1. MyBatis的工作流程
(1)传统工作模式
拿到sqlsession之后直接去执行,直接根据传进来的getUserByName去拿UserMapper.xml中mapper标签中的select标签中的id为getUserByName的sql语句去执行。而不需要去编写UserMapper这个接口。
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream("mybatis-config.xml");
SqlSessionFactory factory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
SqlSession sqlSession = factory.openSession();
List<User> list = sqlSession.selectList("com.demo.mapper.UserMapper.getUserByName");
(2)面向接口编程
在面向接口编程中,MyBatis通过接口调用mapper配置文件的SQL语句。
InputStream in = Resources.getResourceAsStream("SqlMapConfig.xml"); //读取配置文件,InputStream表示一个字节输入流
SqlSessionFactory factory = new SqlSessionFactoryBUilder().build(in); //使用构建者创建工厂对象
SqlSession sqlSession = factory.openSession();
UserMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);//拿到mapper接口的代理对象
List<User> users = mapper.getAllUsers();
User user = mapper.getUserById(1001);
2. 原理分析
(1)SqlSessionFactoryBuilder类
public SqlSessionFactory build(InputStream inputStream) {
return this.build((InputStream)inputStream, (String)null, (Properties)null);//调用下面这个重载的build方法。
}
public SqlSessionFactory build(InputStream inputStream, String environment, Properties properties) {
SqlSessionFactory var5;
try {
//XMLConfigBuilder是用来解析mybatis配置文件的类
XMLConfigBuilder parser = new XMLConfigBuilder(inputStream, environment, properties);
var5 = this.build(parser.parse()); //parser.parse()的返回值对象是一个Configuration对象,然后把这个Configuration对象作为下面这个重载的build方法的参数,
} catch (Exception var14) {
...
} finally {
...
}
return var5;
}
public SqlSessionFactory build(Configuration config) {
return new DefaultSqlSessionFactory(config);
}
也就是说,初始化配置文件的本质就是把xml文件中的配置信息封装到Configuration对象中去。
而同样可以自己创建一个配置类,把这些信息放在配置类里面,就不需要xml配置文件了,可以达到同样的效果。
(2)获得sqlsession
//获得sqlsession——factory.openSession();
//DefaultSqlSessionFactory类,是SqlSessionFactory接口的实现类
//openSessionFromDataSource的三个参数,
//getDefaultExecutorType()传递的是SimpleExecutor,第二个参数表示事务隔离级别,第三个参数表示是否自动提交
public SqlSession openSession() {
return this.openSessionFromDataSource(this.configuration.getDefaultExecutorType(), (TransactionIsolationLevel)null, false);
}
private SqlSession openSessionFromDataSource(ExecutorType execType, TransactionIsolationLevel level, boolean autoCommit) {
Transaction tx = null;
DefaultSqlSession var8;
try {
Environment environment = this.configuration.getEnvironment();
TransactionFactory transactionFactory = this.getTransactionFactoryFromEnvironment(environment);
tx = transactionFactory.newTransaction(environment.getDataSource(), level, autoCommit);
//根据参数创建指定类型的Executor
Executor executor = this.configuration.newExecutor(tx, execType);
//返回的是DefaultSqlSession
var8 = new DefaultSqlSession(this.configuration, executor, autoCommit);
} catch (Exception var12) {
this.closeTransaction(tx);
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error opening session. Cause: " + var12, var12);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
return var8;
}
(3)SqlSession接口的实现类DefaultSqlSession
SqlSession是mybatis中与数据库交互的顶层类,通常与ThreadLocal绑定,一个会话使用一个SqlSession,使用完毕之后要close。SqlSession接口有一个实现类:DefaultSqlSession
DefaultSqlSession里面有两个重要的参数:
private final Configuration configuration; //封装了配置文件的配置类 private final Executor executor; //执行器
(1)传统工作模式
//执行sqlsession中的api,进入DefaultSqlSession类中的selectList方法
public <E> List<E> selectList(String statement) {
return this.selectList(statement, null);
}
public <E> List<E> selectList(String statement, Object parameter) {
return this.selectList(statement, parameter, RowBounds.DEFAULT);
}
public <E> List<E> selectList(String statement, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds) {
try {
//根据传入的全限定名+方法名从映射的Map中取出MappedStatement对象
MappedStatement ms = configuration.getMappedStatement(statement);
//调用Executor中的方法处理
return executor.query(ms, wrapCollection(parameter), rowBounds, Executor.NO_RESULT_HANDLER);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error querying database. Cause: " + e, e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
//MappedStatement与Mapper配置文件中的一个select/update/insert/delete节点相对应。mapper中配置的标签都被封装到了此对象中,主要用途是描述一条SQL语句。
//mappedStatements 是一个HashMap,存储时key = 全限定类名 + 方法名,value = 对应的MappedStatement对象(SQL语句)。
//然后执行executor.query(ms...)将查询的结果返回
面向接口编程:
sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class)
//DefaultSqlSession中的getMapper
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type) {
return this.configuration.<T>getMapper(type, this); //会调用Configuration类中的getMapper
}
//configuration中的getMapper
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type, SqlSession sqlSession) {
return this.mapperRegistry.getMapper(type, sqlSession); //会调用MapperRegistry类中的getMapper
}
//MapperRegistry中的getMapper
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type, SqlSession sqlSession) {
//从MapperRegistry中的HashMap中拿MapperProxyFactory
final MapperProxyFactory<T> mapperProxyFactory = (MapperProxyFactory<T>) knownMappers.get(type);
if (mapperProxyFactory == null) {
throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is not known to the MapperRegistry.");
}
try {
// 通过动态代理工厂生成示例。
return mapperProxyFactory.newInstance(sqlSession);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BindingException("Error getting mapper instance. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
//MapperProxyFactory类中的newInstance方法
public T newInstance(SqlSession sqlSession) {
// 创建了JDK动态代理的Handler类
final MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy = new MapperProxy<>(sqlSession, mapperInterface, methodCache);
// 调用了重载方法
return newInstance(mapperProxy);
}
重要!!!!!!!!!
//MapperProxy类,实现了InvocationHandler接口
public class MapperProxy<T> implements InvocationHandler, Serializable {
//省略部分源码
private final SqlSession sqlSession;
private final Class<T> mapperInterface;
private final Map<Method, MapperMethod> methodCache;
// 构造,传入了SqlSession,说明每个session中的代理对象的不同的!
public MapperProxy(SqlSession sqlSession, Class<T> mapperInterface, Map<Method, MapperMethod> methodCache) {
this.sqlSession = sqlSession;
this.mapperInterface = mapperInterface;
this.methodCache = methodCache;
}
//省略部分源码
}
//重载的方法,由动态代理创建新示例返回。
protected T newInstance(MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy) {
return (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(mapperInterface.getClassLoader(), new Class[] { mapperInterface }, mapperProxy);
