一、监听器模式介绍
将一个监听器(listener)与特定的控件(如按钮等)绑定起来,当发生用户点击等事件(Event)时,调用监听器的处理方法,从而响应用户的动作,就叫做事件/监听器模式。
从上面的语句中,我们可以看出监听器模式有三个要素:
-
事件源
-
事件对象
-
监听器
二、自定义监听器事件
创建天气事件接口和下雨、下雪实现类
public interface WeatherEvent {
String getWeather();
}
public class RainWeatherEvent implements WeatherEvent {
@Override
public String getWeather() {
return "下雨";
}
}
public class SnowWeatherEvent implements WeatherEvent {
@Override
public String getWeather() {
return "下雪";
}
}
创建天气监听实现接口和下雨、下雪监听实现类
public interface WeatherListener {
void onWeatherEvent(WeatherEvent event);
}
public class RainListener implements WeatherListener {
@Override
public void onWeatherEvent(WeatherEvent event) {
if (event instanceof RainWeatherEvent) {
System.out.println(event.getWeather());
}
}
}
public class SnowListener implements WeatherListener {
@Override
public void onWeatherEvent(WeatherEvent event) {
if (event instanceof SnowWeatherEvent) {
System.out.println(event.getWeather());
}
}
}
创建事件广播器接口和天气事件广播实现类
public interface EventMulticaster {
void multicastEvent(WeatherEvent event);
void addListener(WeatherListener listener);
void removeListener(WeatherListener listener);
}
public class WeatherEventMulticaster implements EventMulticaster {
private List<WeatherListener> listenerList = new ArrayList<>();
@Override
public void multicastEvent(WeatherEvent event) {
System.out.println("==========开始事件广播==========");
listenerList.forEach(i -> i.onWeatherEvent(event));
System.out.println("==========结束事件广播==========");
}
@Override
public void addListener(WeatherListener listener) {
listenerList.add(listener);
}
@Override
public void removeListener(WeatherListener listener) {
listenerList.remove(listener);
}
}
创建启动测试类
public class Start {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建广播对象
EventMulticaster eventMulticaster = new WeatherEventMulticaster();
// 创建下雨事件监听对象
RainListener rainListener = new RainListener();
// 创建下雪事件监听对象
SnowListener snowListener = new SnowListener();
// 添加下雨、下雪监听事件对象
eventMulticaster.addListener(rainListener);
eventMulticaster.addListener(snowListener);
// 广播下雨事件
eventMulticaster.multicastEvent(new RainWeatherEvent());
