子查询:在一个查询语句中包含了另外一个查询语句。
select * from commodityinfo
where sortid=
(select sortid from commoditysort where sortname=’手机数码‘)
简单子查询的语法:
select * from 表1 where 列1 >(子查询)
特点:
1.子查询必须放在一对小括号内
2.“=”比较运算符,还可以和其他的比较运算符一起使用,要求子查询的列只能有一个。
3.子查询通常做为where的条件。
4.子查询中不能出现order by子句。
---查询手机数码的商品信息
【1】根据已知项去查未知项,已知项是商品类别名称
select * from commodityinfo
where sortid=
(select sortid from commoditysort where sortname=’手机数码‘)
通常情况下多表连接查询都可以使用子查询替换,反过来则不成立,不是所有的子查询都可以被表连接查询。
多表连接查询与子查询各自的应用场合:
子查询:适合于作为查询的where条件,子查询只能查询主表的字段。
多表连接查询:适用于从多表中查询数据,连接查询可以查看连接表中的任意字段。
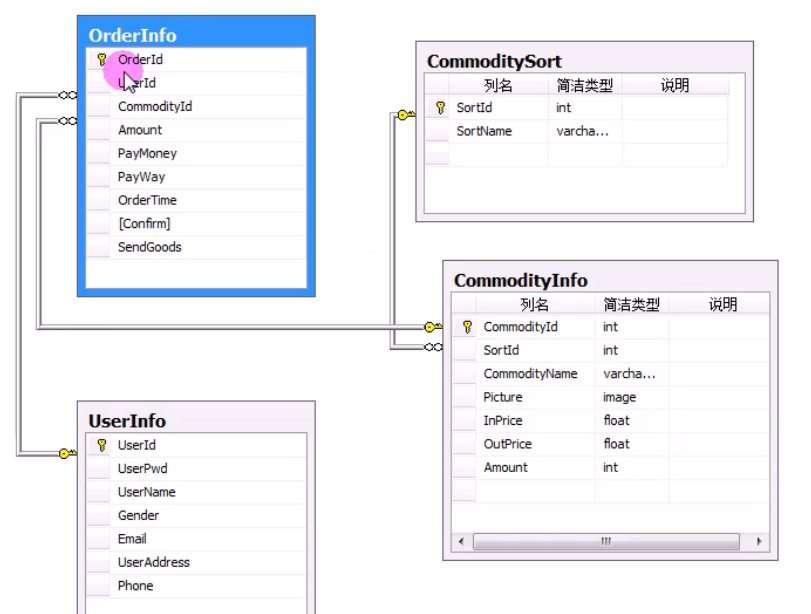
--查询购买苹果Iphone6的客户的姓名和住址
【1】多表连接查询
select u.username,u.useraddress from commodityinfo as c
inner join orderinfo as o on c.commodityid=o.commodityid
inner join userinfo as u on u.userid=o.userid
where c.commodityname = '苹果Iphone6'
【2】子查询:根据已知项查询未知项
select username as 用户名,useraddress as 用户地址 from userinfo
where userid=
(select userid from orderinfo
where commodityid=
(select commodityid from commodityinfo where commodityname='苹果Iphone6))