1、扩展原型上的方法
1.1、原码中的构造函数
Number String Boolean Function Array Object RegExp Date Error
1.2、扩展字符串的index()方法
兼容IE8及以下
if (!Array.prototype.indexOf) { Array.prototype.indexOf = function (val, index) { index = typeof index === 'undefined' ? 0 : index; for (var i = index; i < this.length; i++) { if (this[i] === val) { return i; } } return -1; } } var arr = [2, 3, 42, 3, 3, 2]; console.log(arr.indexOf(3)); // 1 console.log(arr.indexOf(3, 2)); // 3
1.3、扩展字符串的trim方法
兼容IE8及以下
if (!String.prototype.trim) { String.prototype.trim = function () { var re = /^s+|s+$/g; return this.replace(re, ''); } } var str = ' abc '; console.log('(' + str.trim() + ')');
2、继承
子代继承父级,必须得有两方
2.1、原型链继承
// 父类 function Student() { this.job = '学生'; this.ah = ['打游戏', '处对象', '学习']; } Student.prototype.showJob = function () { console.log(this.job); } // 子类 function SmallStudent(name) { this.name = name; } // ------------------------------ // 原型链继承:就父类的实例,赋给子类的原型 // 面试中,如何用一句话实现继承? // 这有很多问题:如果父类有引用类型,会导致一修改,所有新创的的属性都会修改 SmallStudent.prototype = new Student(); var s1 = new SmallStudent('小张'); console.log(s1); // console.log(s1.name); // console.log(s1.job); // console.log(s1.ah); // s1.showJob(); s1.ah.push('烫头'); console.log(s1.ah); var s2 = new SmallStudent('小花'); console.log(s2); console.log(s2.ah);

2.2、对象冒充继承
// 父类 function Student() { this.job = '学生'; this.ah = ['打游戏', '处对象', '学习']; } Student.prototype.showJob = function () { console.log(this.job); } // 子类 function SmallStudent(name) { Student.call(this); // 对象冒充继承:就是在子的构造函数中,调用父的构造函数,然后用call改this指向 this.name = name; } // 对象冒充继承的不足:只能继承属性,不能继承方法 // ----------------------------- var s1 = new SmallStudent('小张'); console.log(s1); s1.ah.push('烫头'); console.log(s1.ah); console.log(s1.showJob); var s2 = new SmallStudent('小花'); console.log(s2); console.log(s2.ah);

2.3、组合继承
// 父类 function Student() { this.job = '学生'; this.ah = ['打游戏', '处对象', '学习']; } Student.prototype.showJob = function () { console.log(this.job); } // 子类 function SmallStudent(name) { Student.call(this); // 对象冒充 this.name = name; } SmallStudent.prototype = new Student(); // 原型链继承 // 组合继承:对象冒充 + 原型链 // 对象冒充:继承属性 // 原型链:继承方法 // -------------------------------- var s1 = new SmallStudent('小张'); console.log(s1); s1.showJob(); console.log(s1.constructor); // 本来应该指向子的构造函数,但是却指向了父的构造函数 // 问题: // 1、constructor指向不对 // 2、同时调用两次父的构造函数 // 3、继承过来的属性,在原型链上会出现两次
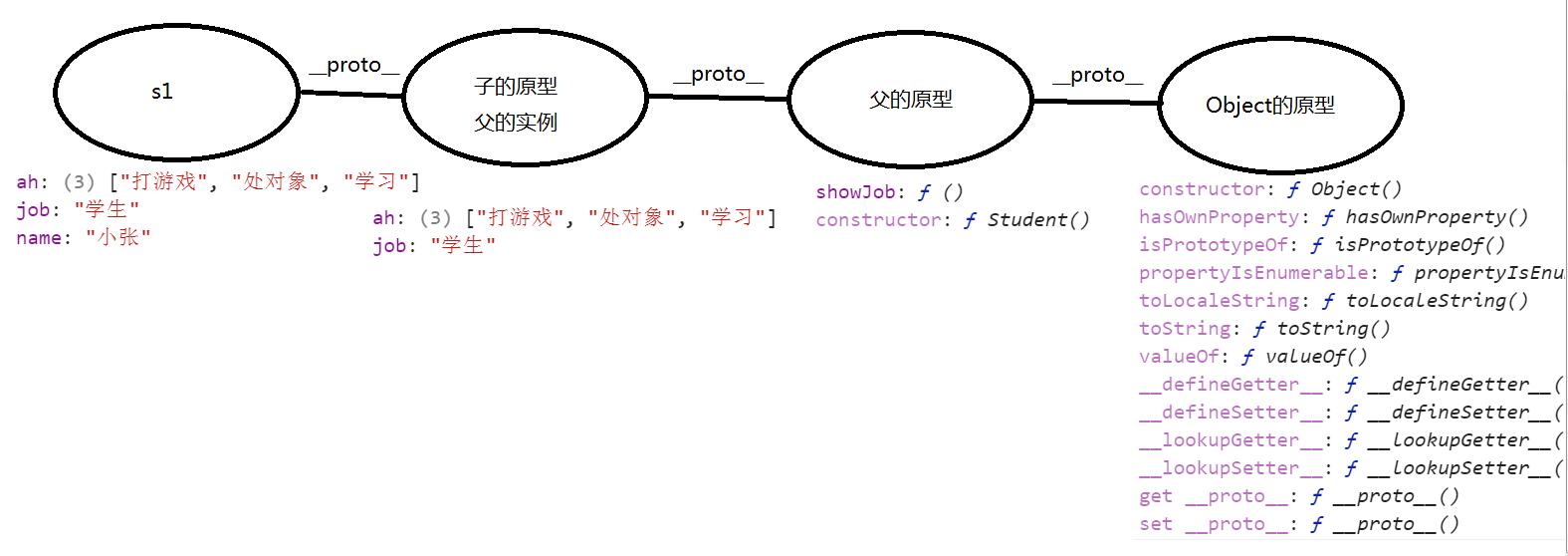
2.4、寄生组合继承
继承的完美实现
// 父类 function Student() { this.job = '学生'; this.ah = ['打游戏', '处对象', '学习']; } Student.prototype.showJob = function () { console.log(this.job); } // 子类 function SmallStudent(name) { Student.call(this); // 继承属性 this.name = name; } inherits(SmallStudent, Student); // 继承方法 // 子类原型上又可以添加方法 SmallStudent.prototype.showName = function () { console.log(this.name); } // -------------------------- var s1 = new SmallStudent('小张'); console.log(s1); // ------------------------------------ // 方法的封装 function inherits(Child, Parent) { var F = function () { }; F.prototype = Parent.prototype; Child.prototype = new F(); Child.prototype.constructor = Child; }
