Enumeration与Iterator的对比
|
|
Enumeration 接口 |
Iterator 接口 |
|
参数的含义 |
枚举类型 |
迭代器元素类型 |
|
所在包 |
java.util |
|
|
父类 |
无 |
|
|
子类 |
StringTokenizer |
BeanContextSupport.BCSIterator, EventReaderDelegate, Scanner |
|
区别 |
实现 Enumeration 接口的对象, 它生成一系列元素,一次生成一 个。连续调用nextElement 方法将 返回一系列的连续元素。 |
迭代器 |
|
方法 |
||
|
判断是否有下一个元素 |
hasMoreElements()测试此枚举是否 包含更多的元素。 |
hasNext()如果仍有元素可以迭代, 则返回 true。 |
|
获取元素 |
nextElement()如果此枚举对象至少 还有一个可提供的元素,则返回此 枚举的下一个元素。 |
next()返回迭代的下一个元素。 |
|
移除 |
|
remove()从迭代器指向的 collection 中移除迭代器返回的最后一个元 素(可选操作)。 |
前言
在数据库连接池分析的代码实例中,看到其中使用Enumeration来遍历Vector集合。后来就找了一些资料查看都有哪些方法可以遍历集合类,在网上找到了如下的使用Enumeration和Iterator遍历集合类的实例。不过这个实例中提到了Enumeration比Iterator的效率更高,其实并不是这样子的,该实例是的时间测试太片面了, 因为数据量太少。随着数据两的增加,两者之间的效率越来越接近,而不会出现倍数的比例。而且现在普遍都使用Iterator来遍历集合类,只有特别明确声明必须使用Enumeration的才会用该类遍历集合。
package edu.sjtu.erplab.hash;
import java.util.Enumeration;
import java.util.Hashtable;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Map.Entry;
//一个遍历hashtable实例
public class TraveseHashTable {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//初始化创建hashtable
Hashtable<String, String> ht = new Hashtable<String, String>();
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
ht.put("Key=" + i, "Val=" + i);
}
// 1. 使用Enumeration
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
Enumeration<String> en = ht.keys();//使用枚举获取key
while (en.hasMoreElements()) {
en.nextElement();
}
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("Enumeration keys costs " + (end - start)
+ " milliseconds");
// 2. 使用Enumeration
start = System.currentTimeMillis();
Enumeration<String> en2 = ht.elements();//使用枚举获取这个key-value对
while (en2.hasMoreElements()) {
en2.nextElement();
}
end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("Enumeration elements costs " + (end - start)
+ " milliseconds");
// 3. Iterator
start = System.currentTimeMillis();
Iterator<String> it = ht.keySet().iterator();//使用迭代器获取这个key
while (it.hasNext()) {
it.next();
}
end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("Iterator keySet costs " + (end - start)
+ " milliseconds");
// 4. Iterator
start = System.currentTimeMillis();
Iterator<Entry<String, String>> it2 = ht.entrySet().iterator();//使用迭代器获取这个key-value对
while (it2.hasNext()) {
it2.next();
}
end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("Iterator entrySet costs " + (end - start)
+ " milliseconds");
}
}
废弃的接口:Enumeration
Enumeration
接口是JDK1.0时推出的,是最好的迭代输出接口,最早使用Vector(现在推荐使用ArrayList)时就是使用Enumeration接口进行
输出。虽然Enumeration是一个旧的类,但是在JDK1.5之后为Enumeration类进行了扩充,增加了泛型的操作应用。
Enumeration接口常用的方法有hasMoreElements()(判断是否有下一个值)和 nextElement()(取出当前元素),这些方法的功能跟Iterator类似,只是Iterator中存在删除数据的方法,而此接口不存在删除操作。
为什么还要继续使用Enumeration接口
Enumeration和Iterator接口功能相
似,而且Iterator的功能还比Enumeration多,那么为什么还要使用Enumeration?这是因为java的发展经历了很长时间,一些
比较古老的系统或者类库中的方法还在使用Enumeration接口,因此为了兼容,还是需要使用Enumeration。
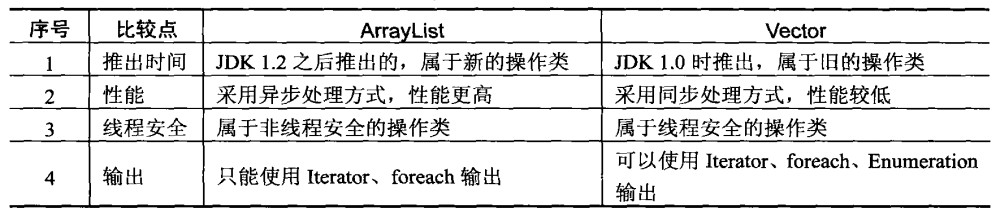
List接口的常用子类
List接口常用的子类有ArrayList和Vector,两者有许多相似的地方,下面给出这两者之间的比较