// 广播下雪事件
eventMulticaster.multicastEvent(new SnowWeatherEvent());
// 移除下雨监听事件对象
eventMulticaster.removeListener(rainListener);
// 广播下雨事件
// 广播下雪事件
eventMulticaster.multicastEvent(new RainWeatherEvent());
eventMulticaster.multicastEvent(new SnowWeatherEvent());
}
}
启动项目,查看控制台输出:
==========开始事件广播==========
下雨
==========结束事件广播==========
==========开始事件广播==========
下雪
==========结束事件广播==========
==========开始事件广播==========
==========结束事件广播==========
==========开始事件广播==========
下雪
==========结束事件广播==========
可以看到当下雨监听器被移除之后,下雨事件就不能被监听处理了。
三、SpringBoot 监听器实现
3.1 监听器
@FunctionalInterface
public interface ApplicationListener<E extends ApplicationEvent> extends EventListener {
void onApplicationEvent(E event);
}
FunctionalInterface是jdk8新增的,表示ApplicationListener接口只有一个方法,如果大于一个方法,将报错。- 接口中有个泛型
<E extends ApplicationEvent>,继承自ApplicationEvent。代表实现接口时,可以声明对哪些事件(如ApplicationEvent)感兴趣,在触发监听器的时候,对其他事件进行过滤。
3.2 系统广播器
public interface ApplicationEventMulticaster {
// 添加事件监听器
void addApplicationListener(ApplicationListener<?> listener);
// 添加事件监听器
void addApplicationListenerBean(String listenerBeanName);
// 移除指定事件监听器
void removeApplicationListener(ApplicationListener<?> listener);
// 移除指定事件监听器
void removeApplicationListenerBean(String listenerBeanName);
// 移除所有事件监听器
void removeAllListeners();
// 事件广播
void multicastEvent(ApplicationEvent event);
// 事件广播
void multicastEvent(ApplicationEvent event, @Nullable ResolvableType eventType);
}
3.3 系统事件
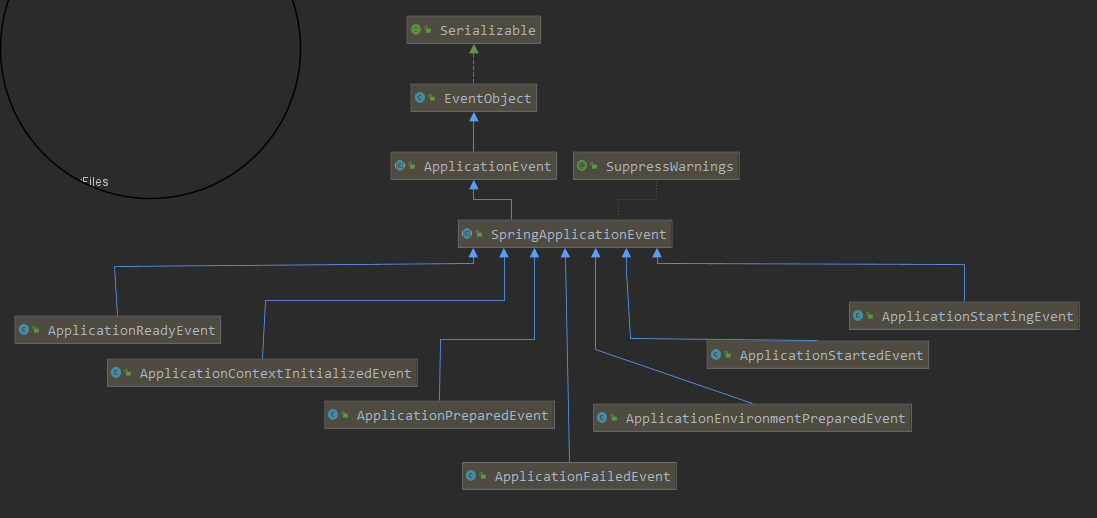
| 事件名 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| ApplicationStartingEvent | 框架启动事件 |
| ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent | 环境准备完毕事件 |
| ApplicationContextInitializedEvent | 上下文初始化 |
| ApplicationPreparedEvent | 上下文创建完毕,但是Bean还没有加载完毕 |
| ApplicationStartedEvent | bean 实例化完成,但是未调用 Runners接口 |
| ApplicationReadyEvent | 调用 Runners 接口完毕 |
| ApplicationFailedEvent | 启动失败事件 |
系统事件发生顺序:
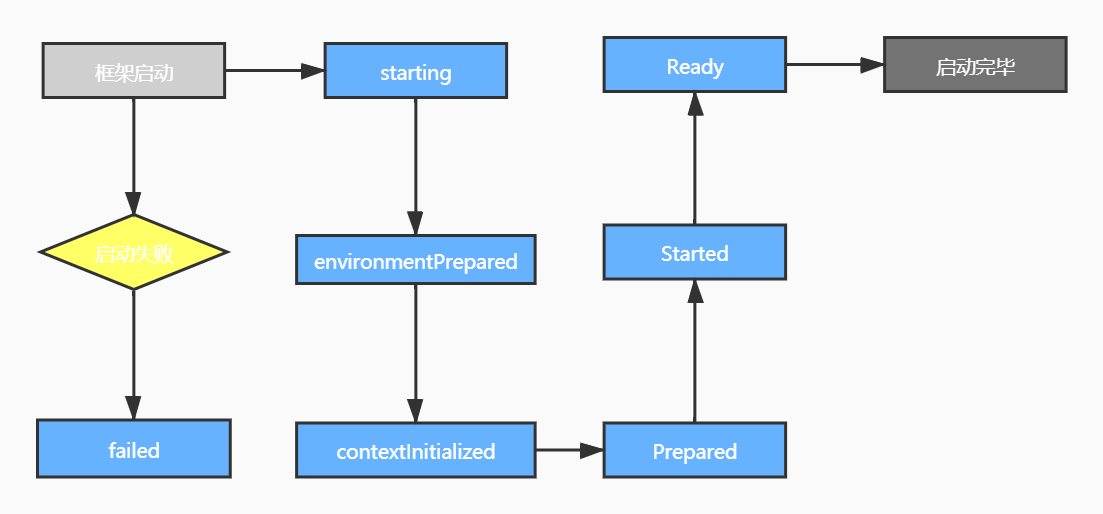
3.4 监听器注册
在 SpringApplication 初始化的时候就进行了监听器注册
public SpringApplication(ResourceLoader resourceLoader, Class<?>... primarySources) {
......
setListeners((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationListener.class));
......
}
3.5 监听器事件触发机制
以 starting 事件为例
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {
......
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args);
listeners.starting();
......
}
进入 starting 方法,里面是遍历所有的 SpringApplicationRunListeners:
void starting() {
for (SpringApplicationRunListener listener : this.listeners) {
listener.starting();
}
}
SpringApplicationRunListeners 接口定义如下,可以看到申明了多个事件:
public interface SpringApplicationRunListener {
default void starting() {}
default void environmentPrepared(ConfigurableEnvironment environment) {}
default void contextPrepared(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {}
default void contextLoaded(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {}
default void started(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {}
default void running(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {}
default void failed(ConfigurableApplicationContext context, Throwable exception){}
}
看下默认的实现类 EventPublishingRunListener:
public class EventPublishingRunListener{
......
private final SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster initialMulticaster;
@Override
public void starting() {
// 调用广播器来发送事件
this.initialMulticaster.multicastEvent(new ApplicationStartingEvent(this.application, this.args));
}
......
}
进入 multicastEvent 方法
@Override
public void multicastEvent(ApplicationEvent event) {
multicastEvent(event, resolveDefaultEventType(event));
}
resolveDefaultEventType 是对 event 的包装,不需要理会。
private ResolvableType resolveDefaultEventType(ApplicationEvent event) {
return ResolvableType.forInstance(event);
}
回到 multicastEvent 方法
@Override
public void multicastEvent(final ApplicationEvent event, @Nullable ResolvableType eventType) {
ResolvableType type = (eventType != null ? eventType : resolveDefaultEventType(event));
// 获得线程池
Executor executor = getTaskExecutor();
// getApplicationListeners --> 获得对当前event感兴趣的监听器列表
for (ApplicationListener<?> listener : getApplicationListeners(event, type)) {
if (executor != null) {
executor.execute(() -> invokeListener(listener, event));
}
else {
invokeListener(listener, event);
}
}
}
获得对当前 event 感兴趣的监听器列表:
protected Collection<ApplicationListener<?>> getApplicationListeners(
ApplicationEvent event, ResolvableType eventType) {
// 获取事件来源,这里的 source 就是 SpringApplication
Object source = event.getSource();
Class<?> sourceType = (source != null ? source.getClass() : null);
ListenerCacheKey cacheKey = new ListenerCacheKey(eventType, sourceType);
// 从缓存中获取结果
ListenerRetriever retriever = this.retrieverCache.get(cacheKey);
if (retriever != null) {
return retriever.getApplicationListeners();
}
if (this.beanClassLoader == null ||
(ClassUtils.isCacheSafe(event.getClass(), this.beanClassLoader) &&
