双端队列(deque):与队列类似,也是项的有序集合,有front和rear之分,但是项的加入和移除两端均可而不限于一端。
Deque()creates a new deque that is empty. It needs no parameters and returns an empty deque.addFront(item)adds a new item to the front of the deque. It needs the item and returns nothing.addRear(item)adds a new item to the rear of the deque. It needs the item and returns nothing.removeFront()removes the front item from the deque. It needs no parameters and returns the item. The deque is modified.removeRear()removes the rear item from the deque. It needs no parameters and returns the item. The deque is modified.isEmpty()tests to see whether the deque is empty. It needs no parameters and returns a boolean value.size()returns the number of items in the deque. It needs no parameters and returns an integer.
python实现:
class Deque: def __init__(self): self.items = [] def isEmpty(self): return self.items == [] def addFront(self, item): self.items.append(item) def addRear(self, item): self.items.insert(0,item) def removeFront(self): return self.items.pop() def removeRear(self): return self.items.pop(0) def size(self): return len(self.items)
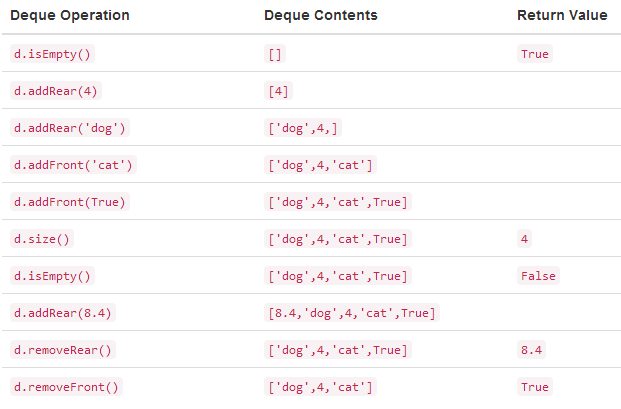
例:
列表(list):抽象数据类型之无序列表
方法:
List()creates a new list that is empty. It needs no parameters and returns an empty list.add(item)adds a new item to the list. It needs the item and returns nothing. Assume the item is not already in the list.remove(item)removes the item from the list. It needs the item and modifies the list. Assume the item is present in the list.search(item)searches for the item in the list. It needs the item and returns a boolean value.isEmpty()tests to see whether the list is empty. It needs no parameters and returns a boolean value.size()returns the number of items in the list. It needs no parameters and returns an integer.append(item)adds a new item to the end of the list making it the last item in the collection. It needs the item and returns nothing. Assume the item is not already in the list.index(item)returns the position of item in the list. It needs the item and returns the index. Assume the item is in the list.insert(pos,item)adds a new item to the list at position pos. It needs the item and returns nothing. Assume the item is not already in the list and there are enough existing items to have position pos.pop()removes and returns the last item in the list. It needs nothing and returns an item. Assume the list has at least one item.pop(pos)removes and returns the item at position pos. It needs the position and returns the item. Assume the item is in the list.
python实现:

class Node: def __init__(self,initdata): self.data = initdata self.next = None def getData(self): return self.data def getNext(self): return self.next def setData(self,newdata): self.data = newdata def setNext(self,newnext): self.next = newnext class UnorderedList: def __init__(self): self.head = None def isEmpty(self): return self.head == None def add(self,item): temp = Node(item) temp.setNext(self.head) self.head = temp def size(self): current = self.head count = 0 while current != None: count = count + 1 current = current.getNext() return count def search(self,item): current = self.head found = False while current != None and not found: if current.getData() == item: found = True else: current = current.getNext() return found def remove(self,item): current = self.head previous = None found = False while not found: if current.getData() == item: found = True else: previous = current current = current.getNext() if previous == None: self.head = current.getNext() else: previous.setNext(current.getNext())
列表(list):抽象数据类型之有序列表
方法:改动了search和add方法
OrderedList()creates a new ordered list that is empty. It needs no parameters and returns an empty list.add(item)adds a new item to the list making sure that the order is preserved. It needs the item and returns nothing. Assume the item is not already in the list.remove(item)removes the item from the list. It needs the item and modifies the list. Assume the item is present in the list.search(item)searches for the item in the list. It needs the item and returns a boolean value.isEmpty()tests to see whether the list is empty. It needs no parameters and returns a boolean value.size()returns the number of items in the list. It needs no parameters and returns an integer.index(item)returns the position of item in the list. It needs the item and returns the index. Assume the item is in the list.pop()removes and returns the last item in the list. It needs nothing and returns an item. Assume the list has at least one item.pop(pos)removes and returns the item at position pos. It needs the position and returns the item. Assume the item is in the list
python实现:

class Node: def __init__(self,initdata): self.data = initdata self.next = None def getData(self): return self.data def getNext(self): return self.next def setData(self,newdata): self.data = newdata def setNext(self,newnext): self.next = newnext class OrderedList: def __init__(self): self.head = None def isEmpty(self): return self.head == None def add(self,item): current = self.head previous = None stop = False while current != None and not stop: if current.getData() > item: stop = True else: previous = current current = current.getNext() temp = Node(item) if previous == None: temp.setNext(self.head) self.head = temp else: temp.setNext(current) previous.setNext(temp) def size(self): current = self.head count = 0 while current != None: count = count + 1 current = current.getNext() return count def search(self,item): current = self.head found = False stop = False while current != None and not found and not stop: if current.getData() == item: found = True else: if current.getData() > item: stop = True else: current = current.getNext() return found def remove(self,item): current = self.head previous = None found = False while not found: if current.getData() == item: found = True else: previous = current current = current.getNext() if previous == None: self.head = current.getNext() else: previous.setNext(current.getNext())