}
//invoke
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
try {
//判断调用是是不是Object中定义的方法,toString,hashCode这类非。是的话直接放行。
if (Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
return method.invoke(this, args);
}
if (this.isDefaultMethod(method)) {
return this.invokeDefaultMethod(proxy, method, args);
}
} catch (Throwable var5) {
throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(var5);
}
//即拦截这个方法进行增强。
MapperMethod mapperMethod = this.cachedMapperMethod(method);
// 重点在这:MapperMethod最终调用了执行的方法
return mapperMethod.execute(this.sqlSession, args);
}
3. 自定义Mybatis
把pom文件中的mybatis依赖去掉,然后自己编写类实现之前的功能。
(1)已有的东西
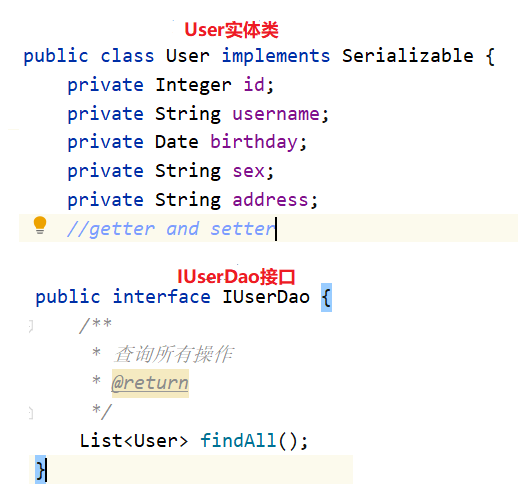
(1)User实体类,IUserDao接口。
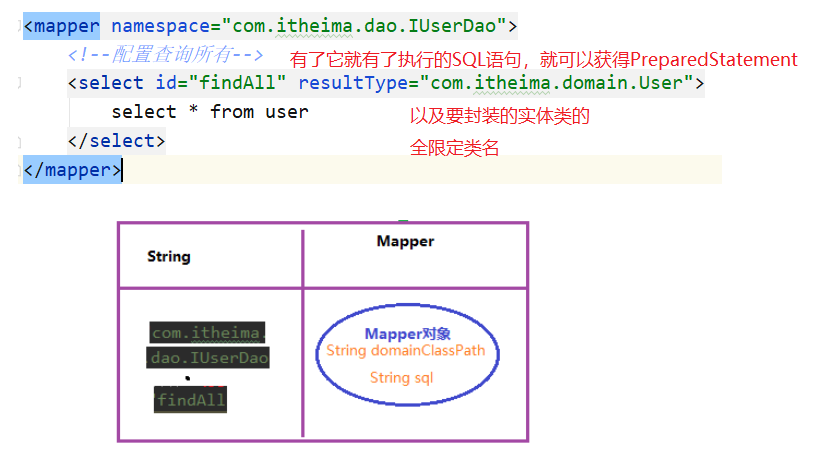
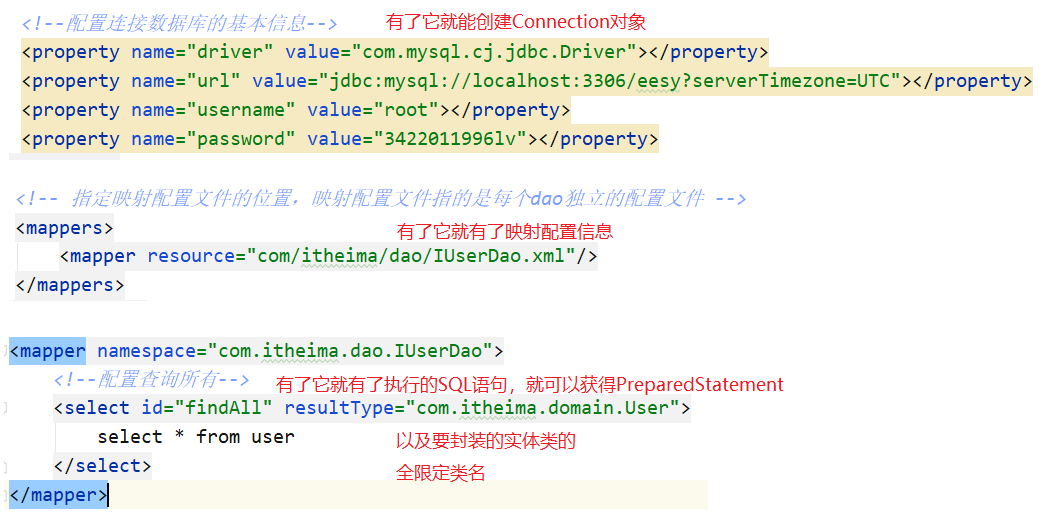
(2)配置文件
可以拿到连接数据库的四个基本信息(可以拿到Connection对象),<mappers>标签下的映射配置信息
映射配置信息<mapper>:可以拿到接口的全限定类名(namespace),以及要执行的sql语句,封装的实体类的全限定类名。
(2)分析流程
(1)selectList()方法伪代码

读取配置文件:可以用到dom4j解析XML文件。
(2)要让上面的selectList方法执行,我们需要提供两个信息
-
-
映射信息
-
执行的SQL语句
-
那么mapper对象应该怎么拿到(即怎么getMapper...),我们应该想到通过方法名来获取mapper。这里要用到一个Hashmap。
(3)谁来调用selectList()方法
在使用SqlSession创建Dao接口的代理对象的时候。有
IUserDao userDao = session.getMapper(IUserDao.class);
这里根据dao接口的字节码来创建dao接口的代理对象。要用到Proxy.newProxyInstance()来创建代理对象,其中第三个参数为InvocationHandler接口的实现类的实例,表示如何代理,通常就是增强的方法,那么在这个增强的方法里面我们去调用selectList()方法,即查询所有的功能。然后把list返回给dao接口的代理对象,我们最后直接就用代理对象userDao去调用findAll()方法。
(3)代码实现
class Resource{} class SqlSessionFactoryBuider{} interface SqlSessionFactory{} 实现类-> DefaultSqlSessionFactory interface SqlSession{} 实现类-> DefaultSqlSession
(1)Resource
/*使用类加载器读取配置文件的类*/ public class Resources { //根据传入的参数,返回一个字节输入流 public static InputStream getResourceAsStream(String filePath){ return Resources.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream(filePath); } }
(2)SqlSessionFactoryBuider
/*用于创建一个SqlSessionFactory对象*/ public class SqlSessionFactoryBuilder { /** * 根据参数的输入流来构建一个SqlSessionFactory */ public SqlSessionFactory build(InputStream config){ Configuration cfg = XMLConfigBuilder.loadConfiguration(config); return new DefaultSqlSessionFactory(cfg); } }
(3)SqlSessionFactory
public interface SqlSessionFactory { /*用于打开一个新的sqlsession对象*/ SqlSession openSession(); }
(4)SqlSession
public interface SqlSession { /** * 根据接口的字节码创建一个代理对象 */ <T> T getMapper(Class<T> daoInterfaceClass); /*释放资源*/ void close(); }
(5)XMLConfigBuilder:是一个解析配置文件的类。把配置文件中的一些信息拿出来封装到我们自定义的Configuration类里面去。
public class XMLConfigBuilder { /** * 解析主配置文件,把里面的内容填充到DefaultSqlSession所需要的地方 * 使用的技术: * dom4j+xpath */ public static Configuration loadConfiguration(InputStream config){ try{ //定义封装连接信息的配置对象(mybatis的配置对象) Configuration cfg = new Configuration(); //1.获取SAXReader对象 SAXReader reader = new SAXReader(); //2.根据字节输入流获取Document对象 Document document = reader.read(config); //3.获取根节点 Element root = document.getRootElement(); //4.使用xpath中选择指定节点的方式,获取所有property节点 List<Element> propertyElements = root.selectNodes("//property"); //5.遍历节点 for(Element propertyElement : propertyElements){ //判断节点是连接数据库的哪部分信息 //取出name属性的值 String name = propertyElement.attributeValue("name"); if("driver".equals(name)){ //表示驱动 //获取property标签value属性的值 String driver = propertyElement.attributeValue("value"); cfg.setDriver(driver); } if("url".equals(name)){ //表示连接字符串 //获取property标签value属性的值 String url = propertyElement.attributeValue("value"); cfg.setUrl(url); } if("username".equals(name)){ //表示用户名 //获取property标签value属性的值 String username = propertyElement.attributeValue("value"); cfg.setUsername(username); } if("password".equals(name)){ //表示密码 //获取property标签value属性的值 String password = propertyElement.attributeValue("value"); cfg.setPassword(password); } } //取出mappers中的所有mapper标签,判断他们使用了resource还是class属性 List<Element> mapperElements = root.selectNodes("//mappers/mapper"); //遍历集合 for(Element mapperElement : mapperElements){ //判断mapperElement使用的是哪个属性 Attribute attribute = mapperElement.attribute("resource"); if(attribute != null){ System.out.println("使用的是XML"); //表示有resource属性,用的是XML //取出属性的值 String mapperPath = attribute.getValue();//获取属性的值"com/itheima/dao/IUserDao.xml" //把映射配置文件的内容获取出来,封装成一个map Map<String, Mapper> mappers = loadMapperConfiguration(mapperPath); //给configuration中的mappers赋值 cfg.setMappers(mappers); }else{ /* System.out.println("使用的是注解"); //表示没有resource属性,用的是注解 //获取class属性的值 String daoClassPath = mapperElement.attributeValue("class"); //根据daoClassPath获取封装的必要信息 Map<String,Mapper> mappers = loadMapperAnnotation(daoClassPath); //给configuration中的mappers赋值 cfg.setMappers(mappers);*/ } } //返回Configuration return cfg; }catch(Exception e){ throw new RuntimeException(e); }finally{ try { config.close(); }catch(Exception e){ e.printStackTrace(); } } } /** * 根据传入的参数,解析XML,并且封装到Map中 * @param mapperPath 映射配置文件的位置 * @return map中包含了获取的唯一标识(key是由dao的全限定类名和方法名组成) * 以及执行所需的必要信息(value是一个Mapper对象,里面存放的是执行的SQL语句和要封装的实体类全限定类名) */ private static Map<String,Mapper> loadMapperConfiguration(String mapperPath)throws IOException { InputStream in = null; try{ //定义返回值对象 Map<String,Mapper> mappers = new HashMap<String,Mapper>(); //1.根据路径获取字节输入流 in = Resources.getResourceAsStream(mapperPath); //2.根据字节输入流获取Document对象 SAXReader reader = new SAXReader(); Document document = reader.read(in); //3.获取根节点 Element root = document.getRootElement(); //4.获取根节点的namespace属性取值 String namespace = root.attributeValue("namespace");//是组成map中key的部分 //5.获取所有的select节点 List<Element> selectElements = root.selectNodes("//select"); //6.遍历select节点集合 for(Element selectElement : selectElements){ //取出id属性的值 组成map中key的部分 String id = selectElement.attributeValue("id"); //取出resultType属性的值 组成map中value的部分 String resultType = selectElement.attributeValue("resultType"); //取出文本内容 组成map中value的部分 String queryString = selectElement.getText(); //创建Key String key = namespace+"."+id; //创建Value Mapper mapper = new Mapper(); mapper.setQueryString(queryString); mapper.setResultType(resultType); //把key和value存入mappers中 mappers.put(key,mapper); } return mappers; }catch(Exception e){ throw new RuntimeException(e); }finally{ in.close(); } } /** * 根据传入的参数,得到dao中所有被select注解标注的方法。 * 根据方法名称和类名,以及方法上注解value属性的值,组成Mapper的必要信息 * @param daoClassPath * @return */ /*private static Map<String,Mapper> loadMapperAnnotation(String daoClassPath)throws Exception{ //定义返回值对象 Map<String,Mapper> mappers = new HashMap<String, Mapper>(); //1.