(sourceType == null || ClassUtils.isCacheSafe(sourceType, this.beanClassLoader)))) {
// 完全同步构建和缓存ListenerRetriever
synchronized (this.retrievalMutex) {
retriever = this.retrieverCache.get(cacheKey);
if (retriever != null) {
return retriever.getApplicationListeners();
}
retriever = new ListenerRetriever(true);
// 检索感兴趣的监听器
Collection<ApplicationListener<?>> listeners =
retrieveApplicationListeners(eventType, sourceType, retriever);
// 存放到缓存中
this.retrieverCache.put(cacheKey, retriever);
return listeners;
}
}
else {
// 无需 ListenerRetriever 缓存->无需同步
return retrieveApplicationListeners(eventType, sourceType, null);
}
}
检索感兴趣的监听器实现:
private Collection<ApplicationListener<?>> retrieveApplicationListeners(
ResolvableType eventType, @Nullable Class<?> sourceType, @Nullable ListenerRetriever retriever) {
List<ApplicationListener<?>> allListeners = new ArrayList<>();
Set<ApplicationListener<?>> listeners;
Set<String> listenerBeans;
// 获取默认事件监听器
synchronized (this.retrievalMutex) {
// 这些监听器定义在 spring.factories 文件中
listeners = new LinkedHashSet<>(this.defaultRetriever.applicationListeners);
listenerBeans = new LinkedHashSet<>(this.defaultRetriever.applicationListenerBeans);
}
for (ApplicationListener<?> listener : listeners) {
// 只有对当前 eventType 感兴趣的 listerer 才会添加到监听器列表中
if (supportsEvent(listener, eventType, sourceType)) {
if (retriever != null) {
retriever.applicationListeners.add(listener);
}
allListeners.add(listener);
}
}
// 通过 bean 名称获取监听器列表
if (!listenerBeans.isEmpty()) {
ConfigurableBeanFactory beanFactory = getBeanFactory();
for (String listenerBeanName : listenerBeans) {
try {
if (supportsEvent(beanFactory, listenerBeanName, eventType)) {
ApplicationListener<?> listener =
beanFactory.getBean(listenerBeanName, ApplicationListener.class);
if (!allListeners.contains(listener) && supportsEvent(listener, eventType, sourceType)) {
if (retriever != null) {
if (beanFactory.isSingleton(listenerBeanName)) {
retriever.applicationListeners.add(listener);
}
else {
retriever.applicationListenerBeans.add(listenerBeanName);
}
}
allListeners.add(listener);
}
}
else {
Object listener = beanFactory.getSingleton(listenerBeanName);
if (retriever != null) {
retriever.applicationListeners.remove(listener);
}
allListeners.remove(listener);
}
}
catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) {
}
}
}
// 对监听器列表进行排序
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(allListeners);
if (retriever != null && retriever.applicationListenerBeans.isEmpty()) {
retriever.applicationListeners.clear();
retriever.applicationListeners.addAll(allListeners);
}
return allListeners;
}
获取感兴趣的事件判断逻辑
protected boolean supportsEvent(
ApplicationListener<?> listener, ResolvableType eventType, @Nullable Class<?> sourceType) {
// 必须是 GenericApplicationListener 监听器类型,如果不是需要进行转换
GenericApplicationListener smartListener = (listener instanceof GenericApplicationListener ?
(GenericApplicationListener) listener : new GenericApplicationListenerAdapter(listener));
return (smartListener.supportsEventType(eventType) && smartListener.supportsSourceType(sourceType));
}
构建为 GenericApplicationListenerAdapter
public GenericApplicationListenerAdapter(ApplicationListener<?> delegate) {
Assert.notNull(delegate, "Delegate listener must not be null");
this.delegate = (ApplicationListener<ApplicationEvent>) delegate;
this.declaredEventType = resolveDeclaredEventType(this.delegate);
}
@Nullable
private static ResolvableType resolveDeclaredEventType(ApplicationListener<ApplicationEvent> listener) {
ResolvableType declaredEventType = resolveDeclaredEventType(listener.getClass());
if (declaredEventType == null || declaredEventType.isAssignableFrom(ApplicationEvent.class)) {
Class<?> targetClass = AopUtils.getTargetClass(listener);
if (targetClass != listener.getClass()) {
declaredEventType = resolveDeclaredEventType(targetClass);
}
}
return declaredEventType;
}
@Nullable
static ResolvableType resolveDeclaredEventType(Class<?> listenerType) {
ResolvableType eventType = eventTypeCache.get(listenerType);
if (eventType == null) {
eventType = ResolvableType.forClass(listenerType).as(ApplicationListener.class).getGeneric();
eventTypeCache.put(listenerType, eventType);
}
return (eventType != ResolvableType.NONE ? eventType : null);
}
进入 GenericApplicationListenerAdapter 类 supportsEventType 和 supportsSourceType 方法
@Override
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public boolean supportsEventType(ResolvableType eventType) {
if (this.delegate instanceof SmartApplicationListener) {
Class<? extends ApplicationEvent> eventClass = (Class<? extends ApplicationEvent>) eventType.resolve();
return (eventClass != null && ((SmartApplicationListener) this.delegate).supportsEventType(eventClass));
}
else {
return (this.declaredEventType == null || this.declaredEventType.isAssignableFrom(eventType));
}
}
@Override
public boolean supportsSourceType(@Nullable Class<?> sourceType) {
return !(this.delegate instanceof SmartApplicationListener) ||
((SmartApplicationListener) this.delegate).supportsSourceType(sourceType);
}
我们回到 invokeListener 方法的实现上来:
protected void invokeListener(ApplicationListener<?> listener, ApplicationEvent event) {
ErrorHandler errorHandler = getErrorHandler();
if (errorHandler != null) {
try {
doInvokeListener(listener, event);
}
catch (Throwable err) {
errorHandler.handleError(err);
}
}
else {
doInvokeListener(listener, event);
}
}
private void doInvokeListener(ApplicationListener listener, ApplicationEvent event) {
try {
// 发送事件
listener.onApplicationEvent(event);
} catch (ClassCastException ex) {
String msg = ex.getMessage();
if (msg == null || matchesClassCastMessage(msg, event.getClass())) {
Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(getClass());
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Non-matching event type for listener: " + listener, ex);
}
}
else {
throw ex;
}
}
}
四、自定义监听器
自定义监听器事件也有三种方式,我们依次来实现下。首先我们先创建三个监听器:
@Order(1)
public class FirstListner implements ApplicationListener<ApplicationStartingEvent> {
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(ApplicationStartingEvent event) {
System.out.println("run firstListner");
}
}
public class SecondListner implements ApplicationListener<ApplicationStartingEvent> {
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(ApplicationStartingEvent event) {
System.out.println("run SecondListner");
}
}
public class ThirdListner implements ApplicationListener<ApplicationStartingEvent> {
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(ApplicationStartingEvent event) {
System.out.println("run ThirdListner");
}
}
4.1 在 application.properties 配置文件中配置
context.listner.classes=com.learn.springboot.listener.FirstListner
4.2 在 META-INF/spring.factories 文件中配置
org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener=com.learn.springboot.listener.SecondListner
4.3 在代码中配置
public static void main(String[] args) {
// SpringApplication.run(SpringbootApplication.class, args);
SpringApplication springApplication = new SpringApplication(SpringbootApplication.class);
springApplication.addListeners(new ThirdListner());
springApplication.run();
}
启动项目,观察控制台输出:
run firstListner
run SecondListner
run ThirdListner
. ____ _ __ _ _
/\ / ___'_ __ _ _(_)_ __ __ _
( ( )\___ | '_ | '_| | '_ / _` |
\/ ___)| |_)| | | | | || (_| | ) ) ) )
' |____| .__|_| |_|_| |_\__, | / / / /
=========|_|==============|___/=/_/_/_/
:: Spring Boot :: (v2.2.5.RELEASE)