
整理一下前一段时间的最小生成树的算法。(其实是刚弄明白
Kruskal其实算是一种贪心算法。先将边按权值排序,每次选一条没选过的权值最小边加入树,若加入后成环就跳过。
先贴张图做个示例。
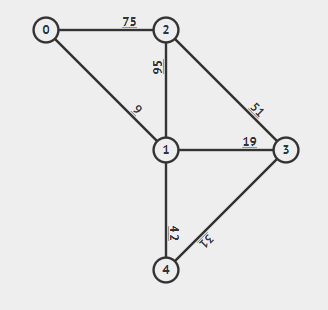 (可视化均来自VisuAlgo)
(可视化均来自VisuAlgo)
1、邻接链表按权值排序后(可以直接写个cmp,sort()结构体):
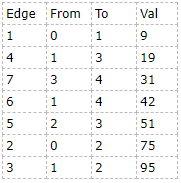
2、依次选边,若成环则跳过,否则加入最小生成树并计数。
这里判断是否成环用的是并查集:如果新加入的边两个端点在同一个集合中,就说明已经有一条路径联通这两个端点。
3、重复2,直到加入了n-1条边或遍历完成(无最小生成树)。
选取1号、4号、7号后:
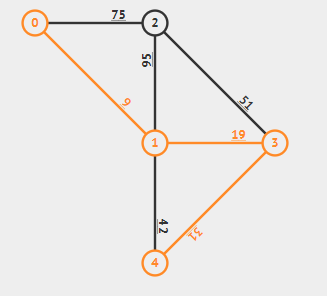
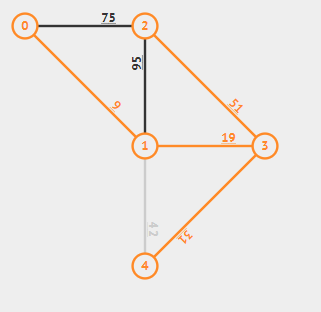
选取6号(1--4),成环,跳过;
加入5号(2--3),达到n-1条,最小生成树形成。
代码实现:
#include <bits/stdc++.h> #define maxn 100010 using namespace std; struct edge{ int from, to, val; }; edge tree[maxn]; bool cmp(const edge &a, const edge &b){ return a.val < b.val; } int m, n, father[maxn], rslt = 0; bool possible = true; int get_father(int x){ if(father[x] == x) return x; return father[x] = get_father(father[x]); } void kruskal(){ int f1, f2, cnt = 0; for(int i=1; i<=n; i++){ father[i] = i; } for(int i=1; i<=m; i++){ f1 = get_father(tree[i].from); f2 = get_father(tree[i].to); if(f1 != f2){ rslt += tree[i].val; father[f1] = f2; if(++cnt == n-1){ return; } } } possible = false; cout << "Impossible!"; return; } int main(){ cin >> n >> m; for(int i=1; i<=m; i++){ cin >> tree[i].from >> tree[i].to >> tree[i].val; } sort(tree+1, tree+m+1, cmp); kruskal(); if(possible) cout << rslt; return 0; }
