本文版权归 远方的风lyh和博客园共有,欢迎转载,但须保留此段声明,并给出原文链接,谢谢合作。
在网上看到一个面试题,没有完全做, 本代码基于JDK8
//下面代码运行结果是 public class Test3 { public static void main(String[] args) { Integer a = 1; Integer b = 2; Integer c = 3; Integer d = 3; Integer e = 11; Integer f = 11; Long g = 3L; Long h = 2L; Integer i =127; Integer k =128; System.out.println(c == d); System.out.println(e == f); System.out.println(c == (a + b)); System.out.println(k == (a + i)); System.out.println(c.equals(a + b)); System.out.println(g == (a + b)); System.out.println(g.equals(a + b)); System.out.println(g.equals(a + h)); Integer a1 = new Integer(1); Integer b1 = new Integer(1); System.out.println("----"+(a1==b1)); } }
先自己做一遍,看看自己能不能完全做作对
答案是如下:
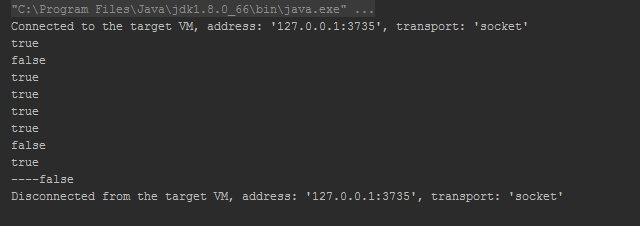
相信挺多人 都或多或少的了解到Integer 有一个 缓存池,缓存的大小是:-128 -127 之间(Long同理)
//缓存结构 private static class IntegerCache { static final int low = -128; static final int high; static final Integer cache[]; static { // high value may be configured by property int h = 127; String integerCacheHighPropValue = sun.misc.VM.getSavedProperty("java.lang.Integer.IntegerCache.high"); if (integerCacheHighPropValue != null) { try { int i = parseInt(integerCacheHighPropValue); i = Math.max(i, 127); // Maximum array size is Integer.MAX_VALUE h = Math.min(i, Integer.MAX_VALUE - (-low) -1); } catch( NumberFormatException nfe) { // If the property cannot be parsed into an int, ignore it. } } high = h; cache = new Integer[(high - low) + 1]; int j = low; for(int k = 0; k < cache.length; k++) cache[k] = new Integer(j++); // range [-128, 127] must be interned (JLS7 5.1.7) assert IntegerCache.high >= 127; } private IntegerCache() {} }
再了解一下 Integer(Long同理)内部一些代码
//Integer 值 是基本类型 int private final int value; //别急 结合后面发编译的代码看 // Integer 赋值 首先会判断 是否是 -128 -127之间(缓存池) // 若没有 超出返回 才会 new 一个对象 public static Integer valueOf(int i) { if (i >= IntegerCache.low && i <= IntegerCache.high) return IntegerCache.cache[i + (-IntegerCache.low)]; return new Integer(i); } //别急 结合后面发编译的代码看 public int intValue() { return value; } //euqals 方法 public boolean equals(Object obj) { if (obj instanceof Integer) { return value == ((Integer)obj).intValue(); } return false; }
首先 用反编译工具 打开 class文件 上下代码 结合思考一下
import java.io.PrintStream; public class Test3 { public static void main(String[] args) { Integer a = Integer.valueOf(1); Integer b = Integer.valueOf(2); Integer c = Integer.valueOf(3); Integer d = Integer.valueOf(3); Integer e = Integer.valueOf(321); Integer f = Integer.valueOf(321); Long g = Long.valueOf(3L); Long h = Long.valueOf(2L); Integer i = Integer.valueOf(127); Integer k = Integer.valueOf(128); //true c、d 取得都是缓存中的3那个对象 System.out.println(c == d); // false 看一下 Integer 中 valueOf这个方法 e、f 会分别 new 一个对象 System.out.println(e == f); /*** true 数值比较 initValue 方法 取的是 Integer 中 final变量 value的值 int a =1; int b =2; int c =3 a+b == c ***/ System.out.println(c.intValue() == a.intValue() + b.intValue()); // true 数值比较 同上 System.out.println(k.intValue() == a.intValue() + i.intValue()); //true equals比较的是数值 System.out.println(c.equals(Integer.valueOf(a.intValue() + b.intValue()))); //true 数值比较 System.out.println(g.longValue() == a.intValue() + b.intValue()); //false Long.equals()首先会判断 传入是否为Long对象 不是 Long !=Integer (a+b自动装箱的是Integer类型) System.out.println(g.equals(Integer.valueOf(a.intValue() + b.intValue()))); // true 了解一下 自动装箱 (Integer +Long) 会转为Long (注意Long也是存在 缓存的 -128 -127) System.out.println(g.equals(Long.valueOf(a.intValue() + h.longValue()))); Integer a1 = new Integer(1); Integer b1 = new Integer(1); System.out.println("----" + (a1 == b1)); //new 出来的对象 地址不同 } }