阅读目录
一:Service是什么
二:布局文件编写
三:代码文件编写
四:项目定义文件编写
五:运行效果
六:Service是新的进程吗?是新的线程吗?
一:Service是什么?
Service是Android系统的组件之一,和Activity,Intent,Conent Provider并称Android四大天王,Service是不可见的,是没有界面的,是在后台运行的,Service一般处理比较耗时以及长时间运行的操作。我以前给一个电子商务网站做过一个Windows服务,就是一直审核用户下达的未审核的订单,如果符合某种规范则这个订单审核通过,这个服务是一直在运行的,就跟这个电子商务网站一直在线上跑一样,它能省掉很多人工的时间,所以说服务一般处理长时间工作的操作。
我之前在看一本书上说到“即便是通过Activity启动的Service,也不会在相同的process进程当中运行,而是各自属于不同的进程”,我翻阅了Android的SDK “A Service is not a separate process. The Service object itself does not imply it is running in its own process; unless otherwise specified, it runs in the same process as the application it is part of.”这句话的意思是说,Service不是一个独立的进程,服务对象本身并不意味着这是运行在其自己的进程内,它与应用程序运行在同一个进程当中。当书本和Android SDK两者的理论发生矛盾的时候,我们以Android SDK为准,所以我们认为Service和带起它的应用程序在一个进程当中。因为我们知道了Service和带起它的应用程序在一个进程当中,如果你的Service里的操作阻塞住了,就会导致整个应用程序没有响应,所以我们在Service里面新开一个线程。
二:布局文件编写
1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> 2 <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" 3 android:orientation="vertical" 4 android:layout_width="fill_parent" 5 android:layout_height="fill_parent">
6
7 <Button android:layout_width="wrap_content" 8 android:layout_height="wrap_content" 9 android:text="启动Service" 10 android:id="@+id/start"/> 11 <Button android:layout_width="wrap_content" 12 android:layout_height="wrap_content" 13 android:text="取消Service" 14 android:id="@+id/end"/> 15 </LinearLayout>
三:代码文件编写
3.1 MainActivity.java
1 package com.menglin.service1; 2 3 import android.app.Activity; 4 import android.content.Intent; 5 import android.content.IntentFilter; 6 import android.os.Bundle; 7 import android.view.View; 8 import android.view.View.OnClickListener; 9 import android.widget.Button; 10 11 public class MainActivity extends Activity 12 { 13 // 声明两个Button对象 14 private Button btn_start, btn_end; 