python 与 c可以相互调用,在做后台服务时底层服务用C/C++编写,通过python调用C库可以极大的提高开发效率。
下面对几种调用方式举例说明
1 python通过指针传递浮点型数组给C函数
bird = cdll.LoadLibrary("./bird.so") aList=[1.0, 1.1, 1.2, 1.3, 1.4, 1.5] arrayMy = (c_float*len(aList)) a = arrayMy() for i in range(0, len(a)): a[i] = aList[i] count = c_int(len(a)) bird.ptr_test(a, count)
这里注意调用C函数时传入的数组类型定义方法与初始值设定,ctypes模块定义了与C语言数据类型对应的python类型,调用C函数时要确保传入类型一致。
2 python通过指针传递字符串数组给C函数
info='Hello , glade to meet you!' pInfo = create_string_buffer(info, len(info)) bird.buf_in_test(info, sizeof(pInfo))
注意create_string_buffer的作用是把python中的字符串类型转换为一个指针指向的字符串数组。
3 python接收C函数返回的字符串以及长度
bufLen = 100 c_pBuf = create_string_buffer('', bufLen) c_bufLen = c_int(bufLen) bird.buf_out_test(c_pBuf, byref(c_bufLen)) print c_bufLen.value print string_at(c_pBuf)
注意byref是通过指针地址传入参数
4 C函数里分配内存传给python使用
ptr_char = pointer(c_char()) retlen = c_int(0) bird.malloc_test(byref(ptr_char), byref(retlen)) print string_at(ptr_char) print retlen.value
bird.free_test(ptr_char)
注意python里定义一个字符指针的方法ptr_char = pointer(c_char()),定义一个整型变量的方法retlen = c_int(0) , byref(ptr_char)取指针的地址传入函数。
5 测试的python与C源码
#!/usr/bin/python from ctypes import * bird = cdll.LoadLibrary("./bird.so") aList=[1.0, 1.1, 1.2, 1.3, 1.4, 1.5] arrayMy = (c_float*len(aList)) a = arrayMy() for i in range(0, len(a)): a[i] = aList[i] count = c_int(len(a)) bird.ptr_test(a, count) info='Hello , glade to meet you!' pInfo = create_string_buffer(info, len(info)) bird.buf_in_test(info, sizeof(pInfo)) bufLen = 100 c_pBuf = create_string_buffer('', bufLen) c_bufLen = c_int(bufLen) bird.buf_out_test(c_pBuf, byref(c_bufLen)) print c_bufLen.value print string_at(c_pBuf) ptr_char = pointer(c_char()) retlen = c_int(0) bird.malloc_test(byref(ptr_char), byref(retlen)) print string_at(ptr_char) print retlen.value bird.free_test(ptr_char)
#include <stdio.h> #include <string.h> #include <stdlib.h> int ptr_test(float * ptr, int count) { if(ptr){ int i = 0; printf(" "); for (i = 0; i < count; ++i){ printf("%f | ", ptr[i]); } printf(" "); } return 0; } int buf_in_test(char*buf, int len) { if(buf){ int i = 0; printf(" "); for (i = 0; i < len; ++i){ printf("%c", buf[i]); } printf(" "); } return 0; } int buf_out_test(char*buf, int *len) { if(buf){ char *test_str = "hello world!"; memcpy(buf, test_str, strlen(test_str)); *len = strlen(test_str); } return 0; } int malloc_test(char **pBuf, int *len) { *pBuf = (char*)malloc(100); printf("malloc add:%p ", *pBuf); *len = 100; memcpy(*pBuf, "hello", 5); return 0; } int free_test(char *pBuf) { if (pBuf){ printf("free add:%p ", pBuf); free(pBuf); } return 0; }
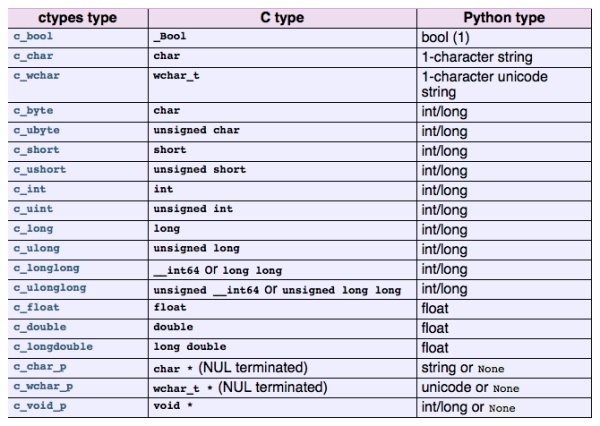
6 ctypes里定义的数据类型与C语言数据类型对应关系