https://github.com/alibaba/spring-cloud-alibaba/wiki/Sentinel
Sentinel 介绍
随着微服务的流行,服务和服务之间的稳定性变得越来越重要。 Sentinel 以流量为切入点,从流量控制、熔断降级、系统负载保护等多个维度保护服务的稳定性。
Sentinel 具有以下特征:
-
丰富的应用场景: Sentinel 承接了阿里巴巴近 10 年的双十一大促流量的核心场景,例如秒杀(即突发流量控制在系统容量可以承受的范围)、消息削峰填谷、实时熔断下游不可用应用等。
-
完备的实时监控: Sentinel 同时提供实时的监控功能。您可以在控制台中看到接入应用的单台机器秒级数据,甚至 500 台以下规模的集群的汇总运行情况。
-
广泛的开源生态: Sentinel 提供开箱即用的与其它开源框架/库的整合模块,例如与 Spring Cloud、Dubbo、gRPC 的整合。您只需要引入相应的依赖并进行简单的配置即可快速地接入 Sentinel。
-
完善的 SPI 扩展点: Sentinel 提供简单易用、完善的 SPI 扩展点。您可以通过实现扩展点,快速的定制逻辑。例如定制规则管理、适配数据源等。
https://github.com/alibaba/Sentinel/wiki/%E5%A6%82%E4%BD%95%E4%BD%BF%E7%94%A8
pom.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> <!-- <parent>--> <!-- <artifactId>springcloudalibaba</artifactId>--> <!-- <groupId>com.wsm.springcloud</groupId>--> <!-- <version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>--> <!-- </parent>--> <parent> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId> <version>2.5.6</version> <relativePath></relativePath> </parent> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <artifactId>sentinel_demo</artifactId> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> <!-- <version>2.5.5</version>--> </dependency> <!-- sentinel 核心库 --> <!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/com.alibaba.csp/sentinel-core --> <dependency> <groupId>com.alibaba.csp</groupId> <artifactId>sentinel-core</artifactId> <version>1.8.2</version> </dependency> <!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.projectlombok/lombok --> <dependency> <groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId> <artifactId>lombok</artifactId> <version>1.18.22</version> <scope>provided</scope> </dependency> <!-- 如果要使用@SentinelResource --> <!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/com.alibaba.csp/sentinel-annotation-aspectj --> <dependency> <groupId>com.alibaba.csp</groupId> <artifactId>sentinel-annotation-aspectj</artifactId> <version>1.8.2</version> </dependency> </dependencies> </project>
application.yml
server: port: 8051
Sentinel 支持以下几种规则:流量控制规则、熔断降级规则、系统保护规则、来源访问控制规则 和 热点参数规则。
流量控制规则 (FlowRule)
流量规则的定义
重要属性:
| Field | 说明 | 默认值 |
|---|---|---|
| resource | 资源名,资源名是限流规则的作用对象 | |
| count | 限流阈值 | |
| grade | 限流阈值类型,QPS 模式(1)或并发线程数模式(0) | QPS 模式 |
| limitApp | 流控针对的调用来源 | default,代表不区分调用来源 |
| strategy | 调用关系限流策略:直接、链路、关联 | 根据资源本身(直接) |
| controlBehavior | 流控效果(直接拒绝/WarmUp/匀速+排队等待),不支持按调用关系限流 | 直接拒绝 |
| clusterMode | 是否集群限流 | 否 |
同一个资源可以同时有多个限流规则,检查规则时会依次检查。
理解上面规则的定义之后,我们可以通过调用 FlowRuleManager.loadRules() 方法来用硬编码的方式定义流量控制规则
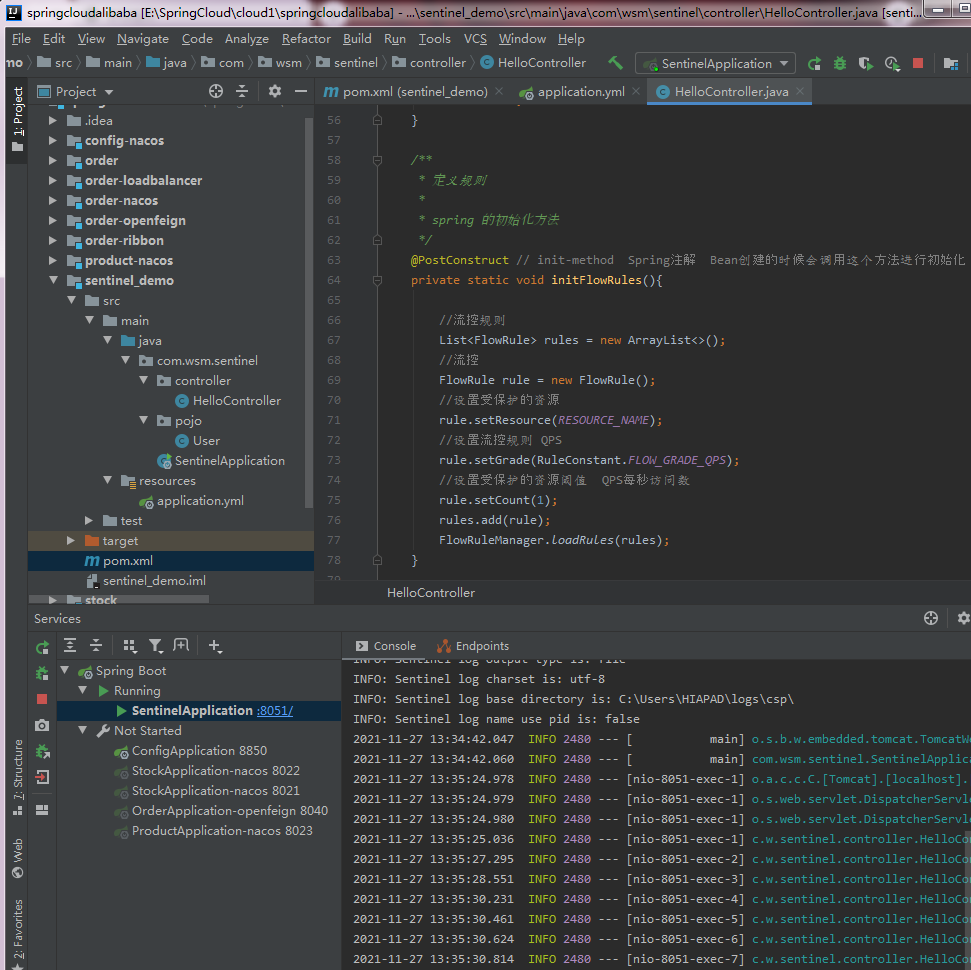
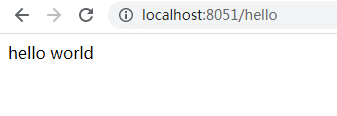
//进行sentinel限流 @RequestMapping(value = "/hello") public String hello() { Entry entry = null; try { //sentinel 针对资源进行限制 entry = SphU.entry(RESOURCE_NAME); //被保护的业务逻辑 String str = "hello world"; log.info("======="+str+"========"); return str; }catch (BlockException el){ //资源访问阻止,被限流或被降级 //进行相应的处理操作 log.info("block!"); return "被流控了!"; }catch (Exception ex){ //若需要配置降级,需要通过这种方式记录业务异常 Tracer.traceEntry(ex,entry); }finally { if(entry != null){ entry.exit(); } } return null; } /** * 定义规则 * * spring 的初始化方法 */ @PostConstruct // init-method Spring注解 Bean创建的时候会调用这个方法进行初始化 private static void initFlowRules(){ //流控规则 List<FlowRule> rules = new ArrayList<>(); //流控 FlowRule rule = new FlowRule(); //设置受保护的资源 rule.setResource(RESOURCE_NAME); //设置流控规则 QPS rule.setGrade(RuleConstant.FLOW_GRADE_QPS); //设置受保护的资源阈值 QPS每秒访问数 rule.setCount(1); rules.add(rule); //流控 FlowRule rule2 = new FlowRule(); //设置受保护的资源 rule2.setResource(USER_RESOURCE_NAME); //设置流控规则 QPS rule2.setGrade(RuleConstant.FLOW_GRADE_QPS); //设置受保护的资源阈值 QPS每秒访问数 rule2.setCount(1); rules.add(rule2); FlowRuleManager.loadRules(rules); }
package com.wsm.sentinel.controller; import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.Entry; import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.SphU; import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.Tracer; import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.block.BlockException; import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.block.RuleConstant; import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.block.degrade.DegradeRule; import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.block.degrade.DegradeRuleManager; import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.block.flow.FlowRule; import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.block.flow.FlowRuleManager; import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.system.SystemRule; import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.system.SystemRuleManager; import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; import javax.annotation.PostConstruct; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; @RestController @Slf4j public class HelloController { private static final String RESOURCE_NAME="hello"; private static final String USER_RESOURCE_NAME = "user"; private static final String DEGRADE_RESOURCE_NAME = "degrade"; //进行sentinel限流 @RequestMapping(value = "/hello") public String hello() { Entry entry = null; try { //sentinel 针对资源进行限制 entry = SphU.entry(RESOURCE_NAME); //被保护的业务逻辑 String str = "hello world"; log.info("======="+str+"========"); return str; }catch (BlockException el){ //资源访问阻止,被限流或被降级 //进行相应的处理操作 log.info("block!"); return "被流控了!"; }catch (Exception ex){ //若需要配置降级,需要通过这种方式记录业务异常 Tracer.traceEntry(ex,entry); }finally { if(entry != null){ entry.exit(); } } return null; } /** * 定义规则 * * spring 的初始化方法 */ @PostConstruct // init-method Spring注解 Bean创建的时候会调用这个方法进行初始化 private static void initFlowRules(){ //流控规则 List<FlowRule> rules = new ArrayList<>(); //流控 FlowRule rule = new FlowRule(); //设置受保护的资源 rule.setResource(RESOURCE_NAME); //设置流控规则 QPS rule.setGrade(RuleConstant.FLOW_GRADE_QPS); //设置受保护的资源阈值 QPS每秒访问数 rule.setCount(1); rules.add(rule); FlowRuleManager.loadRules(rules); } // 限流规则 private void initFlowQpsRule() { List<FlowRule> rules = new ArrayList<>(); FlowRule rule = new FlowRule(RESOURCE_NAME); // set limit qps to 20 rule.setCount(20); rule.setGrade(RuleConstant.FLOW_GRADE_QPS); rule.setLimitApp("default"); rules.add(rule); FlowRuleManager.loadRules(rules); } private void initDegradeRule() { List<DegradeRule> rules = new ArrayList<>(); DegradeRule rule = new DegradeRule(); rule.setResource(DEGRADE_RESOURCE_NAME); // set threshold RT, 10 ms rule.setCount(10); rule.setGrade(RuleConstant.DEGRADE_GRADE_RT); rule.setTimeWindow(10); rules.add(rule); DegradeRuleManager.loadRules(rules); } private void initSystemRule() { List<SystemRule> rules = new ArrayList<>(); SystemRule rule = new SystemRule(); rule.setHighestSystemLoad(10); rules.add(rule); SystemRuleManager.loadRules(rules); } @GetMapping("/rule_setting") //代码配置sentinel限流规则 public String initFlowRule(){ //规则集合 List<FlowRule> rules = new ArrayList<>(); //创建新的规则对象,"/list"就是资源名 FlowRule rule = new FlowRule("/list"); //直接策略 rule.setStrategy(RuleConstant.STRATEGY_DIRECT); //采用QPS限速模式 rule.setGrade(RuleConstant.FLOW_GRADE_QPS); //限制QPS为100 rule.setCount(100); //流控效果设置为“预热” rule.setControlBehavior(RuleConstant.CONTROL_BEHAVIOR_WARM_UP); //预热时间20秒 rule.setWarmUpPeriodSec(20); //来源设置为默认所有default rule.setLimitApp("default"); rules.add(rule); //设置,FlowRuleManager是Sentinel规则管理器 FlowRuleManager.loadRules(rules); return "SUCCESS"; } }
熔断降级规则 (DegradeRule)
熔断降级规则包含下面几个重要的属性:
| Field | 说明 | 默认值 |
|---|---|---|
| resource | 资源名,即规则的作用对象 | |
| grade | 熔断策略,支持慢调用比例/异常比例/异常数策略 | 慢调用比例 |
| count | 慢调用比例模式下为慢调用临界 RT(超出该值计为慢调用);异常比例/异常数模式下为对应的阈值 | |