15 16 @Override 17 public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) 18 { 19 super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); 20 //加载布局文件main.xml 21 setContentView(R.layout.main); 22 //通过findViewById()方法得到两个Button对象 23 btn_start = (Button)findViewById(R.id.start); 24 btn_end = (Button)findViewById(R.id.end); 25 //给两个按钮绑定监听单击事件 26 btn_start.setOnClickListener(btn_start_listener); 27 btn_end.setOnClickListener(btn_end_listener); 28 } 29 30 //监听单击事件 31 private OnClickListener btn_start_listener = new OnClickListener() 32 { 33 @Override 34 public void onClick(View v) 35 { 36 //创建一个Intent对象 37 Intent intent = new Intent(); 38 //第一个参数是自己的这个类的对象,第二个参数是要调用的Service的对象 39 intent.setClass(MainActivity.this, Service1.class); 40 //启动服务 41 startService(intent); 42 } 43 }; 44 45 //监听单击事件 46 private OnClickListener btn_end_listener = new OnClickListener() 47 { 48 @Override 49 public void onClick(View v) 50 { 51 //创建一个Intent对象 52 Intent intent = new Intent(); 53 //第一个参数是自己的这个类的对象,第二个参数是要调用的Service的对象 54 intent.setClass(MainActivity.this, Service1.class); 55 //关闭服务 56 stopService(intent); 57 } 58 }; 59 }
3.2 Service1.java
1 package com.menglin.service1; 2 3 import android.app.Service; 4 import android.content.Intent; 5 import android.os.IBinder; 6 import android.util.Log; 7 8 public class Service1 extends Service 9 { 10 11 private String TAG = "service"; 12 13 @Override 14 public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) 15 { 16 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 17 return null; 18 } 19 20 //当启动Service的时候会调用这个方法 21 @Override 22 public void onCreate() 23 { 24 Log.i(TAG, "onCreate"); 25 super.onCreate(); 26 } 27 28 //当系统被销毁的时候会调用这个方法 29 @Override 30 public void onDestroy() 31 { 32 Log.i(TAG, "onDestroy"); 33 super.onDestroy(); 34 } 35 36 //当启动Service的时候会调用这个方法 37 @Override 38 public int onStartCommand(Intent intent, int flags, int startId) 39 { 40 Log.i(TAG, "onStartCommand"); 41 return super.onStartCommand(intent, flags, startId); 42 } 43 44 }