得到dao接口的字节码对象 Class daoClass = Class.forName(daoClassPath); //2.得到dao接口中的方法数组 Method[] methods = daoClass.getMethods(); //3.遍历Method数组 for(Method method : methods){ //取出每一个方法,判断是否有select注解 boolean isAnnotated = method.isAnnotationPresent(Select.class); if(isAnnotated){ //创建Mapper对象 Mapper mapper = new Mapper(); //取出注解的value属性值 Select selectAnno = method.getAnnotation(Select.class); String queryString = selectAnno.value(); mapper.setQueryString(queryString); //获取当前方法的返回值,还要求必须带有泛型信息 Type type = method.getGenericReturnType();//List<User> //判断type是不是参数化的类型 if(type instanceof ParameterizedType){ //强转 ParameterizedType ptype = (ParameterizedType)type; //得到参数化类型中的实际类型参数 Type[] types = ptype.getActualTypeArguments(); //取出第一个 Class domainClass = (Class)types[0]; //获取domainClass的类名 String resultType = domainClass.getName(); //给Mapper赋值 mapper.setResultType(resultType); } //组装key的信息 //获取方法的名称 String methodName = method.getName(); String className = method.getDeclaringClass().getName(); String key = className+"."+methodName; //给map赋值 mappers.put(key,mapper); } } return mappers; }*/ }
(6)Configuration配置类。要在里面定义一个hashMap,key为String(Dao接口的包名 + 要执行的方法名),value为Mapper对象。Mapper对象有两个属性,sql语句和实体类的全限定类名。
/*自定义mybatis的配置类*/ public class Configuration { private String driver; private String url; private String username; private String password; private Map<String, Mapper> mappers = new HashMap<>(); public void setMappers(Map<String, Mapper> mappers) { this.mappers.putAll(mappers);/*把后面的内容都追加上,而不是覆盖掉*/ } //setters and getters } /*用于封装执行的SQL语句和结果类型的全限定类名*/ public class Mapper { private String queryString; //SQL语句 private String resultType; //实体类的全限定类名 //setters and getters }
(7)DefaultSqlSessionFactory
/*SqlSessionFactory接口的实现类*/ public class DefaultSqlSessionFactory implements SqlSessionFactory { Configuration cfg; public DefaultSqlSessionFactory(Configuration cfg){ this.cfg = cfg; } //省略抛出异常 @Override public SqlSession openSession() { return new DefaultSqlSession(cfg); } }
(8)DefaultSqlSession:最重要的一个SqlSession接口的实现类
public class DefaultSqlSession implements SqlSession { private Configuration cfg; private Connection conn; public DefaultSqlSession(Configuration cfg) throws SQLException, ClassNotFoundException { this.cfg = cfg; this.conn = DataSourceUtil.getConnection(cfg); } /*用于创建代理对象*/ @Override public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> daoInterfaceClass) { return (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(daoInterfaceClass.getClassLoader(), new Class[]{daoInterfaceClass}, new MapperProxy(cfg.getMappers(), conn)); //MapperProxy:如何代理,如何增强(传进去的参数为mappers,连接对象connection,根据代理对象使用不同的方法时,可以getMappers到不同的Mapper对象(sql语句以及要封装的实体类的全限定类名))。然后在invoke方法里面去调用Executor().selectList(mapper, conn);(Executor()为执行器,根据sql语句的不同类型来选择不同的执行器。)来执行sql语句并且把结果封装到实体类里面 } @Override public void close() { conn.close(); } }
(9)DataSourceUtil
/*用于创建数据源的工具类*/ public class DataSourceUtil { public static Connection getConnection(Configuration cfg) throws SQLException, ClassNotFoundException { Class.forName(cfg.getDriver()); return DriverManager.getConnection(cfg.getUrl(), cfg.getUsername(), cfg.getPassword()); } }
