前言
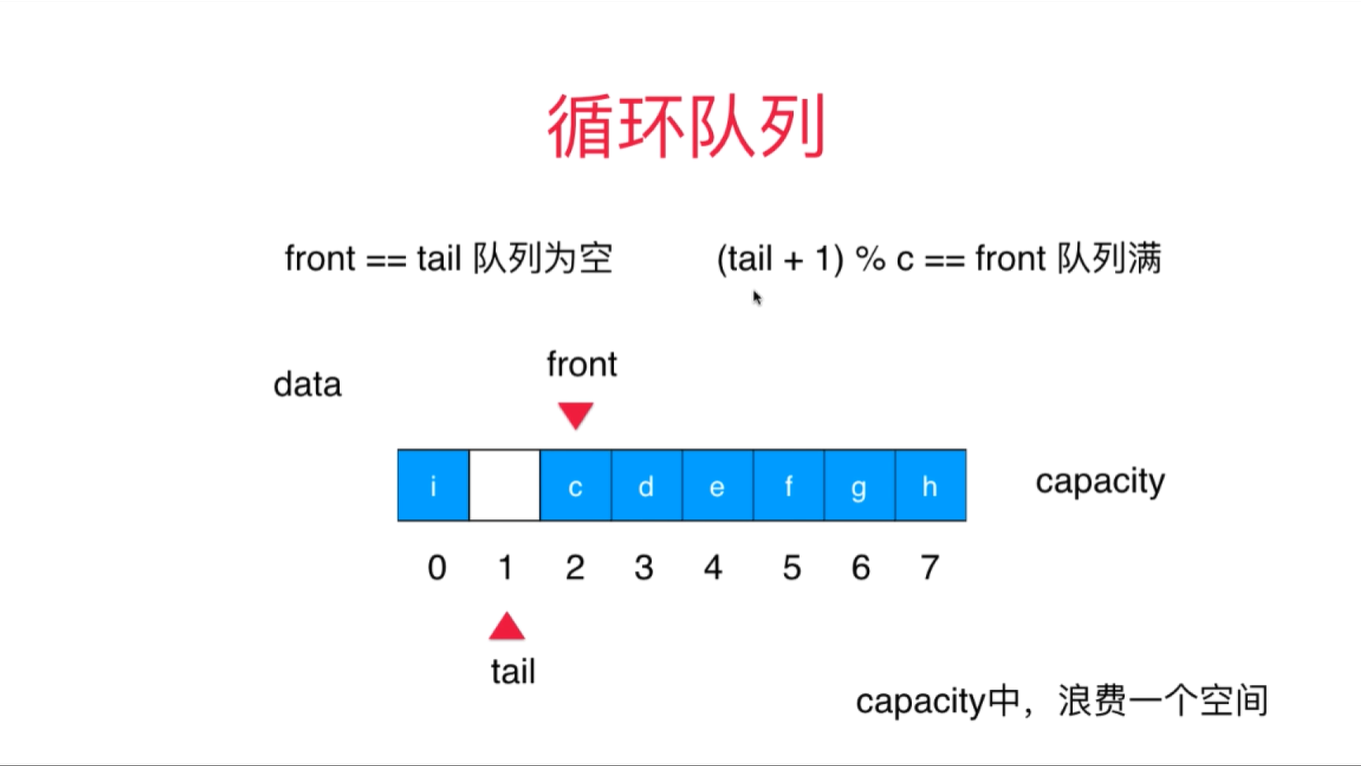
循环队列是把顺序队列首尾相连,把存储队列元素的表从逻辑上看成一个环,成为循环队列。其将队列存储空间的最后一个位置绕到第一个位置,形成逻辑上的环状空间,供队列循环使用。在循环队列结构中,当存储空间的最后一个位置已被使用而再要进入队运算时,只需要存储空间的第一个位置空闲,便可将元素加入到第一个位置,即将存储空间的第一个位置作为队尾。循环队列可以更简单防止伪溢出的发生,但队列大小是固定的。在循环队列中,当队列为空时,有front=tail,而当所有队列空间全占满时,也有front=tail。为了区别这两种情况,规定循环队列最多只能有capacity-1个队列元素,当循环队列中只剩下一个空存储单元时,队列就已经满了。因此,队列判空的条件是front=tail,而队列判满的条件是front =(tail+1)%capacity,如下图所示:
具体实现
- 接口
public interface Queue<T> {
/**
* 添加元素
* @param t
*/
void enqueue(T t);
/**
* 元素出队
* @return
*/
T dequeue();
/**
* 获取队首元素
* @return
*/
T getFront();
/**
* 获取队列长度
* @return
*/
int getSize();
/**
* 是否为空
* @return
*/
boolean isEmpty();
}
- 实现类
public class LoopQueue<T> implements Queue<T> {
/**
* 数组
*/
private T[] data;
/**
* 元素起始与结束位置
*/
private int front, tail;
/**
* 大小
*/
private int size;
/**
* 构造函数
* @param capacity
*/
public LoopQueue(int capacity) {
data = (T[]) new Object[capacity + 1];
front = 0;
tail = 0;
size = 0;
}
/**
* 无参构造函数
*/
public LoopQueue() {
this(10);
}
/**
* 获取容量
* @return
*/
public int getCapacity() {
return data.length - 1;
}
/**
* 是否为空
* @return
*/
@Override
public boolean isEmpty() {
return front == tail;
}
/**
* 获取大小
* @return
*/
@Override
public int getSize() {
return size;
}
/**
* 添加元素
* @param t
*/
@Override
public void enqueue(T t) {
if ((tail + 1) % data.length == front) {
// 数组扩容
resize(2 * getCapacity());
}
data[tail] = t;
tail = (tail + 1) % data.length;
size ++;
}
/**
* 数组增减容
* @param newCapacity
*/
private void resize(int newCapacity) {
T[] newData = (T[]) new Object[newCapacity + 1];
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
newData[i] = data[(i + front) % data.length];
}
data = newData;
front = 0;
tail = size;
}
/**
* 元素出队
* @return
*/
@Override
public T dequeue() {
if (isEmpty()) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Cannot dequeue from an empty dequeue.");
}
T res = data[front];
data[front] = null;
front = (front + 1) % data.length;
size --;
// 数组减容
if (size == getCapacity() / 4 && getCapacity() / 2 != 0) {
resize(getCapacity() / 2);
}
return res;
}
/**
* 获取队首元素
* @return
*/
@Override
public T getFront() {
if (isEmpty()) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Queue is Empty.");
}
return data[front];
}
/**
* 重写toString方法
* @return
*/
@Override
public String toString() {
StringBuilder resp = new StringBuilder();
resp.append(String.format("Queue: size = %d, capacity = %d, front [", size, getCapacity()));
for (int i = front; i != tail; i = (i + 1) % data.length) {
resp.append(data[i]);
if ((i + 1) % data.length != tail) {
resp.append(",");
}
}
resp.append("] tail");
return resp.toString();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
LoopQueue<Integer> arrayQueue = new LoopQueue<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
arrayQueue.enqueue(i);
System.out.println(arrayQueue);
if (i % 3 == 2) {
arrayQueue.dequeue();
System.out.println(arrayQueue);
}
}
}
}
