一.填空题
1.方法 2.堆内存 3.构造方法 4.this 5.this 6.static 7.使用类名进行访问 8.package import class 9.关键字 10.lang
二.选择题
1.D 2.B 3.D 4.AC 5.AC
三.判断题
1.√ 2.× 3.√ 4.× 5.√ 6.× 7.√
四.
1.构造方法的作用是给对象进行初始化。
特点:1.方法名与类名相同(大小写也一致)
2.没有返回值类型,连void也没有
3.没有具体的返回值return
注意事项:
1.如果我们没有给出构造方法,系统将自动给出一个无参构造方法。
2.如果我们给出了构造方法,系统将不会提供默认的无参构造方法。
可以不写return语句。
2.setXxx()方法和构造方法
3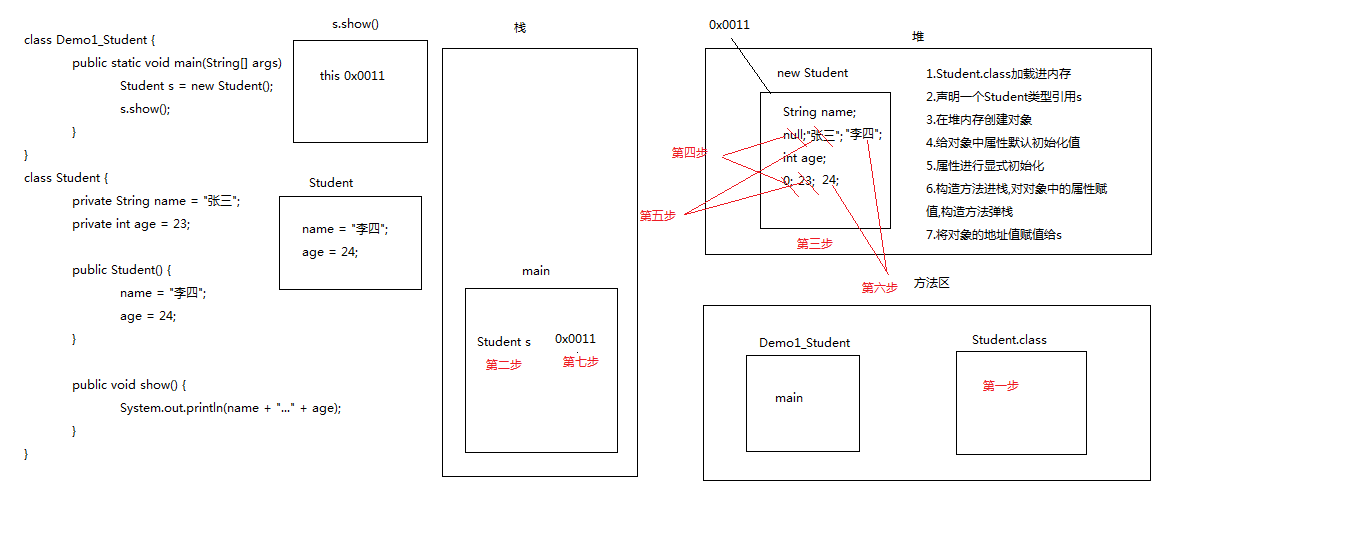
4.a. 随着类的加载而加载
b:优先于对象存在
c:被类的所有对象共享
d.可以通过类名调用
当对象出现共享数据时,该数据用static修饰。
5.public static void main(String[] args){}
public : 被jvm调用,所以权限要足够大
static : 被jvm调用,不需要创建对象,直接类名.调用即可
void : 被jvm调用,不需要有任何的返回值
main : 只有这样写才能被jvm识别,main不是关键字
String[] args : 以前是用来接收键盘录入的
class Test13_Vehicle { public static void main(String[] args) { Vehicle a = new Vehicle(); a.setSpeed(10); a.setSize(10); System.out.println(a.speedUp() + " " + a.speedDown()); } } class Vehicle { private int speed; private int size; public Vehicle(){} public Vehicle(int speed,int size){ this.speed = speed; this.size = size; } public void setSpeed(int speed){ this.speed = speed; } public int getSpeed(){ return speed; } public void setSize(int size){ this.size = size; } public int getSize(){ return size; } public int speedUp(){ return speed += 1; } public int speedDown(){ return speed -= 1; } }
class Test10_Person { public static void main(String[] args) { Person p = new Person(); p.setName("张三"); p.setAge(24); p.display(); } } class Person { private String name; private int age; public Person(){} public Person(String name,int age){ this.name = name; this.age = age; } public void setName(String name){ this.name = name; } public String getName(){ return name; } public void setAge(int age){ this.age = age; } public int getAge(){ return age; } public void display(){ System.out.println("姓名:" + name + " " + "年龄:" + age); } }
class Test11_Circle { public static void main(String[] args) { Circle c = new Circle(1.5); System.out.println(c.getArea() + " " + c.getPerimeter()); } } class Circle { private double radius; public Circle(){} public Circle(double radius){ this.radius = radius; } public void setRadius(double radius){ this.radius = radius; } public double getRadius(){ return radius; } public double getArea(){ return 3.14 * radius * radius; } public double getPerimeter(){ return 2 * 3.14 * radius; } }
class Test12_Network { public static void main(String[] args) { Network a = new Network("Mike","123456","123456"); System.out.println("用户ID:" + a.getId() + " " + "用户密码:" + a.getPassword() + " " + "用户邮箱:" + a.getEmail() + "@gameschool.com"); } } class Network { private String id; private String password; private String email; public Network(){} public Network(String id,String password,String email){ this.id = id; this.password = password; this.email = email; } public void setId(String id){ this.id = id; } public String getId(){ return id; } public void setPassword(String password){ this.password = password; } public String getPassword(){ return password; } public void setEmail(String Email){ this.email = email; } public String getEmail(){ return email; } }
