Thread类:





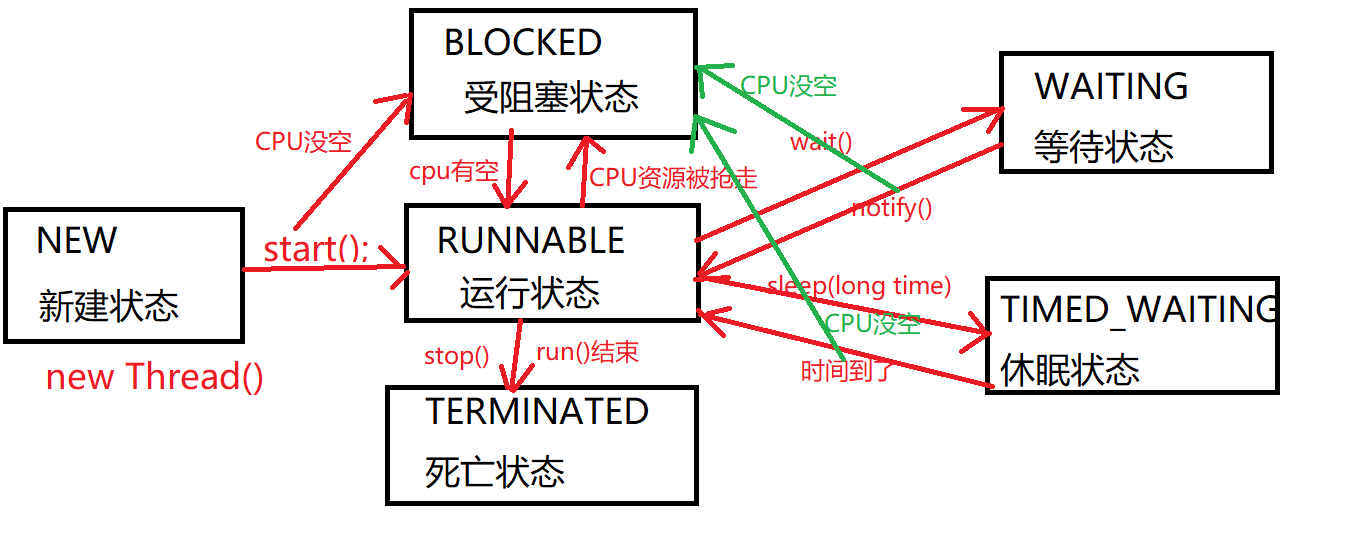
当new Thread()时,线程处于新建状态,当start()时,线程处于运行状态,并且CPU没空时,处于受阻塞状态,当CPU有空时,有处于运行状态,当stop()时或run()结束时,线程处于死亡状态,同时,
当运行时,调用wait()方法,线程处于等待状态,在调用notify()方法,又处于运行状态,如果CPU被抢走,则处于被阻塞状态,当调用sleep()方法,线程处于休眠状态,时间到了之后,又处于运行状态,如果CPU被抢走,又处于被阻塞状态。
线程安全问题:
public class Tickets implements Runnable{ //100张票 //多线程共享数据容易出现安全问题 private int t=100; public void run() { //循环卖票 while(true){ if(t>0){ try { Thread.sleep(100); } catch (InterruptedException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() .getName()+"卖了第:"+t--+"张票"); } } } }
public class Demo01 { public static void main(String[] args) { //创建线程任务 Tickets t=new Tickets(); //创建三个线程对象 Thread t1=new Thread(t); Thread t2=new Thread(t); Thread t3=new Thread(t); //开启线程 t1.start(); t2.start(); t3.start(); } }

