#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
const int maxn=100005;
#define lson l,m,rt<<1
#define rson m+1,r,rt<<1|1
int a[maxn<<2],n,m;
int OR[maxn<<2];
struct IA
{
int l,r,q;
}ia[maxn];
void push_up(int rt)
{
a[rt]=a[rt<<1]&a[rt<<1|1];
}
void push_down(int rt)
{
if(OR[rt])
{
a[rt<<1]|=OR[rt]; a[rt<<1|1]|=OR[rt];
OR[rt<<1]|=OR[rt]; OR[rt<<1|1]|=OR[rt];
OR[rt]=0;
}
}
void update(int L,int R,int C,int l,int r,int rt)
{
if(L<=l&&r<=R)
{
OR[rt]|=C;
a[rt]|=C;
return ;
}
push_down(rt);
int m=(l+r)/2;
if(L<=m) update(L,R,C,lson);
if(R>m) update(L,R,C,rson);
push_up(rt);
}
int query(int L,int R,int l,int r,int rt)
{
if(L<=l&&r<=R)
{
return a[rt];
}
int m=(l+r)/2;
push_down(rt);
int part1=-1,part2=-1;
if(L<=m) part1=query(L,R,lson);
if(R>m) part2=query(L,R,rson);
if(part1==-1) return part2;
if(part2==-1) return part1;
return part1&part2;
}
vector<int> ans;
void showit(int l,int r,int rt)
{
if(l==r)
{
ans.push_back(a[rt]);
return ;
}
int m=(l+r)/2;
push_down(rt);
showit(lson);
showit(rson);
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d%d",&n,&m);
for(int i=0;i<m;i++)
{
scanf("%d%d%d",&ia[i].l,&ia[i].r,&ia[i].q);
update(ia[i].l,ia[i].r,ia[i].q,1,n,1);
}
bool flag=true;
for(int i=0;i<m&&flag;i++)
{
int Q=query(ia[i].l,ia[i].r,1,n,1);
if(Q!=ia[i].q) flag=false;
}
if(!flag) puts("NO");
else
{
puts("YES");
ans.clear();
showit(1,n,1);
for(int i=0,sz=ans.size();i<sz;i++)
printf("%d ",ans[i]);
putchar(10);
}
return 0;
}
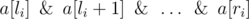 should
be equal to
should
be equal to