获取成功的结果
1 // 摇骰子函数
2 function ysz() {
3 return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
4 let sino = parseInt(Math.random() * 6 + 1)
5 setTimeout(() => {
6 resolve(sino)
7 }, 3000);
8 })
9 }
定义一个变量接收sino值,并打印其结果
- 直接打印
-
1 function test() { 2 let n = ysz() 3 console.log(n); 4 } 5 test()
-
- 延迟到resolve()执行完毕再打印
-
1 function test() { 2 let n = ysz() 3 setTimeout(() => { 4 console.log(n); 5 }, 4000); 6 } 7 test()
-
- 使用async和await
-
1 async function test() { 2 let n = await ysz() 3 console.log(n); 4 } 5 test()
-
上面这段代码async中使await ysz()先执行,等到三秒后执行完再把得到的结果赋值给左边的n,也就是说test函数需要三秒钟才执行完成,所以test函数是异步的,因此前面必须写async
获取失败的结果
1 function ysz(guess) { 2 return new Promise((resolve, reject) => { 3 let sino = parseInt(Math.random() * 6 + 1) 4 if (sino > 3) { 5 if (guess === 'big') { 6 setTimeout(() => { 7 resolve(sino) 8 }, 2000) 9 } else { 10 setTimeout(() => { 11 reject(sino) 12 }, 2000) 13 } 14 } else { 15 if (guess === 'big') { 16 setTimeout(() => { 17 reject(sino) 18 }, 2000) 19 } else { 20 setTimeout(() => { 21 resolve(sino) 22 }, 2000) 23 } 24 } 25 }) 26 } 27 async function test(sz) { 28 try { 29 //把await及获取它的值的操作放在try里 30 let n = await ysz(sz) 31 console.log('赢了' + n) 32 } catch (error) { 33 //失败的操作放在catch里 34 console.log('输了' + error) 35 } 36 } 37 test('big')


把await和成功后的操作放到try里,失败的放在catch
-
为什么要用await
为了使我们的异步代码,更像同步的代码 -
有多个promise,怎么拿到所有的promise都结束后的结果
比如有两个色子,我想得到这两个色子的点数
1.使用promise.all
1 function ysz(guess) { 2 return new Promise((resolve, reject) => { 3 let sino = parseInt(Math.random() * 6 + 1) 4 if (sino > 3) { 5 if (guess === 'big') { 6 resolve(sino) 7 } else { 8 console.log('error') 9 reject(sino) 10 } 11 } else { 12 if (guess === 'big') { 13 console.log('error') 14 reject(sino) 15 } else { 16 resolve(sino) 17 } 18 } 19 setTimeout(() => { 20 resolve(sino) 21 }, 300) 22 }) 23 } 24 Promise.all([ysz('big'), ysz('big')]).then((x) => { console.log(x) }, (y) => { console.log(y) })


2.使用await
1 async function test() { 2 try { 3 let n = await Promise.all([ysz('big'), ysz('big')]) 4 console.log(n) 5 } catch (error) { 6 console.log(error) 7 } 8 } 9 test()


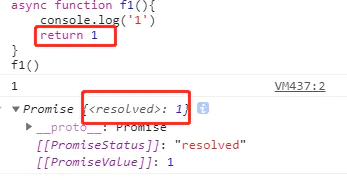
- async函数会返回一个promise,并且Promise对象的状态值是resolved(成功的)
- 如果你没有在async函数中写return,那么Promise对象resolve的值就是是undefined

- 如果你写了return,那么return的值就会作为你成功的时候传入的值
await 等到之后,做了一件什么事情?
那么右侧表达式的结果,就是await要等的东西。
等到之后,对于await来说,分2个情况
- 不是promise对象
- 是promise对象
如果不是 promise , await会阻塞后面的代码,先执行async外面的同步代码,同步代码执行完,再回到async内部,把这个非promise的东西,作为 await表达式的结果。
如果它等到的是一个 promise 对象,await 也会暂停async后面的代码,先执行async外面的同步代码,等着 Promise 对象 fulfilled,然后把 resolve 的参数作为 await 表达式的运算结果。
- 如果asycn里的代码都是同步的,那么这个函数被调用就会同步执行
1 async function fn(){ 2 console.log('a') 3 } 4 fn() 5 console.log('b') 6 //a 7 //b
引用文章:https://www.jianshu.com/p/b4fd76c61dc9