注:本文系作者原创,但可随意转载。
最近做一个Web平台系统,系统包含3个角色,“管理员, 企业用户, 评审专家”, 分别有不同的功能。一直以来都是使用微软封装好的Microsoft.AspNet.Identity.dll程序集来进行身份验证和角色控制。
在MVC项目中,生成项目结构中,甚至已经包含了创建好的AccountController,可以直接使用进行账号管理。不过最近一次使用Identity功能,是在Visual Studio 2013的Preview版本中,现在升级到了RC和Ultimate版,整个程序集已经彻底翻新了。想进行角色控制,我了个擦发现Account控制器中初始化的一个控制类UserManager已经根本不包含角色控制的方法了。。。于是乎,开始上网查资料,搜索"ASP.NET Identity Role(Manager)",但发现大部分都是零几年的文章了,微软官方博客里倒是看到了相关的讲解,很详细,但尼玛是Preview版本的啊,后面有人追问正式版的也没有答复。于是懒得再找了,打开dotPeek对整个程序集进行反编译,看一下内部代码到底是如何实现角色控制的。
先看一下本文问题背景的具体情况。下面有一段代码介绍了AccountController的构造方法,其中的LCDEUser,LCDEDbContext是我定义的继承了IdentityUser和DbContext的应用程序的账号实体类和数据库上下文类,由于Identity本身是基于EntityFramework来实现的。这里就不再介绍EF,假定您对EF已经了解。Account控制器的构造方法中初始化了一个UserManager管理类,这个类可以进行创建账号,修改密码。。。等各种账号管理功能,还有一个方法叫AddToRole(..),意思是把一个账号(User)与一个角色(Role)进行关联,关键是现在根本就不存在任何角色,UserManager类也不提供创建角色的方法。

1 public class AccountController : Controller 2 { 3 public AccountController() 4 : this(new UserManager<LCDEUser>(new UserStore<LCDEUser>(new LCDEDbContext()))) 5 { 6 } 7 8 public AccountController(UserManager<LCDEUser> userManager) 9 { 10 UserManager = userManager; 11 } 12 13 public UserManager<LCDEUser> UserManager { get; private set; } 14 }
Identity功能主要由3个程序集组成。Microsoft.AspNet.Identity.Core / EntityFramework / Owin 其中Owin和第三方登陆相关,此处我暂时用不到就先不看了。
用反编译工具打开程序集后如图1。

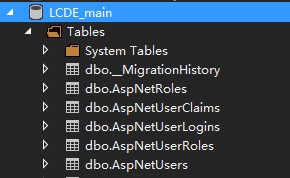
图1 图2
图2中是Identity自动生成的几张数据库表,看起来和左边程序中的几个类名一致。打开一看果然 左侧程序集中的IdentityRole, IdentityUser, IdentityUserClaim, IdentityUserLogin, IdentityUserRole分别是实体模型类,包含的属性和数据库中的表的字段一致。其中的EntityStore作为泛型类提供了几个基本操作Create,Delete,GetById。 RoleStore<T>用来操作和角色控制相关的实体数据,UserStore<T>用来操作和账号相关的实体数据,其中提供了诸多的方法,而这两个类的访问权限又是Public的,可以认为只是使用这两个类也可以进行一些数据实体的访问和存储操作。
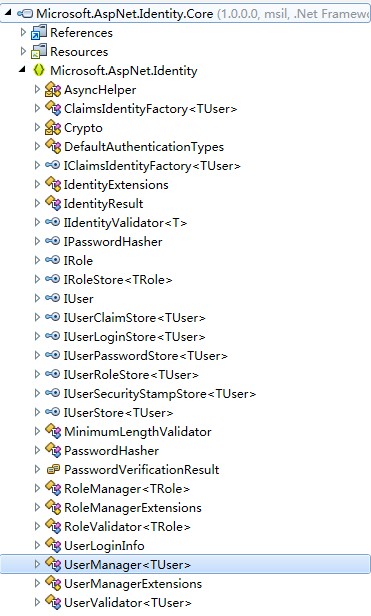 图3
图3
图3是使用反编译工具打开Core.dll后看到的内部构造。其中东西颇多不一一介绍,主要介绍一下我们要用到的。打开后发现其中有一个UserManager类,这不正是我们用来进行账号管理的类么,还有一个RoleManager类,肯定就是进行角色控制的了,可是没有相关文档,项目的初始架构中又没有帮我们初始化这个东西,而它的构造函数又有点复杂(主要是传入参数中还要new 一些RoleStore, DbContext之类的东西),不打开看看相关代码或文档,想要直接使用还是有点困难撒,主要是万一用错了折腾起来太费时间。
打开RoleManager类后看到这么一段代码:

