问题描述
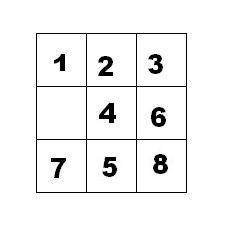
如下面第一个图的九宫格中,放着 1~8 的数字卡片,还有一个格子空着。与空格子相邻的格子中的卡片可以移动到空格中。经过若干次移动,可以形成第二个图所示的局面。
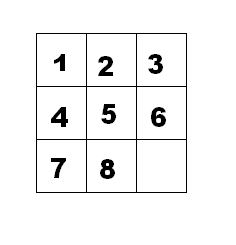
我们把第一个图的局面记为:12345678.
把第二个图的局面记为:123.46758
显然是按从上到下,从左到右的顺序记录数字,空格记为句点。
本题目的任务是已知九宫的初态和终态,求最少经过多少步的移动可以到达。如果无论多少步都无法到达,则输出-1。
我们把第一个图的局面记为:12345678.
把第二个图的局面记为:123.46758
显然是按从上到下,从左到右的顺序记录数字,空格记为句点。
本题目的任务是已知九宫的初态和终态,求最少经过多少步的移动可以到达。如果无论多少步都无法到达,则输出-1。
输入格式
输入第一行包含九宫的初态,第二行包含九宫的终态。
输出格式
输出最少的步数,如果不存在方案,则输出-1。
样例输入
12345678.
123.46758
123.46758
样例输出
3
样例输入
13524678.
46758123.
46758123.
样例输出
22
Algorithm
昨天做的是我的上一篇博客的问题,在查找方法的图中发现了这个问题用的方法也是一样的。广搜用的很少,这次算是学到了。而且还把之前我看见过的康拓展开也给用上了!
这是一个经典的八数码问题,非常适合练习广搜。这是我参考的一篇文章。
AC

1 /* 2 * BFS ? 3 */ 4 #include<iostream> 5 #include<string> 6 #include<queue> 7 #include<vector> 8 #include<cstring> 9 10 using namespace std; 11 12 // 打表 0 - 9 的阶乘 13 int fac[] = {1, 1, 2, 6, 24, 120, 720, 5040, 40320, 362880}; 14 /*-------------------------------------*/ 15 typedef int state[9]; 16 // 据说 STL 的队列不行, 所以手打队列 17 state q[362880]; // 队列扩展不超过 9! 18 state a, b; // 初始状态与最终状态 19 bool sure[362880]; // 判重 20 int step[362880]; // 步数 21 22 /*-------------------------------------*/ 23 // 康拓展开 24 int cantor(int *a, int n) 25 { 26 int ret = 0, num = 0; 27 for(int i=0;i<n-1;i++){ 28 for(int j=i+1;j<n;j++){ 29 if(a[j] < a[i]) num++; 30 } 31 ret += num*fac[n-1-i]; 32 num = 0; 33 } 34 return ret; 35 } 36 37 // 逆康拓展开 38 void r_cantor(int x, int n) 39 { 40 vector<int> V; // 可选数 41 vector<int> ret; 42 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) 43 V.push_back(i); 44 while(--n) 45 { 46 int a = x%fac[n]; // 模 47 int b = x/fac[n]; // 商 48 x = a; 49 ret.push_back(V.at(b)); 50 V.erase(V.begin()+b); 51 } 52 ret.push_back(V.at(0)); 53 /* cout */ 54 for(int i=0;i<ret.size();i++) 55 cout<<ret.at(i)<<" "; 56 } 57 58 // 康拓展开判重 59 bool kangtuo(int *x) 60 { 61 int ret = 0, sum = 0; 62 for(int i=0;i<8;i++){ 63 for(int j=i+1;j<9;j++){ 64 if(x[j] < x[i]) sum++; 65 } 66 ret += sum*fac[8-i]; 67 sum = 0; // 最开始忘了归 0, 但是想不明白为什么过了 75% 的数据 68 } 69 if(sure[ret]) 70 return false; 71 else{ 72 sure[ret] = true; 73 return true; 74 } 75 } 76 77 /*--------------------------------------*/ 78 // 模拟四种走法 79 int go[4][2] = {{1, 0}, {-1, 0}, {0, 1}, {0, -1}}; 80 int BFS() 81 { 82 memset(sure, false, sizeof(sure)); 83 memcpy(q[0], a, sizeof(a)); // 初始状态入队 84 int front = 0; // 队头 85 int rear = 1; // 队尾 86 step[front] = 0; 87 int loc = 0; 88 state temp1, temp2; 89 while(front < rear) // 非空 90 { 91 // 取出队头元素 92 memcpy(temp1, q[front], sizeof(temp1)); 93 if(memcmp(temp1, b, sizeof(b)) == 0) 94 return step[front]; 95 // 找到 空格 的位置 96 for(loc=0;loc<9;loc++) 97 if(temp1[loc] == 0) 98 break; 99 // 计算空格二维坐标 100 int x = loc/3; 101 int y = loc%3; 102 for(int i=0;i<4;i++){ 103 int nx = x + go[i][0]; 104 int ny = y + go[i][1]; 105 if(nx < 0 || ny < 0 || nx >= 3 || ny >= 3) // 越界 ? 106 continue; 107 int loc_0 = nx*3 + ny; // 计算移动后的空格数组坐标 108 memcpy(temp2, temp1, sizeof(temp1)); 109 // 移动 110 temp2[loc] = temp2[loc_0]; 111 temp2[loc_0] = 0; 112 if(kangtuo(temp2)){ 113 memcpy(q[rear], temp2, sizeof(temp2)); 114 step[rear] = step[front]+1; 115 rear++; 116 } 117 } 118 front++; 119 } 120 121 return -1; 122 } 123 /*--------------------------------------*/ 124 125 int main() 126 { 127 string s1, s2; 128 cin>>s1>>s2; 129 for(int i=0;i<9;i++){ 130 if(s1.at(i) != '.') a[i] = int(s1.at(i) - '0'); 131 else a[i] = 0; 132 } 133 for(int i=0;i<9;i++){ 134 if(s2.at(i) != '.') b[i] = int(s2.at(i) - '0'); 135 else b[i] = 0; 136 } 137 138 int c = BFS(); 139 140 cout<<((c == -1)?-1:c)<<endl; 141 142 return 0; 143 }
2019-02-21
10:36:27
