MapReduce(二)
mapreduce 将Text转化为对象进行处理数据。
根据一来说,将date,classname,name,subject,score变为对象属性
我的数据是:是有重复的。
package com.huhu.day02;
import java.io.DataInput;
import java.io.DataOutput;
import java.io.IOException;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.WritableComparable;
public class Score implements WritableComparable<Score> {
private String date;
private String classname;
private String name;
private String subject;
private int score;
public Score() {
super();
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
public Score(String date, String classname, String name, String subject, int score) {
super();
this.date = date;
this.classname = classname;
this.name = name;
this.subject = subject;
this.score = score;
}
public String getDate() {
return date;
}
public void setDate(String date) {
this.date = date;
}
public String getClassname() {
return classname;
}
public void setClassname(String classname) {
this.classname = classname;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getSubject() {
return subject;
}
public void setSubject(String subject) {
this.subject = subject;
}
public int getScore() {
return score;
}
public void setScore(int score) {
this.score = score;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Score [date=" + date + ", classname=" + classname + ", name=" + name + ", subject=" + subject
+ ", score=" + score + "]";
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
final int prime = 31;
int result = 1;
result = prime * result + ((classname == null) ? 0 : classname.hashCode());
result = prime * result + ((date == null) ? 0 : date.hashCode());
result = prime * result + ((name == null) ? 0 : name.hashCode());
result = prime * result + score;
result = prime * result + ((subject == null) ? 0 : subject.hashCode());
return result;
}
@Override
public void readFields(DataInput in) throws IOException {
this.date = in.readUTF();
this.classname = in.readUTF();
this.name = in.readUTF();
this.subject = in.readUTF();
this.score = in.readInt();
}
@Override
public void write(DataOutput out) throws IOException {
out.writeUTF(this.date);
out.writeUTF(this.classname);
out.writeUTF(this.name);
out.writeUTF(this.subject);
out.writeInt(this.score);
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if (this == obj)
return true;
if (obj == null)
return false;
if (getClass() != obj.getClass())
return false;
Score other = (Score) obj;
if (classname == null) {
if (other.classname != null)
return false;
} else if (!classname.equals(other.classname))
return false;
if (date == null) {
if (other.date != null)
return false;
} else if (!date.equals(other.date))
return false;
if (name == null) {
if (other.name != null)
return false;
} else if (!name.equals(other.name))
return false;
if (score != other.score)
return false;
if (subject == null) {
if (other.subject != null)
return false;
} else if (!subject.equals(other.subject))
return false;
return true;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Score o) {
if (this.date.equals(o.date)) {
if (this.classname.equals(o.classname)) {
if (this.name.equals(o.name)) {
if (this.subject.equals(o.subject)) {
return this.score - o.score;
} else {
return this.subject.compareTo(o.subject);
}
} else {
return this.name.compareTo(o.name);
}
} else {
return this.classname.compareTo(o.classname);
}
} else {
return this.date.compareTo(o.date);
}
}
}该自定义类使用实现了WritableComparable<>类是为了序列化该类然后进入mapreduce方法中,实现compareTo是为了mapreduce根据key排序,当该int字段返回 0 证明key相同。如果返回大于1则是升序,返回小于1降序。
package com.huhu.day02;
import java.io.IOException;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.NullWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.util.GenericOptionsParser;
import org.apache.hadoop.util.Tool;
import org.apache.hadoop.util.ToolRunner;
public class ScoreCount extends ToolRunner implements Tool {
public static class MyMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Score, NullWritable> {
@Override
protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
String[] line = value.toString().split(" ");
Score score = null;
if (line.length == 5) {
score = new Score(line[0], line[1], line[2], line[3], Integer.parseInt(line[4]));
}
context.write(score, NullWritable.get());
}
}
public static class MyReduce extends Reducer<Score, NullWritable, Score, Text> {
@Override
protected void reduce(Score key, Iterable<NullWritable> values, Context context)
throws IOException, InterruptedException {
int count = 1;
for (NullWritable v : values) {
context.write(key, new Text(count + "-------" ));
count++;
}
}
}
@Override
public Configuration getConf() {
return new Configuration();
}
@Override
public void setConf(Configuration arg0) {
}
@Override
public int run(String[] other) throws Exception {
Job job = Job.getInstance(getConf(), "ScoreCount");
job.setJarByClass(ScoreCount.class);
job.setMapperClass(MyMapper.class);
job.setMapOutputKeyClass(Score.class);
job.setMapOutputValueClass(NullWritable.class);
job.setReducerClass(MyReduce.class);
job.setOutputKeyClass(Score.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(Text.class);
FileInputFormat.addInputPath(job, new Path(other[0]));
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path(other[1]));
return job.waitForCompletion(true) ? 0 : 1;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Configuration conf = new Configuration();
String[] other = new GenericOptionsParser(conf, args).getRemainingArgs();
if (other.length != 2) {
System.out.println("your input args number is fail,you need input <in> and <out>");
System.exit(0);
}
ToolRunner.run(conf, new ScoreCount(), other);
}
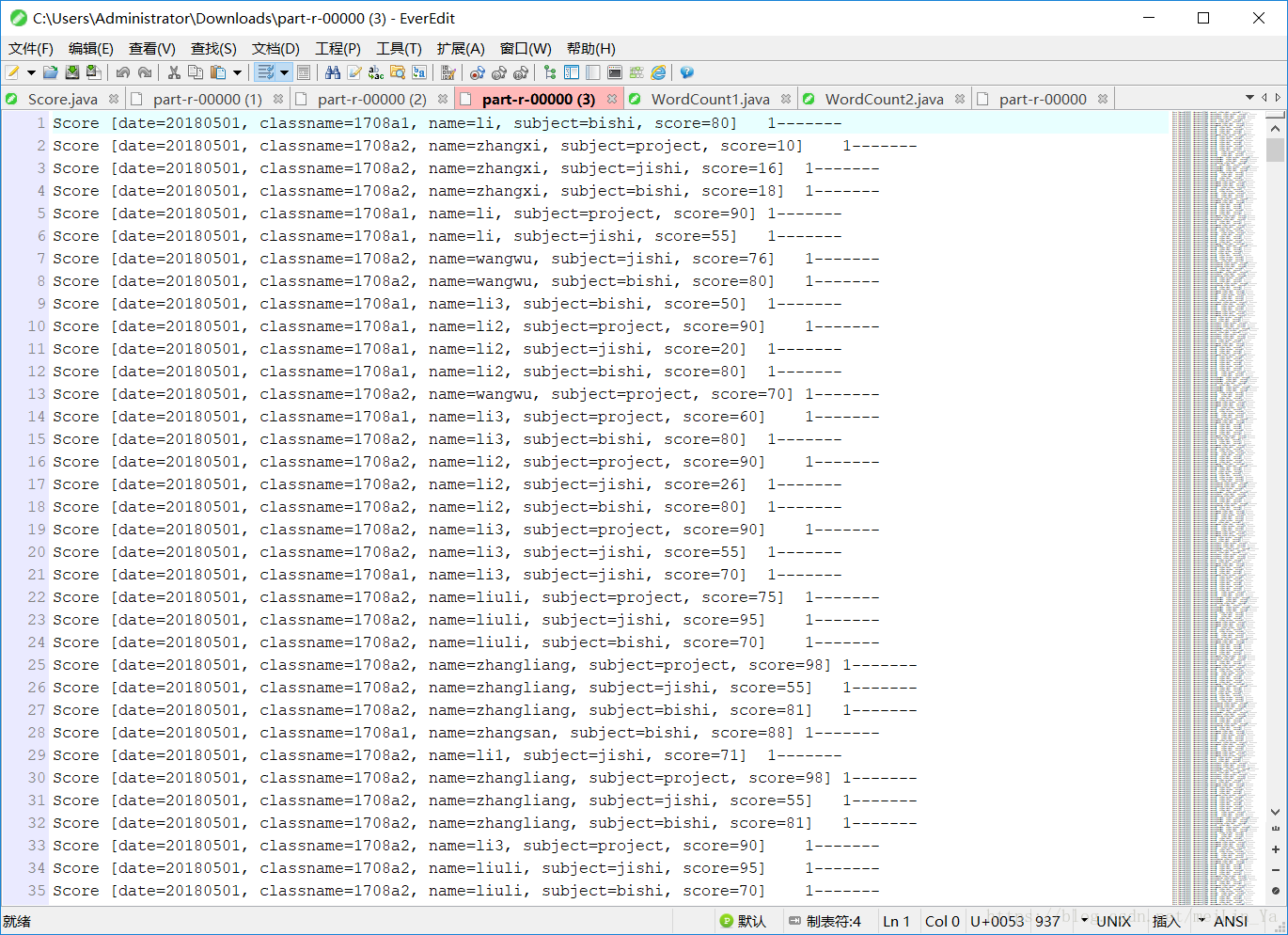
}此时输出的结果是:此时equalse和compareTo方法都有
数据相同的可以认识,然后后面的计数器就赋予它原来的值,而不是累加。
让我们去掉equals方法再测试一遍。
发现并没有什么不同,好的,那我们去掉将compareto的方法的内容去掉,直接返回1;
发现计数器都是1,也就是说没有一个数据是相同的,但是我的数据里面明明是相同的数据啊,是为什么,因为
此时数据按升序排列,然后我们将compareto返回值调为-1
此时数据是按降序排序。
在compareto中String字符串是将字符串转化为ascii码表的值(字符所对应的十进制值) 相加然后进行比较大小。
MapReduce
将Text文本对象化,传一个序列化对象后,利用对象属性字段取值并使用值,比切割字符串方式取值方便,并且在自定义类中使用添加方法如equalse方法和comparto方法是mapreduce中的key进行排序。从而简化yarn对的数据操作过程,利用了java的一切皆对象的思想。