链表是一种用于存储数据集合的数据结构。链表有以下属性:
-
相邻元素之间通过指针连接。
-
最后一个元素的后继指针为NULL。
-
在程序执行过程中,链表的长度可以增加或缩小。
-
链表的空间能按需分配(直到内存耗尽)。
-
没有内存空间的浪费(但链表中的指针需要一些额外的内存开销)
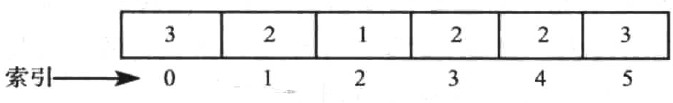
与链表对应的数组
整个数组所有的元素都存储在操作系统分配的一块内存中。访问该数组内的元素时,根据数组元素数据类型的存储空间大小,数组对象的基地址和要访问的元素距基地址的偏移量,就可以在常数时间内计算出元素的地址。
1、因此数组的优点有
- 简单且易用
- 访问元素快(常数时间)
2、数组的缺点有
- 大小固定:数组的大小静态的(在使用前指定数组的大小)
- 分配一个连续的空间块
- 基于位置的插入操作实现复杂
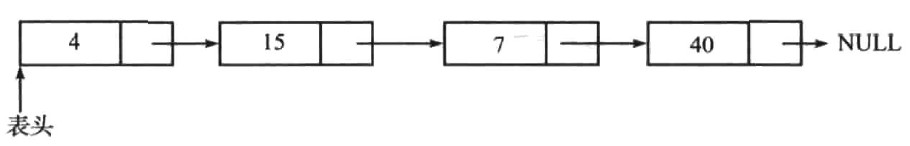
单向链表
链表通常指单向链表,它包含多个结点,每个结点有一个指向后继元素的next(下一个)指针。表中最后一个结点的next指针为NULL,表示该链表的结束:
实现:
public class ListNode {
private int data;
private ListNode next;
public ListNode(int data) {
this.data = data;
}
public int getData() {
return data;
}
public void setData(int data) {
this.data = data;
}
public ListNode getNext() {
return next;
}
public void setNext(ListNode next) {
this.next = next;
}
// 链表的遍历
public void listPrint(ListNode headNode) {
ListNode currentNode = headNode;
while(currentNode != null) {
System.out.print(currentNode.getData()+" ");
currentNode = currentNode.getNext();
}
}
// 统计链表的长度
public int listlength(ListNode headNode) {
int length = 0;
ListNode currentNode = headNode;
while(currentNode != null) {
length++;
currentNode = currentNode.getNext();
}
return length;
}
// 链表的插入
public ListNode InsertLinkedList(ListNode headNode, ListNode nodeToInsert, int position) {
if (headNode == null){ // 若链表为空,插入
return nodeToInsert;
}
int size = listlength(headNode);
if(position > size+1 || position < 1) {
System.out.println("Position of node to insert is invalid. The valid inputs are 1 to"+ (size+1));
return headNode;
}
if(position == 1) { // 在链表开头插入
nodeToInsert.setNext(headNode);
return nodeToInsert;
} else { // 在中间或者末尾插入
ListNode previousNode = headNode;
int count = 1;
while(count < position-1) {
previousNode = previousNode.getNext();
count++;
}
ListNode currentNode = previousNode.getNext();
nodeToInsert.setNext(currentNode);
previousNode.setNext(nodeToInsert);
}
return headNode;
}
// 删除链表的结点
public ListNode deleteNodeFromLinkedList(ListNode headNode, int position) {
int size = listlength(headNode);
if (position > size || position < 1) {
System.out.println("Position of node to delete is invalid,The valid inputs are 1 to "+size);
return headNode;
}
if (position == 1) { // 删除表头结点
ListNode currentNode = headNode.getNext();
headNode = null;
return currentNode;
} else { // 删除中间或表尾结点
ListNode previousNode = headNode;
int count = 1;
while(count < position-1) {
previousNode = previousNode.getNext();
count++;
}
ListNode currentNode = previousNode.getNext();
previousNode.setNext(currentNode.getNext());
currentNode = null;
}
return headNode;
}
// 删除链表
public void deleteLinkedList(ListNode head) {
ListNode auxiliaryNode, iterator = head;
while(iterator != null) {
auxiliaryNode = iterator.getNext();
iterator = null; // 在Java中,垃圾回收器自动处理
iterator = auxiliaryNode;
}
}
双向链表
双向链表:对于表中的一个结点,可以从两个方向进行操作,每个结点有前驱指针和后继指针。