wait(),notify(),notifyAll()三个方法不是Thread的方法,而是Object的方法。意味着所有对象都有这三个方法,因为每个对象都有锁,所以自然也都有操作锁的方法了。这三个方法最终调用的都是jvm级的native方法。随着jvm运行平台的不同可能有些许差异。
java文档的解释
wait导致当前的线程等待,直到其他线程调用此对象的 notify() 方法或 notifyAll() 方法。当前的线程必须拥有此对象监视器。该线程发布对此监视器的所有权并等待,直到其他线程通过调用 notify 方法,或 notifyAll 方法通知在此对象的监视器上等待的线程醒来。然后该线程将等到重新获得对监视器的所有权后才能继续执行.
notify唤醒在此对象监视器上等待的单个线程。如果所有线程都在此对象上等待,则会选择唤醒其中一个线程。直到当前的线程放弃此对象上的锁定,才能继续执行被唤醒的线程。此方法只应由作为此对象监视器的所有者的线程来调用.
"当前的线程必须拥有此对象监视器"与"此方法只应由作为此对象监视器的所有者的线程来调用"说明wait方法与notify方法必须在同步块内执行,即synchronized(obj之内).
调用对像wait方法后,当前线程释放对像锁,进入等待状态.直到其他线程(也只能是其他线程)通过notify 方法,或 notifyAll.该线程重新获得对像锁.
例子代码:
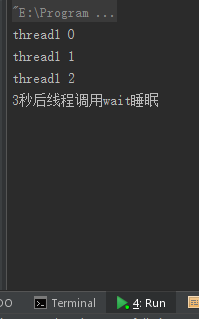
说明:线程运行3秒后调用wait等待,6秒后主线程调用notify唤醒等待线程。
1 /** 2 * Created on 2016/1/31. 3 */ 4 public class MyThread implements Runnable { 5 private Object flag; 6 private String threadName; 7 8 public MyThread(Object flag,String threadName) { 9 this.flag = flag; 10 this.threadName = threadName; 11 } 12 13 @Override 14 public void run(){ 15 try{ 16 for(int i = 0; i < 10;i++){ 17 if(i == 3){ 18 synchronized (this.flag){ 19 System.out.println("3秒后线程调用wait睡眠"); 20 this.flag.wait(); 21 } 22 } 23 System.out.println(this.threadName + " " + i); 24 Thread.sleep(1000); 25 } 26 } catch(InterruptedException e){ 27 e.printStackTrace(); 28 } 29 30 } 31 }
main方法:
1 import java.io.IOException; 2 3 /** 4 * Created on 2016/1/31. 5 */ 6 public class TestMain { 7 public static void main(String[] args) { 8 Object object = new Object(); 9 MyThread myThread1 = new MyThread(object,"thread1"); 10 // MyThread myThread2 = new MyThread(object,"thread2"); 11 Thread test1 = new Thread(myThread1); 12 test1.start(); 13 14 // Thread test2 = new Thread(myThread1); 15 // test2.start(); 16 17 try{ 18 Thread.sleep(6000); 19 System.out.println("6秒后唤醒线程"); 20 synchronized (object){ 21 object.notify(); 22 } 23 System.in.read(); 24 } catch(InterruptedException e){ 25 e.printStackTrace(); 26 } catch(IOException e){ 27 e.printStackTrace(); 28 } 29 30 } 31 }
结果:

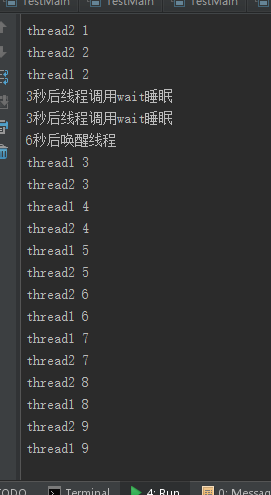
测试notifyAll(MyThread代码不变)
main方法代码:
1 import java.io.IOException; 2 3 /** 4 * Created on 2016/1/31. 5 */ 6 public class TestMain { 7 public static void main(String[] args) { 8 Object object = new Object(); 9 MyThread myThread1 = new MyThread(object,"thread1"); 10 MyThread myThread2 = new MyThread(object,"thread2"); 11 Thread test1 = new Thread(myThread1); 12 test1.start(); 13 14 Thread test2 = new Thread(myThread2); 15 test2.start(); 16 17 try{ 18 Thread.sleep(6000); 19 System.out.println("6秒后唤醒线程"); 20 synchronized (object){ 21 object.notifyAll(); 22 } 23 System.in.read(); 24 } catch(InterruptedException e){ 25 e.printStackTrace(); 26 } catch(IOException e){ 27 e.printStackTrace(); 28 } 29 30 } 31 }
结果截图: