一.选择控制
多重if结构:


1 package operator; 2 3 import java.util.Scanner; 4 5 public class Luoji { 6 7 public static void main(String[] args) { 8 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 9 System.out.println("请输入成绩:"); 10 Scanner s =new Scanner(System.in); 11 int score=s.nextInt(); 12 if(score>=90) 13 System.out.println("优秀"); 14 else if(score>=80) 15 System.out.println("良好"); 16 else if(score>=60) 17 System.out.println("及格"); 18 else 19 System.out.println("不及格"); 20 } 21 22 }
嵌套if结构:成对if else,从内部先匹配


1 package operator; 2 3 import java.util.Scanner; 4 5 public class Luoji { 6 7 public static void main(String[] args) { 8 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 9 int x=10,y=5; 10 if(x!=y){ 11 if(x>y){ 12 System.out.println("x大于y");} 13 14 else{ 15 System.out.println("x小于y");} 16 } 17 else{ 18 System.out.println("x和y相等"); 19 } 20 } 21 22 }
switch结构:


Python中无switch结构

switch例:

1 package operator; 2 3 import java.util.Scanner; 4 5 public class Luoji { 6 7 public static void main(String[] args) { 8 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 9 System.out.println("请输入1~7:"); 10 Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in); 11 int n=sc.nextInt(); 12 switch(n){ 13 case 1:System.out.print("星期一");break; 14 case 2:System.out.print("星期二");break; 15 case 3:System.out.print("星期三");break; 16 case 4:System.out.print("星期四");break; 17 case 5:System.out.print("星期五");break; 18 case 6:System.out.print("星期六");break; 19 case 7:System.out.print("星期天");break; 20 default: 21 System.out.print("输入非法");break; 22 } 23 } 24 }
二.循环控制
1.while:

注意:为避免死循环,小括号后面不要加分号(;),如while(xxx);
while例:

1 package operator; 2 3 public class WhileTest { 4 5 public static void main(String[] args) { 6 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 7 int n=1; 8 while(n<5){ 9 System.out.println(n); 10 n++; 11 } 12 } 13 14 }
while求100以内奇数和:

1 package operator; 2 3 public class WhileTest { 4 5 public static void main(String[] args) { 6 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 7 int n=1; 8 int sum=0; 9 while(n<=100){ 10 sum+=n; 11 n+=2; 12 } 13 System.out.println("100以内中的奇数和为:"+sum); 14 } 15 16 }
while输出26个英文字母:

1 package com.imooc.Ha; 2 3 public class CharDemo { 4 5 public static void main(String[] args) { 6 //输出26个英文字母,分两行输出 7 char ch='a'; 8 int count=0; 9 while(ch<='z'){ 10 System.out.print(ch+" "); 11 count++; 12 ch++; 13 if (count%13==0){ 14 System.out.println(); 15 } 16 } 17 18 } 19 20 }
2.do while:(Pyhton中无)


do while例:求1~5和

1 package com.imooc.Ha; 2 3 public class DoWhile { 4 5 public static void main(String[] args) { 6 int n=1,sum=0; 7 do{ 8 sum+=n; 9 n++; 10 }while(n<=5); 11 System.out.println(sum); 12 13 } 14 15 }
do while:猜数字

1 package com.imooc.Ha; 2 3 import java.util.Scanner; 4 5 public class DoWhile { 6 7 public static void main(String[] args) { 8 //用随机数生成0-10的整数,Math.random()表示[0,1) 9 int number=(int)(Math.random()*10+1); 10 int guss; 11 System.out.print("猜一个0—10的数字!"); 12 do{ 13 Scanner s=new Scanner(System.in); 14 guss=s.nextInt(); 15 if(guss>number){ 16 System.out.println("输入的数字太大了"); 17 } 18 else{ 19 System.out.println("输入的数字太小了"); 20 } 21 }while(guss!=number); 22 System.out.println("哈哈,你猜对了"); 23 } 24 25 }
3.for循环:(Python3中for i in range(10))

三个表达式都可以缺失
for例:

1 package com.imooc.Ha; 2 3 public class ForDemo { 4 public static void main(String[] args){ 5 //局部变量只在定义它的{}中有效,如n 6 int sum=0; 7 for(int n=1;n<=5;n++){ 8 sum+=n; 9 } 10 System.out.println(sum); 11 } 12 13 }
for求阶乘:(数字太大可以用长整型存取(还不行可以用类))

1 package com.imooc.Ha; 2 3 public class ForDemo2 { 4 5 public static void main(String[] args) { 6 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 7 int sum=0; 8 int _sum=1; 9 for(int i=1;i<=100;i++){ 10 for(int j=1;j<=i;j++){ 11 _sum*=j; 12 } 13 sum+=_sum; 14 } 15 System.out.println("1!+2!+3!...+100!="+sum); 16 } 17 18 }
while输出*例:

1 package com.imooc.Ha; 2 3 public class WhileDemo { 4 5 public static void main(String[] args) { 6 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 7 int m=1,n=1; 8 System.out.println("输出4行4列*"); 9 while(m<=4){ 10 n=1; 11 while(n<=m){ 12 System.out.print("*"); 13 n++; 14 } 15 System.out.println(); 16 m++; 17 } 18 19 } 20 21 }
4.break语句:

注:break语句是跳出当前循环
5.continue语句:


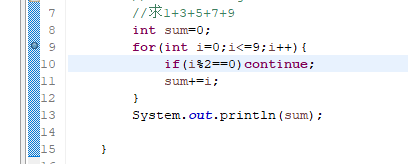
1 package com.imooc.Ha; 2 3 public class Continue_test { 4 5 public static void main(String[] args) { 6 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 7 //求1+3+5+7+9 8 int sum=0; 9 for(int i=0;i<=9;i++){ 10 if(i%2==0)continue; 11 sum+=i; 12 } 13 System.out.println(sum); 14 15 } 16 17 }
三.调试
1.设置断点
2.执行调试:
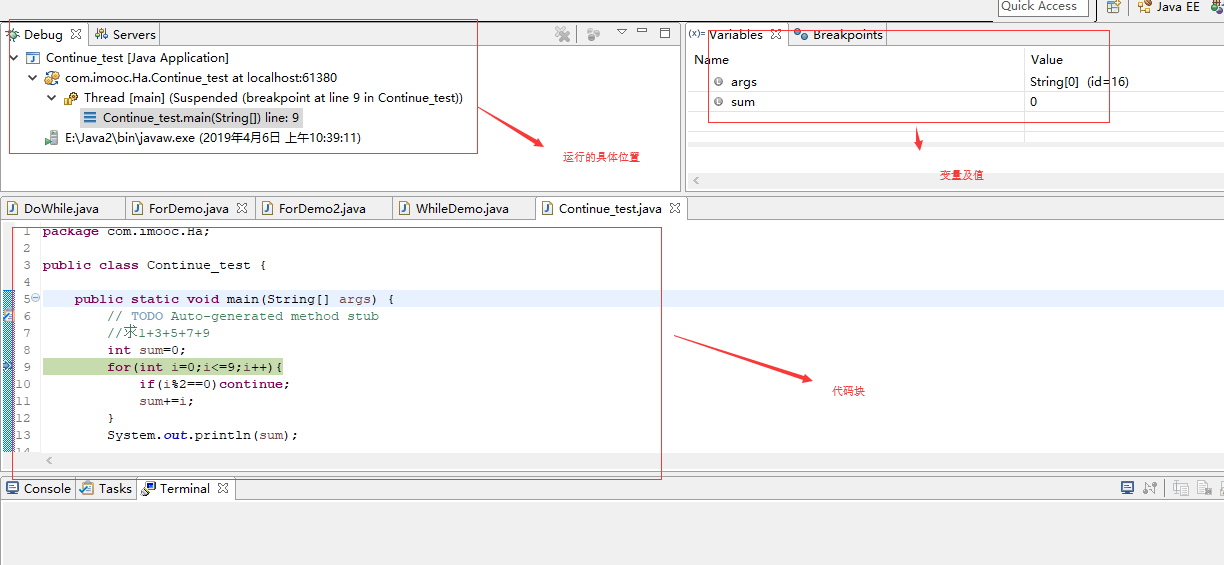
F6单步调试,F5运行到自定义方法时跳到方法执行
3.多断点调试:F8跳转到下一个断点
