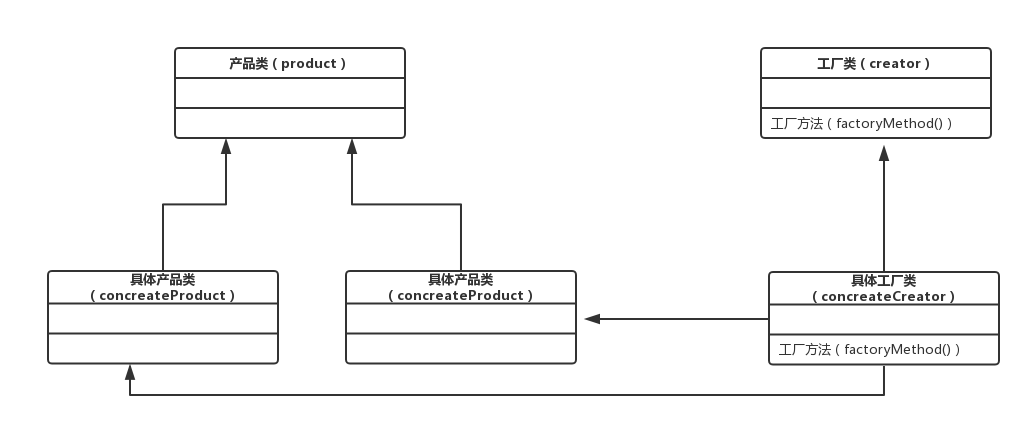
工厂方法的作用是创造对象(生成产品),用来从一组实现特定逻辑的类中实例化某个对象。(多用于日志功能)
产品类:定义了工厂方法创建的对象接口
具体产品类:实现了产品类的接口
工厂类:创建产品类,声明工厂方法,返回一个产品类对象
具体工厂类:重写用于具体产品类对象的方法
例子

1 #include<iostream> 2 #include<stdio.h> 3 using namespace std; 4 class product { 5 6 public: 7 product(); 8 ~product(); 9 public: 10 virtual void productMethod() = 0; 11 }; 12 13 class productA :public product { 14 public: 15 productA(); 16 ~productA(); 17 void productMethod(); 18 }; 19 20 class productB :public product { 21 public: 22 productB(); 23 ~productB(); 24 void productMethod(); 25 };

#include "Product.h" using namespace std; product::product() { } product::~product() { } productA::productA() { } productA::~productA() { } productB::productB() { } productB::~productB() { } void productA::productMethod() { cout << "I am product A" << endl; } void productB::productMethod() { cout << "I am product B" << endl; }

1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include<iostream> 3 #include"Product.h" 4 using namespace std; 5 class Factory { 6 public: 7 Factory(); 8 ~Factory(); 9 virtual product* createProduct(int type) = 0; 10 }; 11 12 class FactoryA :public Factory { 13 public: 14 FactoryA(); 15 ~FactoryA(); 16 product* createProduct(int type); 17 }; 18 class FactoryB :public Factory { 19 public: 20 FactoryB(); 21 ~FactoryB(); 22 product* createProduct(int type); 23 };

1 #include "Factory.h" 2 #include "Product.h" 3 using namespace std; 4 Factory::Factory() { 5 6 } 7 Factory::~Factory() { 8 9 } 10 11 FactoryA::FactoryA() { 12 13 } 14 FactoryA::~FactoryA() { 15 16 } 17 18 product* FactoryA::createProduct(int type) { 19 product* _product = NULL; 20 switch (type) 21 { 22 case 1: 23 _product = new productA(); 24 break; 25 case 2: 26 _product = new productB(); 27 break; 28 default: 29 break; 30 } 31 return _product; 32 } 33 FactoryB::FactoryB() { 34 35 } 36 FactoryB::~FactoryB() { 37 38 } 39 40 product* FactoryB::createProduct(int type) { 41 product* _product = NULL; 42 switch (type) 43 { 44 case 1: 45 _product = new productA(); 46 break; 47 case 2: 48 _product = new productB(); 49 break; 50 default: 51 break; 52 } 53 54 return _product; 55 }

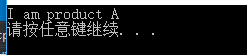
#include "Factory.h" using namespace std; int main(int agrc, char* argv[]) { Factory* factory = new FactoryA(); product* _pro = factory->createProduct(1); _pro->productMethod(); delete _pro; _pro = NULL; system("pause"); }
下面以宠物为例:

1 #include<iostream> 2 #include<stdio.h> 3 #include<string> 4 using namespace std; 5 class Pet { 6 public: 7 Pet(); 8 ~Pet(); 9 public: 10 virtual string petSound() = 0; 11 }; 12 13 class Dog :public Pet { 14 public: 15 Dog(); 16 ~Dog(); 17 string petSound(); 18 }; 19 20 class Cat :public Pet { 21 public: 22 Cat(); 23 ~Cat(); 24 string petSound(); 25 }; 26 27 class Duck :public Pet { 28 public: 29 Duck(); 30 ~Duck(); 31 string petSound(); 32 };

1 #include "Product.h" 2 3 using namespace std; 4 5 Pet::Pet() { 6 7 } 8 Pet::~Pet() { 9 10 } 11 12 Dog::Dog() { 13 14 } 15 16 Dog::~Dog() { 17 18 } 19 string Dog::petSound() { 20 return "Dog-->Wang Wang...."; 21 } 22 23 Cat::Cat() { 24 25 } 26 Cat::~Cat() { 27 28 } 29 30 string Cat::petSound() { 31 return "Cat-->Miao miao...."; 32 } 33 Duck::Duck() { 34 35 } 36 Duck::~Duck() { 37 38 } 39 40 string Duck::petSound() { 41 return "Duck-->Ga ga...."; 42 }

1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include<iostream> 3 #include"Product.h" 4 using namespace std; 5 6 #ifdef Simple_Factoy 7 class PetFactory { 8 public: 9 PetFactory(); 10 ~PetFactory(); 11 virtual Pet* createPet(int type) = 0; 12 }; 13 14 class simPetFactory :public PetFactory { 15 public: 16 simPetFactory(); 17 ~simPetFactory(); 18 Pet* createPet(int type); 19 }; 20 21 #else 22 class petFactory { 23 public: 24 petFactory(); 25 ~petFactory(); 26 virtual Pet* _createPet() = 0; 27 }; 28 29 class FactoryDog :public petFactory { 30 public: 31 FactoryDog(); 32 ~FactoryDog(); 33 Pet* _createPet(); 34 }; 35 class FactoryCat :public petFactory { 36 public: 37 FactoryCat(); 38 ~FactoryCat(); 39 Pet* _createPet(); 40 }; 41 class FactoryDuck :public petFactory { 42 public: 43 FactoryDuck(); 44 ~FactoryDuck(); 45 Pet* _createPet(); 46 }; 47 #endif

1 #include "Factory.h" 2 #include "Product.h" 3 using namespace std; 4 #ifdef Simple_Factoy 5 PetFactory::PetFactory() { 6 7 } 8 PetFactory::~PetFactory() { 9 10 } 11 simPetFactory::simPetFactory() { 12 13 } 14 simPetFactory::~simPetFactory() { 15 16 } 17 18 Pet* simPetFactory::createPet(int type) { 19 Pet* pet = NULL; 20 switch (type) 21 { 22 case 1: 23 pet = new Dog(); 24 break; 25 case 2: 26 pet = new Cat(); 27 break; 28 case 3: 29 pet = new Duck(); 30 break; 31 default: 32 break; 33 } 34 return pet; 35 } 36 37 #else 38 petFactory::petFactory() { 39 40 } 41 petFactory::~petFactory() { 42 43 } 44 45 FactoryDog::FactoryDog() { 46 47 } 48 FactoryDog::~FactoryDog() { 49 50 } 51 52 Pet* FactoryDog::_createPet() { 53 return (new Dog()); 54 } 55 56 FactoryCat::FactoryCat() { 57 58 } 59 FactoryCat::~FactoryCat() { 60 61 } 62 Pet* FactoryCat::_createPet() { 63 return (new Cat()); 64 } 65 66 FactoryDuck::FactoryDuck() { 67 68 } 69 FactoryDuck::~FactoryDuck() { 70 71 } 72 73 Pet* FactoryDuck::_createPet() { 74 return (new Duck()); 75 } 76 #endif

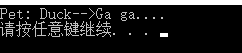
1 #include "Factory.h" 2 #define Simple_Factoy 3 using namespace std; 4 5 int main(int agrc, char* argv[]) { 6 #ifdef Simple_Factoy 7 PetFactory* petfactory = new simPetFactory(); 8 Pet* pet = petfactory->createPet(2); 9 string str = pet->petSound(); 10 cout << "Pet: " << str << endl; 11 #else 12 petFactory* petfactory = new FactoryDuck(); 13 Pet* pet = petfactory->_createPet(); 14 string str = pet->petSound(); 15 cout << "Pet: " << str << endl; 16 #endif 17 system("pause"); 18 }
若#define Simple_Factoy则定义了简单工厂模式,未遵循开放-封闭原则
如图:
执行结果:
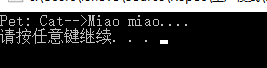
若未定义则执行工厂方法模式遵循开放-封闭原则
如图:
执行结果: