IO流结构图:
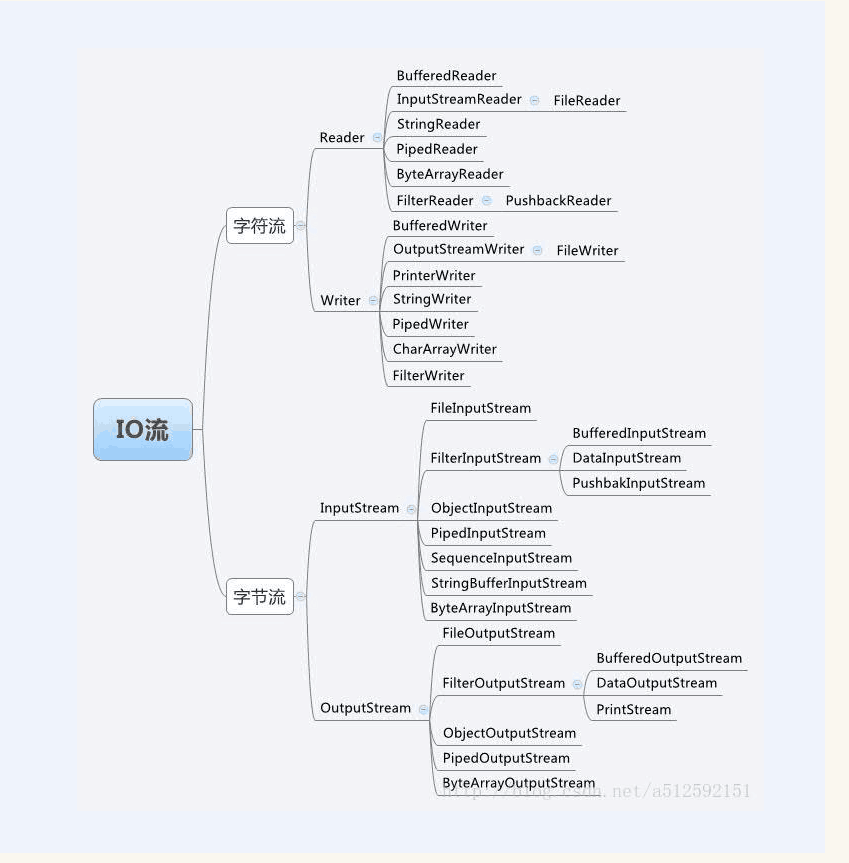
I O流的分类:
OutputStream(输出字节流),InputStream(输入字节流).
Writer(输出字符流),Reader (输入字符流).
输出字节流OutputStream
OutputStream是所有输出字节流的父类,它是一个抽象类,应该通过它的子类对象实例化.
范例: 向文件中写入字符串
class Hello{ public static void main(String[] arges){ File file = new File("d:/a.txt"); //覆盖原文件中数据 OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(file); //向原文件中追加数据 //OutputStram out = new FileOutputStram(file,true); String str = "我不羡慕太阳 照不亮你的过往"; out.write(str.getBytes());; out.close(); }} }
输入字节流: InputStream
InputStream是所有输入流的父类,它是一个抽象类,应该通过它的子类对象实例化.
范例: 字节流读取文件中内容
class Hello{ public static void main(String[] arges){ File file = new File("d:/a.txt"); InputStream in = new FileInputStream(file); byte[] bytes = new byte[1024]; int len = 0; while((len = in.read(bytes)) != -1) System.out.write(bytes, 0, len); in.close(); } }
范例: 复制文件
class Hello { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { Hello file=new Hello(); File srcFile=new File("d:/a.txt"); File destFile=new File("d:/c.txt"); file.CopyFile(srcFile,destFile); } public void CopyFile (File sourceFile,File destFile) throws IOException { InputStream in = new FileInputStream(sourceFile); OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(destFile); byte []bytes = new byte[1024]; int len=0; while((len= in.read(bytes)) != -1 ){ out.write(bytes,0,len); } out.close(); in.close(); } }
Writer 输出字符流
范例: 向文件中写入字符串
class Hello { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { //File.separator代表系统目录中的间隔符 File file = new File("d:"+File.separator+"a.txt"); if(!file.getParentFile().exists()) { file.getParentFile().mkdir();//父目录必须存在 } Writer out = new FileWriter(file); String str = "Hello"; out.write(str);
out.append("World");//追加内容 out.close(); } }
Reder输入字符流
范例:字符读取文件内容
class Hello { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { File file = new File("d:"+File.separator+"a.txt"); if(file.exists()) { Reader in = new FileReader(file); char [] data = new char[1024]; int len = in.read(data); System.out.print(new String(data,0,len)); in.close(); } } }
字节流与字符流的区别:字节流在进行处理的时候并不会用到缓冲区,而字符流会用到缓冲区(适用中文数据的处理).