class Test14_Calculaion { public static void main(String[] args) { Calculaion n = new Calculaion(10); System.out.println(n.add() + " " + n.sub() + " " + n.times() + " " + n.div()); } } class Calculaion { private int num; public Calculaion(){} public Calculaion(int num){ this.num = num; } public void setNum(int num){ this.num = num; } public int getNum(){ return num; } public int add(){ return num += 2; } public int sub(){ return num -= 2; } public int times(){ return num *= 2; } public int div(){ return num /= 2; } }
class Test15_Draw { public static void main(String[] args) { Draw p = new Draw(10,3); p.drawTrian(); p.drawRec(); p.drawPra(); } } class Draw { private int count; private int lines; public Draw(){} public Draw(int count,int lines){ this.count = count; this.lines = lines; } public void setCount(){ this.count = count; } public int getCount(){ return count; } public void setLines(){ this.lines = lines; } public int getLines(){ return lines; } public void drawTrian(){ int m = 0; a:for (int i = 0;i < lines ;i++ ) { for (int k = 0;k < lines - i ;k++ ) { System.out.print(" "); } for (int j = 1;j <= 2 * i - 1 ;j++ ) { System.out.print("*"); m++; if (m == count) { break a; } } System.out.println(); } } public void drawRec(){ int row = count / lines; int m = 0; a:for (int i = 0;i < lines ;i++ ) { for (int j = 0;j <= row ;j++ ) { System.out.print("*"); m++; if (m == count) { break a; } } System.out.println(); } } public void drawPra(){ int row = count / lines; int m = 0; a:for (int i = 0;i < lines ;i++ ) { for (int j = 1;j < i ;j++ ) { System.out.print(" "); } for (int k = 0;k <= row;k++ ) { System.out.print("*"); m++; if (m == count) { break a; } } System.out.println(); } } }
class Test16_Fridge { public static void main(String[] args) { Fridge f = new Fridge(); f.setBrand("海尔"); f.setHorsepower("100匹"); f.setTemperature("零下5℃"); f.heat(); f.refrigeration(); f.ventilate(); } } class Fridge { private String brand; private String horsepower; private String temperature; public Fridge(){} public Fridge(String brand,String horsepower,String temperature){ this.brand = brand; this.horsepower = horsepower; this.temperature = temperature; } public void setBrand(String brand){ this.brand = brand; } public String getBrand(){ return brand; } public void setHorsepower(String horsepower){ this.horsepower = horsepower; } public String getHorsepower(){ return horsepower; } public void setTemperature(String temperature){ this.temperature = temperature; } public String getTemperature(){ return temperature; } public void heat(){ System.out.println("加热"); } public void refrigeration(){ System.out.println("制冷"); } public void ventilate(){ System.out.println("通风"); } }