GCD Array
Time Limit: 11000/5500 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/65536 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 1765 Accepted Submission(s): 559
Problem Description
Teacher Mai finds that many problems about arithmetic function can be reduced to the following problem:
Maintain an array a with index from 1 to l. There are two kinds of operations:
1. Add v to ax for every x that gcd(x,n)=d.
2. Query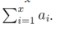
Maintain an array a with index from 1 to l. There are two kinds of operations:
1. Add v to ax for every x that gcd(x,n)=d.
2. Query
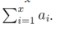
Input
There are multiple test cases, terminated by a line "0 0".
For each test case, the first line contains two integers l,Q(1<=l,Q<=5*10^4), indicating the length of the array and the number of the operations.
In following Q lines, each line indicates an operation, and the format is "1 n d v" or "2 x" (1<=n,d,v<=2*10^5,1<=x<=l).
For each test case, the first line contains two integers l,Q(1<=l,Q<=5*10^4), indicating the length of the array and the number of the operations.
In following Q lines, each line indicates an operation, and the format is "1 n d v" or "2 x" (1<=n,d,v<=2*10^5,1<=x<=l).
Output
For each case, output "Case #k:" first, where k is the case number counting from 1.
Then output the answer to each query.
Then output the answer to each query.
Sample Input
6 4
1 4 1 2
2 5
1 3 3 3
2 3
0 0
Sample Output
Case #1:
6 7
析:长度为n的序列,初始为0,有2种操作:
1.输入n,d,v,对序列中元素ax加上v,其中x满足gcd(n,x) = d
2.输入x,查询1-x前缀和
给所有满足gcd(n,x) = d的数加上v 等价于[gcd(n,x) == d]*v 等价于 [gcd(n/d,x/d) == 1]*v
于是由莫比乌斯反演公式a_i=$sumlimits_{d|i}^{n} f(d)$ ,于是 a_x += $v imes[gcd(x/d,n/d)=1]$ = a_x+=$v imes sumlimits_{p|frac{n}{d},p|frac{x}{d}}mu(p)$,
发现枚举n/d的所有因数的d倍就是添加操作会影响的f数组的位置,所以添加f(pd) += $v∗μ(p)$
查询时,a[x]= $sumlimits_{d|x}f(d)$= $sumlimits_{i=1}^{x}f(d) sumlimits_{d|x}f(d)$,而$sumlimits_{d|x}f(d)$部分可对d进行枚举,即$sumlimits_{d=1}^{x}frac{x}{d}f(d)$,
然后针对$frac{x}{d}$进行分块

#include <math.h> #include <vector> #include <stdio.h> #include <string.h> #include <iostream> #include <algorithm> #define ll long long using namespace std; const int N = 200005; int t, n, m, ans; int mo[N], prm[N], isP[N]; ll a[N]; vector<int>f[N]; void Mobius(){ ans = mo[1] = 1; for(int i = 2; i < N; i ++){ if(!isP[i]){ prm[ans++] = i; mo[i] = -1; } for(int j = 1; j < ans; j ++){ int tmp = i*prm[j]; if(tmp >= N)break; isP[tmp] = 1; if(i%prm[j] == 0){ mo[tmp] = 0; break; }else{ mo[tmp] = -mo[i]; } } } for(int i = 1; i < N; i ++){ for(int j = i; j < N; j += i) f[j].push_back(i); } } void add(int x, int v){ while(x <= n){ a[x] += v; x += x&(-x); } } ll sum(int x){ ll res = 0; while(x > 0){ res += a[x]; x -= x&(-x); } return res; } void update(int x, int d, int v){ if(x%d) return; x /= d; for(int i = 0; i < f[x].size(); i ++){ int q = f[x][i]; add(q*d, mo[q]*v); } } ll query(int x){ ll res = 0; for(int l = 1, r; l <= x; l = r+1){ r = x/(x/l); res += x/l*(sum(r)-sum(l-1)); } return res; } int main(){ Mobius(); int x, d, v, op, tot = 1; while(scanf("%d%d", &n, &m)){ if(n+m == 0) break; fill(a, a+n+1, 0); printf("Case #%d: ", tot++); while(m--){ scanf("%d", &op); if(op&1){ scanf("%d%d%d", &x, &d, &v); update(x, d, v); }else{ scanf("%d", &x); printf("%I64d ", query(x)); } } } return 0; }