转换流: OutputStreamWriter和InputStreamReader
范例: 实现字符与字节之间的相互转换
class Hello { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { File file = new File("d:"+File.separator+"a.txt"); OutputStream output = new FileOutputStream(file);
Writer out = new OutputStreamWriter(output);
InputStream input = new FileInputStream(file); Reader in = new InputStreamReader(input); out.write("hello"); in.read(); out.close(); in.close(); } }
内存操作流: ByteArrayInputStram和ByteArrayOutputStream
范例: 实现小写字母转大写字母
class Hello { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { String str = " hello"; InputStream input = new ByteArrayInputStream(str.getBytes()); ByteArrayOutputStream output = new ByteArrayOutputStream(); int data = 0; while((data=input.read()) != -1) { output.write(Character.toLowerCase(data)); } byte[] result = output.toByteArray(); System.out.println(new String (result)); System.out.println(output); }
管道流: PipedOutputStream ,PipedInputStream(字节管道留) PipedReader ,PipedWriter(字符管道流)
范例:实现线程之间的信息传递
class SendThread implements Runnable{ private PipedOutputStream output; public SendThread() { this.output = new PipedOutputStream(); } @Override public void run() { for(int x = 0 ; x < 10 ; x++) { try { this.output.write(("【第"+(x+1)+Thread.currentThread().getName()+"发送消息】 ").getBytes()); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } try { output.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } public PipedOutputStream getOutput() { return output; } } class ReceiveThread implements Runnable{ private PipedInputStream input; public ReceiveThread() { this.input = new PipedInputStream(); } @Override public void run() { byte[] data = new byte [1024]; int len = 0; ByteArrayOutputStream bos = new ByteArrayOutputStream(); try { while ((len = this.input.read(data)) != -1){ bos.write(data, 0 , len); } System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"接收消息 "+new String (bos.toString())); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } try { this.input.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } public PipedInputStream getInput() { return input; } } public class Hello { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { SendThread send = new SendThread(); ReceiveThread receive = new ReceiveThread(); send.getOutput().connect(receive.getInput()); new Thread(send,"消息发送线程").start(); new Thread(receive,"消息接收线程").start(); } }
RandomAccessFile(实现文件跳跃式读取)
前提: 需要有一个完整的保存形式
写入
class Hello { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { File file = new File("d:"+File.separator+"a.txt"); RandomAccessFile raf = new RandomAccessFile(file,"rw"); String names [] = new String []{"zhangsan", "wangwu ", "lisi "}; int ages [] = new int []{30,20,16}; for(int x = 0; x < names.length; x ++ ) { raf.write(names[x].getBytes()); raf.writeInt(ages[x]); } } }
读: 跳跃式读取一部分内容
class Hello { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { File file = new File("d:"+File.separator+"a.txt"); RandomAccessFile raf = new RandomAccessFile(file,"rw"); raf.skipBytes(24); byte [] data = new byte[8]; int len = raf.read(data); System.out.println("姓名: " + new String (data, 0, len).trim() + "、年龄"+ raf.readInt()); } }
打印流:PrintSream与PrintWriter
范例:自己实现打印
class Hello { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { String dirPath = "/Users/fzc/Documents/mydir/mldn.txt"; File file = new File(dirPath); PrintUtil util = new PrintUtil(new FileOutputStream(file)); util.println("姓名:小强子"); util.print("年龄:"); util.print(78); } } class PrintUtil implements AutoCloseable {//实现数据常用的输出功能 private OutputStream output;//不管现在如何进行输出操作,核心使用的就是OutputStream public PrintUtil(OutputStream output) { this.output = output; } public void print(String str) {//输出字符串 try { this.output.write(str.getBytes());//输出 } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } public void println(String str) { this.print(str + " "); } public void print(long num) { this.print(String.valueOf(num)); } public void println(long num) { this.println(String.valueOf(num)); } @Override public void close() throws IOException { if (output != null) { output.close(); } } }
使用PrintWriter来实现数据的输出操作。
范例:数据输出
class Hello { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { String dirPath = "/Users/fzc/Documents/mydir/mldn.txt"; File file = new File(dirPath); PrintWriter util = new PrintWriter(new FileOutputStream(file)); util.println("姓名:小强子"); util.print("年龄:"); util.print(78); util.close(); } }
System类对IO的支持:
范例:实现键盘输入
class Hello { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { InputStream in=System.in;//此时的输入流为键盘输入 System.out.print("请输入信息:"); byte[] data=new byte[1024];//长度限制 int len=in.read(data); System.out.println("输入的内容为:"+new String(data,0,len)); in.close(); //请输入信息:asdasda //输入的内容为:asdasda } }
缓冲字输入符流 :BufferedReader
范例:实现键盘数据输入
class Hello{ public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { BufferedReader reader=new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in)); System.out.print("请输入信息:"); String msg=reader.readLine(); System.out.println("输入的内容为:"+msg); reader.close(); //请输入信息:123 //输入的内容为:123 } }
范例:接收整型输入并且验证
class Hello{ public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { BufferedReader reader=new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in)); System.out.print("请输入您的年龄:"); String msg=reader.readLine(); if(msg.matches("\d{1,3}")){ int age=Integer.valueOf(msg); System.out.println("您输入的年龄:"+msg); }else{ System.err.println("输入错误,你输入的内容:"+msg); } reader.close(); } }
Scanner类
范例:使用Scanner读取文件信息
class Hello { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { //使用Scanner从文件读取内容(不能有空格,有空格不会读取完整) String dirPath = "/Users/fzc/Documents/mydir/mldn.txt";//定义操作的文件 File file = new File(dirPath); Scanner sc = new Scanner(file); sc.useDelimiter(" ");//默认以空格作为换行,设置以 为换行符 while (sc.hasNext()) { System.out.println(sc.next()); } } }
范例:输入一个人的生日
class Hello{ public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { String birthdayRegex="\d{4}-\d{2}-\d{2}"; Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.println("请输入您的生日:"); if (sc.hasNext(birthdayRegex)) { System.out.println("您输入的生日:" + sc.next());//换行不算输入 } else { System.err.println("输入有误,未获取到内容"); } } }