1 public class RoleManager<TRole> : IDisposable where TRole : IRole 2 { 3 private bool _disposed; 4 private IIdentityValidator<TRole> _roleValidator; 5 6 protected IRoleStore<TRole> Store { get; private set; } 7 8 public IIdentityValidator<TRole> RoleValidator 9 { 10 get 11 { 12 return this._roleValidator; 13 } 14 set 15 { 16 if (value == null) 17 throw new ArgumentNullException("value"); 18 this._roleValidator = value; 19 } 20 } 21 22 public RoleManager(IRoleStore<TRole> store) 23 { 24 if (store == null) 25 throw new ArgumentNullException("store"); 26 this.Store = store; 27 this.RoleValidator = (IIdentityValidator<TRole>) new RoleValidator<TRole>(this); 28 } 29 }
它的构造函数需要传递一个RoleStore进去,实际上RoleManager就是提供了比RoleStore更多方法,方法名称更具可读性,更方便编程的一个类,因此不推荐直接使用RoleStore来进行数据的访问及存储。而RoleStore的构造方法需要传递一个DbContext给它,搞清楚怎么初始化它,就可以正式使用了。下面参考一段,对数据库进行初始化,建立种子数据的代码,其中包括的对UserManager和RoleManager的具体使用。

1 public class LCDEDbInitializer : DropCreateDatabaseIfModelChanges<LCDEDbContext> 2 { 3 protected override void Seed(Models.LCDEDbContext context) 4 { 5 using (var userManager = new UserManager<LCDEUser>(new UserStore<LCDEUser>(context))) 6 { 7 using (var roleManager = new RoleManager<IdentityRole>(new RoleStore<IdentityRole>(context))) 8 { 9 // 添加系统角色 10 if (!roleManager.RoleExists("admin")) 11 { 12 roleManager.Create(new IdentityRole("admin")); 13 } 14 if (!roleManager.RoleExists("expert")) 15 { 16 roleManager.Create(new IdentityRole("expert")); 17 } 18 if (!roleManager.RoleExists("enterprise")) 19 { 20 roleManager.Create(new IdentityRole("enterprise")); 21 } 22 // 创建账号 23 var user = new LCDEUser() { UserName = "admin", Name = "admin", Phone = "00000000000" }; 24 if (userManager.Create(user, "000000") != IdentityResult.Success) 25 { 26 throw new Exception("初始化系统管理员账号失败"); 27 } 28 var expert = new LCDEUser() { UserName = "expert", Name = "专家", Phone = "15888888888" }; 29 if (userManager.Create(expert, "000000") != IdentityResult.Success) 30 { 31 throw new Exception("初始化专家账号失败"); 32 } 33 var enterprise = new LCDEUser() { UserName = "enterprise", Name = "XXXXXXXX科技有限公司", Phone = "15888888888" }; 34 if (userManager.Create(enterprise, "000000") != IdentityResult.Success) 35 { 36 throw new Exception("初始化企业账号失败"); 37 } 38 // 为账号分配角色 39 userManager.AddToRole(user.Id, "admin"); 40 userManager.AddToRole(expert.Id, "expert"); 41 userManager.AddToRole(enterprise.Id, "enterprise"); 42 43 context.SaveChanges(); 44 base.Seed(context); 45 } 46 } 47 } 48 }
在使用中还有一些其他需要注意的事项,在MVC中,通常我会做一个BaseController,其中包含了dbcontext,usermanager的实例创建, 假如首先实例化一个dbcontext,再去实例化一个usermanager,由于usermanager的实例化需要传入一个dbcontext,我尝试将实例化好的dbcontext实体传入,在本机运行时,没有问题,但发布到服务器上时,会出现DataReader的使用冲突,于是在usermanager进行构造时,要传入一个new DbContext()给它。