(10)MapperProxy表示如何去代理,增强的方法
public class MapperProxy implements InvocationHandler { //key是全限定类名加方法名 private Map<String, Mapper> mappers; private Connection conn; public MapperProxy(Map<String, Mapper> mappers, Connection conn){ //有了连接对象,有了mappers this.mappers = mappers; this.conn = conn; } /** * 用于对方法进行增强 */ @Override public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable { //1.获取方法名 String methodName = method.getName(); //2.获取方法所在类的名称 String className = method.getDeclaringClass().getName(); //一般是获得接口里面的接口全路径名称 //3.组合key String key = className + "." + methodName; //4. 获取mappers中的mapper对象 Mapper mapper = mappers.get(key); //5.判断是否有mapper if(mapper == null){ throw new IllegalArgumentException("传入参数有误!"); } //6.执行工具类执行查询所有 return new Executor().selectList(mapper, conn); } }
(11)Executor类:负责执行SQL语句,并且封装结果集
public class Executor { public <E> List<E> selectList(Mapper mapper, Connection conn) { PreparedStatement pstm = null; ResultSet rs = null; try { //1.取出mapper中的数据 String queryString = mapper.getQueryString();//select * from user String resultType = mapper.getResultType();//com.itheima.domain.User Class domainClass = Class.forName(resultType); //2.获取PreparedStatement对象 pstm = conn.prepareStatement(queryString); //3.执行SQL语句,获取结果集 rs = pstm.executeQuery(); //4.封装结果集 List<E> list = new ArrayList<E>();//定义返回值 while(rs.next()) { //实例化要封装的实体类对象 E obj = (E)domainClass.newInstance(); //取出结果集的元信息:ResultSetMetaData ResultSetMetaData rsmd = rs.getMetaData(); //取出总列数 int columnCount = rsmd.getColumnCount(); //遍历总列数 for (int i = 1; i <= columnCount; i++) { //获取每列的名称,列名的序号是从1开始的 String columnName = rsmd.getColumnName(i); //根据得到列名,获取每列的值 Object columnValue = rs.getObject(columnName); //给obj赋值:使用Java内省机制(借助PropertyDescriptor实现属性的封装) PropertyDescriptor pd = new PropertyDescriptor(columnName,domainClass);//要求:实体类的属性和数据库表的列名保持一致 //获取它的写入方法 Method writeMethod = pd.getWriteMethod(); //把获取的列的值,给对象赋值 writeMethod.invoke(obj,columnValue); //使用反射的方式给实体类里面的属性赋值,即setters } //把赋好值的对象加入到集合中 list.add(obj); } return list; } catch (Exception e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } finally { release(pstm,rs); } } private void release(PreparedStatement pstm,ResultSet rs){ if(rs != null){ try { rs.close(); }catch(Exception e){ e.printStackTrace(); } } if(pstm != null){ try { pstm.close(); }catch(Exception e){ e.printStackTrace(); } } } }
(12)总结
UserMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class); List<User> users = mapper.findAll();
通过sqlsession拿到UserMapper的代理对象。
getMapper方法:具体在DefaultSqlSession类中实现。返回的是Proxy.newProxyInstance(UserMapper.class.getClassLoader(), new Class[]{UserMapper.class}, new MapperProxy(cfg.getMappers(), conn));
第三个参数表示如何代理,就是增强的方法,继承了InvocationHandler接口。
MapperProxy类里面的构造方法传入了两个参数,第一个是mappers,即一个HashMap,key是String,value是Mapper对象,Mapper对象是封装了sql语句以及要封装的实体类类名。
那么MapperProxy类里面要去重写一个invoke方法。表示通过代理对象去调用一个方法method的时候,实际上都是去调用这个invoke方法。
那么在invoke方法里面可以拿到这个method的类名加方法名method.getDeclaringClass().getName() + "."+method.getName(),这个字符串作为key去mappers这个map里面查询到Mapper对象mapper。根据mapper和conn就可以调用工具类执行查询,Executor().selectList(mapper, conn);执行查询的返回值为object,通过invoke方法返回,即返回给代理对象调用method的返回值。