以下内容均为转载,,只有代码是自己写的=-=
http://blog.csdn.net/morgan_xww/article/details/7834801 转载地址 博主写的很好
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------我是分割线
| Time Limit: 1000MS | Memory Limit: 65536K | |
| Total Submissions: 16585 | Accepted: 6408 |
Description
Suppose that DNA sequences of a species is a sequence that consist of A, C, T and G,and the length of sequences is a given integer n.
Input
Next m lines each line contain a DNA genetic disease segment, and length of these segments is not larger than 10.
Output
Sample Input
4 3 AT AC AG AA
Sample Output
36
2 1 0 0 1
2 1 1 0 0
1 1 0 1 1
2 1 0 0 1
2 1 0 0 1
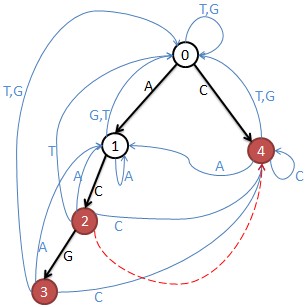
M[i,j]表示从结点i到j只走一步有几种走法。
那么M的n次幂就表示从结点i到j走n步有几种走法。
注意:危险结点要去掉,也就是去掉危险结点的行和列。结点3和4是单词结尾所以危险,结点2的fail指针指向4,当匹配”AC”时也就匹配了”C”,所以2也是危险的。
矩阵变成M:
2 1
2 1
计算M[][]的n次幂,然后 Σ(M[0,i]) mod 100000 就是答案。
由于n很大,可以使用二分来计算矩阵的幂
#include<cstdio>
#include<map>
#include<queue>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
typedef long long ll;
using namespace std;
const int N=101;
const int mod=1e5;
struct Mat
{
ll mat[N][N];
Mat operator *(const Mat &B)const
{
Mat C;
memset(C.mat,0,sizeof(C.mat));
for(int k=0; k<N; ++k)
{
for(int i=0; i<N; ++i)
{
if(mat[i][k]==0) continue;
for(int j=0; j<N; ++j)
{
if(B.mat[k][j]==0) continue;
C.mat[i][j]=(C.mat[i][j]+mat[i][k]*B.mat[k][j])%mod;
}
}
}
return C;
}
int operator ^(int &k)
{
Mat C;
memset(C.mat,0,sizeof(C.mat));
for(int i=0; i<N; ++i)
C.mat[i][i]=1;
while(k)
{
if(k&1)
{
C=C*(*this);
--k;
}
k>>=1;
(*this)=(*this)*(*this);
}
int cnt=0;
for(int i=0; i<N; ++i)
cnt=(cnt+C.mat[0][i])%mod;
return cnt;
}
};
struct AC{
int ch[58][4],fail[58],val[58],sz,rt,id[128];
void init(){
sz=rt=0;
memset(ch[rt],-1,sizeof(ch[rt]));
id['A']=0,id['G']=1,id['T']=2,id['C']=3;
}
void insert(char *str){
int u=rt,len=strlen(str);
for(int i=0;i<len;++i){
int op=id[str[i]];
if(ch[u][op]==-1) {
++sz;
memset(ch[sz],-1,sizeof(ch[sz]));
val[sz]=0;
ch[u][op]=sz;
}
u=ch[u][op];
}
val[u]=1;
}
void build(){
queue<int>Q;
int u=rt;
for(int i=0;i<4;++i){
if(ch[u][i]==-1) ch[u][i]=rt;
else {
fail[ch[u][i]]=rt;
Q.push(ch[u][i]);
}
}
while(!Q.empty()){
u=Q.front();
Q.pop();
val[u]|=val[fail[u]];
for(int i=0;i<4;++i){
if(ch[u][i]==-1) ch[u][i]=ch[fail[u]][i];
else {
fail[ch[u][i]]=ch[fail[u]][i];
Q.push(ch[u][i]);
}
}
}
}
void work(int n){
Mat A;
memset(A.mat,0,sizeof(A.mat));
for(int i=0;i<=sz;++i)
for(int j=0;j<4;++j)
if(!val[ch[i][j]]) ++A.mat[i][ch[i][j]];
printf("%d
",A^n);
}
}ac;
char s[55];
int main(){
int m,n;
while(scanf("%d%d",&m,&n)!=EOF){
ac.init();
while(m--){
scanf("%s",s);
ac.insert(s);
}
ac.build();
ac.work(n);
}
}