32 # (11,22): 123, 33 # # {'k1':'v1'}: 123 34 # 35 # } 36 # print(info) 37 38 # 4 字典无序 39 40 # info = { 41 # "k1": 18, 42 # "k2": True, 43 # "k3": [ 44 # 11, 45 # [], 46 # (), 47 # 22, 48 # 33, 49 # { 50 # 'kk1': 'vv1', 51 # 'kk2': 'vv2', 52 # 'kk3': (11,22), 53 # } 54 # ], 55 # "k4": (11,22,33,44) 56 # } 57 # print(info) 58 59 # 5、索引方式找到指定元素 60 # info = { 61 # "k1": 18, 62 # 2: True, 63 # "k3": [ 64 # 11, 65 # [], 66 # (), 67 # 22, 68 # 33, 69 # { 70 # 'kk1': 'vv1', 71 # 'kk2': 'vv2', 72 # 'kk3': (11,22), 73 # } 74 # ], 75 # "k4": (11,22,33,44) 76 # } 77 # # v = info['k1'] 78 # # print(v) 79 # # v = info[2] 80 # # print(v) 81 # v = info['k3'][5]['kk3'][0] 82 # print(v) 83 84 # 6 字典支持 del 删除 85 # info = { 86 # "k1": 18, 87 # 2: True, 88 # "k3": [ 89 # 11, 90 # [], 91 # (), 92 # 22, 93 # 33, 94 # { 95 # 'kk1': 'vv1', 96 # 'kk2': 'vv2', 97 # 'kk3': (11,22), 98 # } 99 # ], 100 # "k4": (11,22,33,44) 101 # } 102 # del info['k1'] 103 # 104 # del info['k3'][5]['kk1'] 105 # print(info) 106 107 # 7 for循环 108 # dict 109 # info = { 110 # "k1": 18, 111 # 2: True, 112 # "k3": [ 113 # 11, 114 # [], 115 # (), 116 # 22, 117 # 33, 118 # { 119 # 'kk1': 'vv1', 120 # 'kk2': 'vv2', 121 # 'kk3': (11,22), 122 # } 123 # ], 124 # "k4": (11,22,33,44) 125 # } 126 # for item in info: 127 # print(item) 128 # 129 # for item in info.keys(): 130 # print(item) 131 132 # for item in info.values(): 133 # print(item) 134 135 # for item in info.keys(): 136 # print(item,info[item]) 137 138 # for k,v in info.items(): 139 # print(k,v) 140 141 # True 1 False 0 142 # info ={ 143 # "k1": 'asdf', 144 # True: "123", 145 # # [11,22]: 123 146 # (11,22): 123, 147 # # {'k1':' v1'}: 123 148 # 149 # } 150 # print(info)

1 def clear(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 2 # 清空字典 3 4 def copy(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 5 # 复制字典 6 @staticmethod # known case 7 def fromkeys(*args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 8 # 根据序列,创建字典,并指定统一的值 9 # dic = { 10 # "k1": 'v1', 11 # "k2": 'v2' 12 # } 13 # v = dict.fromkeys("k1",123) 14 # print(v) 15 def get(self, k, d=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 16 # 根据Key获取值,key不存在时,可以指定默认值(None) 17 # v = dic['k1'] 18 # print(v) 19 # v = dic.get('k11',111111) 20 # print(v) 21 22 def items(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 23 # 可以利用for来遍历键值对 24 # dic = { 25 # "k1": 'v1', 26 # "k2": 'v2' 27 # } 28 # for k,v in dic.items(): 29 # print(k,v) 30 31 def keys(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 32 # 字典的key 33 # dic = { 34 # "k1": 'v1', 35 # "k2": 'v2' 36 # } 37 # for k in dic.keys(): 38 # print(k) 39 40 def pop(self, k, d=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 41 # 删除并获取值 42 # dic = { 43 # "k1": 'v1', 44 # "k2": 'v2' 45 # } 46 # v = dic.pop('k1',90) 47 # print(dic,v) 48 49 def popitem(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 50 # 删除键值对然后可以获取删除的键值对 51 # dic = { 52 # "k1": 'v1', 53 # "k2": 'v2' 54 # } 55 # k,v = dic.popitem() 56 # print(dic,k,v) 57 58 def setdefault(self, k, d=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 59 # 设置值, 60 # 已存在,不设置,获取当前key对应的值 61 # 不存在,设置添加,获取当前key对应的值 62 # dic = { 63 # "k1": 'v1', 64 # "k2": 'v2' 65 # } 66 # v = dic.setdefault('k1111','123') 67 # print(dic,v) 68 69 def update(self, E=None, **F): # known special case of dict.update 70 # 更新 71 # dic = { 72 # "k1": 'v1', 73 # "k2": 'v2' 74 # } 75 # dic.update({'k1': '111111','k3': 123}) #形式一 76 # print(dic) 77 # dic.update(k1=123,k3=345,k5="asdf") #形式二 78 # print(dic) 79 80 def values(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 81 # 字典的值values 82 # dic = { 83 # "k1": 'v1', 84 # "k2": 'v2' 85 # } 86 # for v in dic.values(): 87 # print(v)
其他
1、编码与进制转换
- utf-8与gbk编码转换,python3里默认的编码方式为unicode
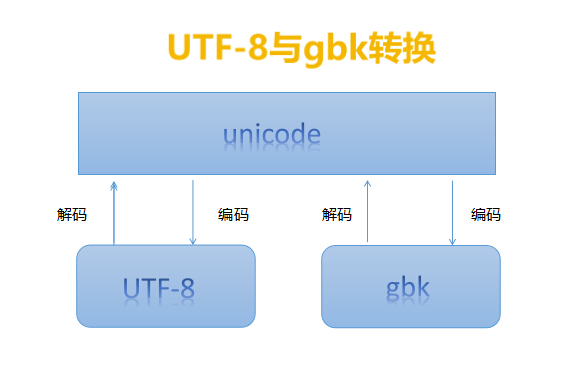
2、range
1 #python 2.7 版本 2 3 print range(1, 10) 4 5 # 结果:[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9] 6 7 8 9 print range(1, 10, 2) 10 11 # 结果:[1, 3, 5, 7, 9] 12 13 14 15 print range(30, 0, -2) 16 17 # 结果:[30, 28, 26, 24, 22, 20, 18, 16, 14, 12, 10, 8, 6, 4, 2] 18 19 20 21 22 23 #python 3.5 版本 24 25 a = range(10) 26 27 print(a) 28 29 #结果:range(0, 10)
3、for循环
用户按照顺序循环可迭代对象中的内容
1 name = ('ocean','alex') 2 3 for i in name: 4 5 print(i)
4、while循环
1 while 条件: 2 .... 3 4 print('...') 5 6 补充: 7 a. while else 8 b. continue break 9 continue ,终止当前循环,开始下一次循环 10 break ,终止所有循环 11 ******continue 是跳出本次循环,break是跳出整个循环(当前的while or for循环)! ****** 12 用户登陆(三次机会重试) 13 count = 0 14 while count < 3: 15 user = input('>>>') 16 pwd = input('>>>') 17 if user == 'alex' and pwd == '123': 18 print('欢迎登陆') 19 print('..........') 20 break 21 else: 22 print('用户名或者密码错误') 23 count = count + 1