四:项目定义文件编写
AndroidMainfest.xml
为了让Android的系统知道有这个我们自定义的服务,所以我们需要加上service节点<service android:name=".Service1"></service>。
1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> 2 <manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" 3 package="com.david.beginservice" 4 android:versionCode="1" 5 android:versionName="1.0" > 6 7 <uses-sdk 8 android:minSdkVersion="8" 9 android:targetSdkVersion="21" /> 10 11 <application 12 android:allowBackup="true" 13 android:icon="@drawable/ic_launcher" 14 android:label="@string/app_name" 15 android:theme="@style/AppTheme" > 16 <service android:name=".firstService"></service> 17 <activity 18 android:name=".MainActivity" 19 android:label="@string/app_name" > 20 <intent-filter> 21 <action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" /> 22 23 <category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" /> 24 </intent-filter> 25 </activity> 26 </application> 27 28 </manifest>
五:运行效果
当我们单击"启动Service"按钮后,发现系统输出了"onCreate"我们要的信息,我们再次点击"启动Service"按钮发现没有再次调用onCreate()方法,而是调用了onStartCommand()方法,一个服务启动起来后,一直在后台运行,当你再想启动这个服务的话,就不会再调用onCreate()方法了,因为这个服务已被创建了,而是直接调用onStartCommand()方法,一些主要的操作我们都是在onStartCommand()方法中实现的,就是我们在onStartCommand()方法中开启新的线程,根据Activity传进来的Inetent对象来完成一些操作,当我们不需要这个Service的时候,我们可以单击"取消Service"按钮,在这里我们单击"取消Service"按钮,不仅会停止服务还会输出"onDestroy"。




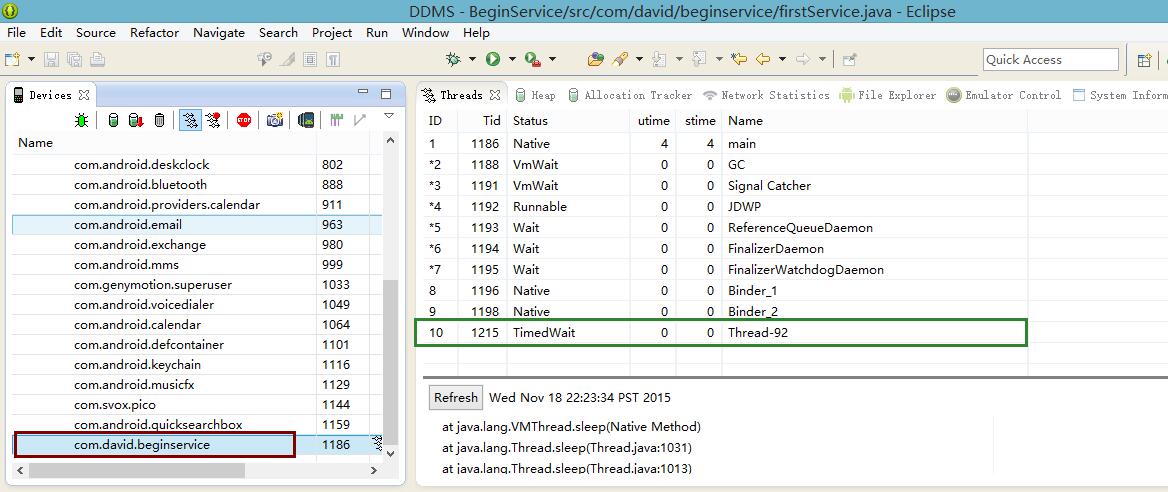
六:Service不是一个新的进程,也不是一个新的线程,是与当前进程绑定
从下图中看到,并没有一个新的进程产生,这个进程只是Activity进程
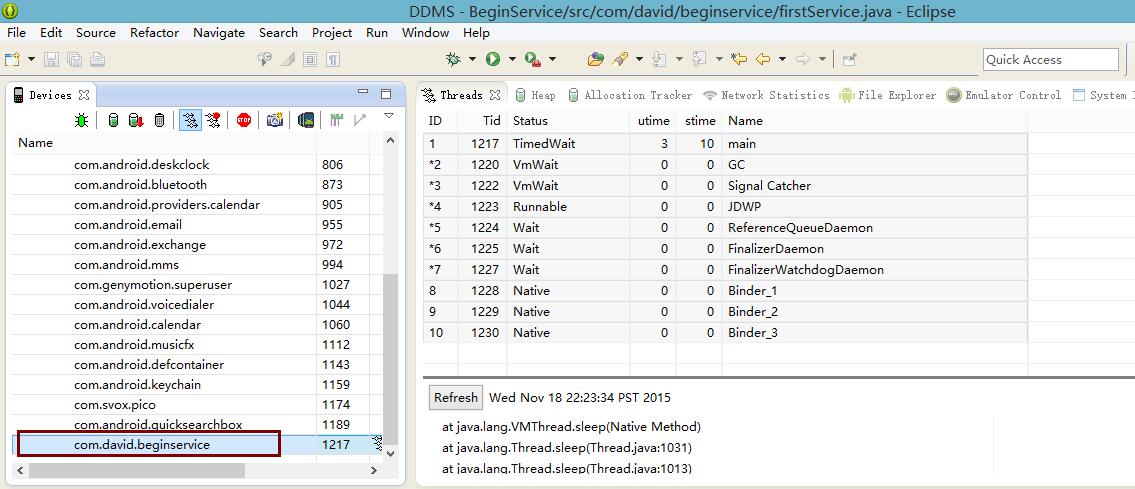
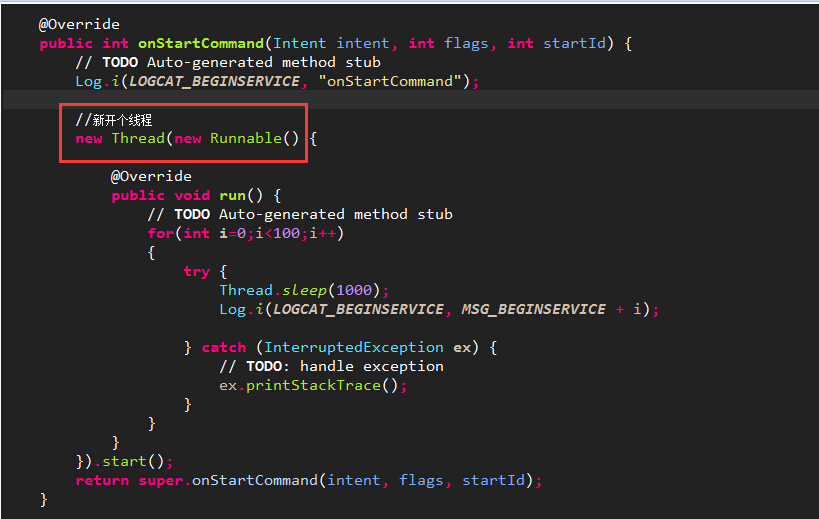
从下图看到是有个新的线程产生了,但是这个新的线程是我自己在Service的onStartCommand方法里自己开启的