| timeWindow | 熔断时长,单位为 s | |
| minRequestAmount | 熔断触发的最小请求数,请求数小于该值时即使异常比率超出阈值也不会熔断(1.7.0 引入) | 5 |
| statIntervalMs | 统计时长(单位为 ms),如 60*1000 代表分钟级(1.8.0 引入) | 1000 ms |
| slowRatioThreshold | 慢调用比例阈值,仅慢调用比例模式有效(1.8.0 引入) |
同一个资源可以同时有多个降级规则。
Sentinel 的三种失败指标
- 一秒内(请求数大于等于 5)响应时间超过某个值:RuleConstant.DEGRADE_GRADE_RT;
- 一秒内(请求数大于等于 5)的错误比率:RuleConstant.DEGRADE_GRADE_EXCEPTION_RATIO;
- 一分钟内的错误数量:RuleConstant.DEGRADE_GRADE_EXCEPTION_COUNT;
理解上面规则的定义之后,我们可以通过调用 DegradeRuleManager.loadRules() 方法来用硬编码的方式定义流量控制规则。
@PostConstruct public void initDegradeRules(){ // 一秒内(请求数大于等于 5)响应时间超过某个值:RuleConstant.DEGRADE_GRADE_RT; // 一秒内(请求数大于等于 5)的错误比率:RuleConstant.DEGRADE_GRADE_EXCEPTION_RATIO; // 一分钟内的错误数量:RuleConstant.DEGRADE_GRADE_EXCEPTION_COUNT; List<DegradeRule> rules = new ArrayList<>(); DegradeRule rule = new DegradeRule(); rule.setResource(DEGRADE_RESOURCE_NAME); //异常比例/异常数模式下为对应的阈值 rule.setCount(0.1); //熔断策略,异常比例/异常数策略 rule.setGrade(RuleConstant.DEGRADE_GRADE_EXCEPTION_RATIO); // 熔断时长,单位为 s rule.setTimeWindow(10); // rule.setMinRequestAmount(2); // rule.setStatIntervalMs(60*1000*60);//时间太短不好测 rules.add(rule); DegradeRule rule2 = new DegradeRule(); rule2.setResource(DEGRADE_RESOURCE_NAME); //慢调用比例模式下为慢调用临界 RT(超出该值计为慢调用); // set threshold RT, 10 ms rule2.setCount(10); //熔断策略,支持慢调用比例 -- DEGRADE_GRADE_RT rule2.setGrade(RuleConstant.DEGRADE_GRADE_RT); // 熔断时长,单位为 s rule2.setTimeWindow(10); // 请求总数小于minRequestAmount(2); rule2.setMinRequestAmount(2); // 在这个时间段内2次请求 rule2.setStatIntervalMs(60*1000*60);//时间太短不好测 // 慢请求率: 慢请求数/总请求数> SlowRatioThreshold , 这里要设置小于1 因为慢请求数/总请求数就远不会大于1 rule2.setSlowRatioThreshold(0.9); rules.add(rule2); DegradeRuleManager.loadRules(rules); }
系统保护规则 (SystemRule)
Sentinel 系统自适应限流从整体维度对应用入口流量进行控制,结合应用的 Load、CPU 使用率、总体平均 RT、入口 QPS 和并发线程数等几个维度的监控指标,通过自适应的流控策略,让系统的入口流量和系统的负载达到一个平衡,让系统尽可能跑在最大吞吐量的同时保证系统整体的稳定性。
系统规则包含下面几个重要的属性:
| Field | 说明 | 默认值 |
|---|---|---|
| highestSystemLoad | load1 触发值,用于触发自适应控制阶段 |
-1 (不生效) |
| avgRt | 所有入口流量的平均响应时间 | -1 (不生效) |
| maxThread | 入口流量的最大并发数 | -1 (不生效) |
| qps | 所有入口资源的 QPS | -1 (不生效) |
| highestCpuUsage | 当前系统的 CPU 使用率(0.0-1.0) | -1 (不生效) |
理解上面规则的定义之后,我们可以通过调用 SystemRuleManager.loadRules() 方法来用硬编码的方式定义流量控制规则。
访问控制规则 (AuthorityRule)
很多时候,我们需要根据调用方来限制资源是否通过,这时候可以使用 Sentinel 的访问控制(黑白名单)的功能。黑白名单根据资源的请求来源(origin)限制资源是否通过,若配置白名单则只有请求来源位于白名单内时才可通过;若配置黑名单则请求来源位于黑名单时不通过,其余的请求通过。
授权规则,即黑白名单规则(AuthorityRule)非常简单,主要有以下配置项:
resource:资源名,即规则的作用对象limitApp:对应的黑名单/白名单,不同 origin 用,分隔,如appA,appBstrategy:限制模式,AUTHORITY_WHITE为白名单模式,AUTHORITY_BLACK为黑名单模式,默认为白名单模式