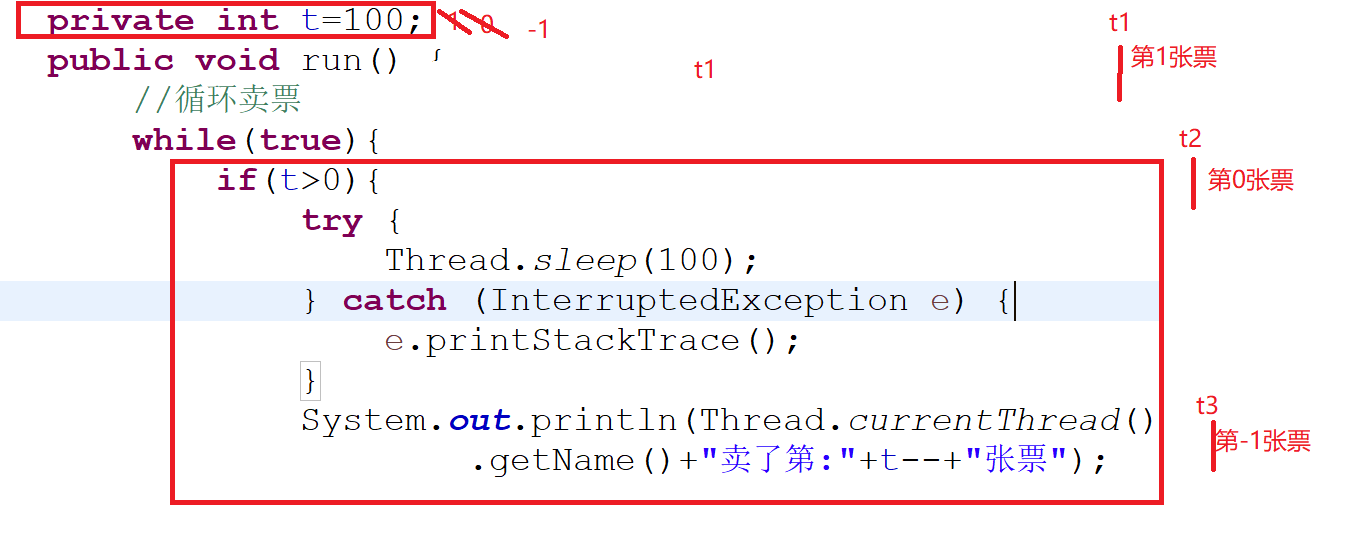
首先100张票必须三条线程同时卖,所以100张票要定义在成员变量中,当只有一张票时,t1>0,t1进入程序,t1开始等着,t2>0,满足条件,t2进入,t2开始等着,t3>0,满足条件,t3进入,t3等着,t1开始执行,卖第一张票,t2执行,卖0张票,t3卖-1张票。
总结:当有多个线程共享一个资源时,会出现线程安全问题.
第一种解决方式:
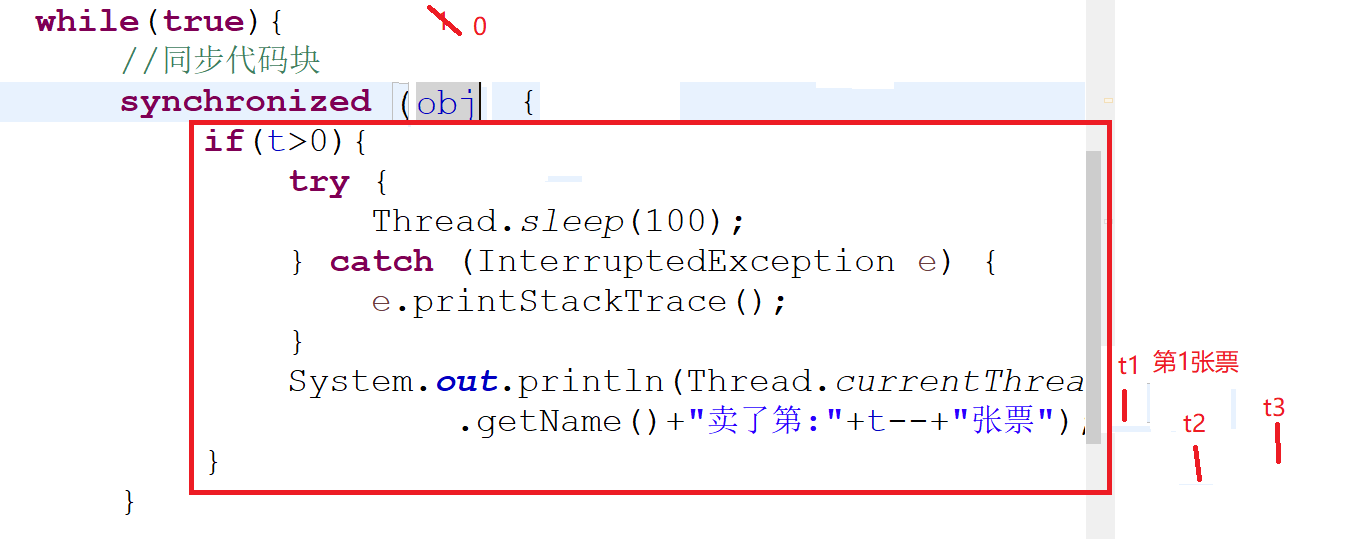
同步代码块:
public class Tickets02 implements Runnable{ //100张票 //多线程共享数据容易出现安全问题 private int t=100; private Object obj=new Object(); public void run() { //循环卖票 while(true){ //同步代码块 synchronized (obj) { if(t>0){ try { Thread.sleep(100); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() .getName()+"卖了第:"+t--+"张票"); } } } } }
第二种方式:
同步方法:
public class Tickets03 implements Runnable{ //100张票 //多线程共享数据容易出现安全问题 private int t=100; public void run() { //循环卖票 while(true){ sale(); } } //写一个同步方法 public synchronized void sale(){ if(t>0){ try { Thread.sleep(100); } catch (InterruptedException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() .getName()+"卖了第:"+t--+"张票"); } } }
第三种方式:lock接口

public class Tickets04 implements Runnable{ //100张票 //多线程共享数据容易出现安全问题 private int t=100; //创建lock锁对象 private Lock lock=new ReentrantLock(); public void run() { //循环卖票 while(true){ //获得锁 lock.lock(); if(t>0){ try { Thread.sleep(100); } catch (InterruptedException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() .getName()+"卖了第:"+t--+"张票"); } //释放锁 lock.unlock(); } } }
StringBuffer与StringBuilder:
StringBuffer安全,但速度慢。
StringBuilder快,但相对来说不安全。
因为StringBuffer中的方法都用了synchronized。
public synchronized int capacity() { return value.length; } @Override public synchronized void ensureCapacity(int minimumCapacity) { super.ensureCapacity(minimumCapacity); } /** * @since 1.5 */ @Override public synchronized void trimToSize() { super.trimToSize(); }