spring boot整合redis
1、SpringBoot配置类
注解标签
1 @Configuration 2 3 @Configuration底层是含有@Component ,所以@Configuration 具有和 @Component 的作用。 4 @Configuration可理解为用spring的时候xml里面的<beans>标签。 5 注: 6 1) 配置类必须以类的形式提供(不能是工厂方法返回的实例),允许通过生成子类在运行时增强(cglib 动态代理)。 7 2) 配置类不能是 final 类(没法动态代理)。 8 3) 配置注解通常为了通过 @Bean 注解生成 Spring 容器管理的类。 9 4) 配置类必须是非本地的(即不能在方法中声明,不能是 private)。 10 5) 任何嵌套配置类都必须声明为static。 11 6) @Bean方法不能创建进一步的配置类(也就是返回的bean如果带有@Configuration,也不会被特殊处理,只会作为普通的 bean)。 12 @EnableCaching 13 1) @EnableCaching注解是spring framework中的注解驱动的缓存管理功能。自spring版本3.1起加入了该注解。 14 2) 如果你使用了这个注解,那么你就不需要在XML文件中配置cache manager了。 15 3) 当你在配置类(@Configuration)上使用@EnableCaching注解时,会触发一个post processor,这会扫描每一个spring bean,查看是否已经存在注解对应的缓存。如果找到了,就会自动创建一个代理拦截方法调用,使用缓存的bean执行处理。 16 @Bean 17 @Bean可理解为用spring的时候xml里面的<bean>标签。 18 注: 19 1) @Bean注解在返回实例的方法上,如果未通过@Bean指定bean的名称,则默认与标注的方法名相同; 20 21 2) @Bean注解默认作用域为单例singleton作用域,可通过@Scope(“prototype”)设置为原型作用域; 22 23 3) 既然@Bean的作用是注册bean对象,那么完全可以使用@Component、@Controller、@Service、@Repository等注解注册bean(在需要注册的类上加注解),当然需要配置@ComponentScan注解进行自动扫描。
导入pom依赖
1 <dependency> 2 <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> 3 <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId> 4 </dependency> 5 <dependency> 6 <groupId>redis.clients</groupId> 7 <artifactId>jedis</artifactId> 8 </dependency>
配置application.yml文件
1 redis: 2 database: 0 3 host: 192.168.147.144 4 port: 6379 5 password: 123456 6 jedis: 7 pool: 8 max-active: 100 9 max-idle: 3 10 max-wait: -1 11 min-idle: 0 12 timeout: 1000
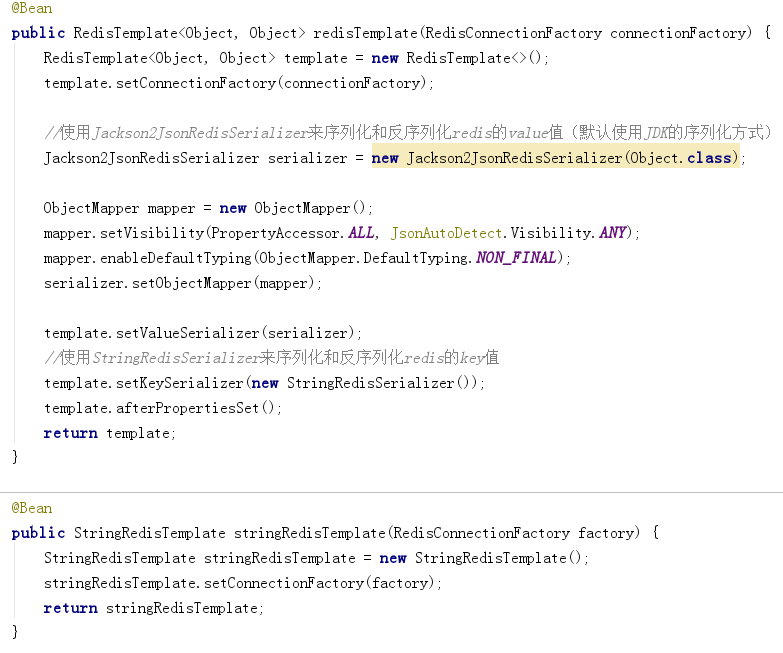
RedisConfig类用于Redis数据缓存。
//继承CachingConfigurerSupport,为了自定义生成KEY的策略。可以不继承。
1 package com.yuan.springboot02.config; 2 3 import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonAutoDetect; 4 import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.PropertyAccessor; 5 import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper; 6 import org.springframework.cache.CacheManager; 7 import org.springframework.cache.annotation.CachingConfigurerSupport; 8 import org.springframework.cache.annotation.EnableCaching; 9 import org.springframework.cache.interceptor.KeyGenerator; 10 import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; 11 import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; 12 import org.springframework.data.redis.cache.RedisCacheConfiguration; 13 import org.springframework.data.redis.cache.RedisCacheManager; 14 import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.RedisConnectionFactory; 15 import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate; 16 import org.springframework.data.redis.core.StringRedisTemplate; 17 import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer; 18 import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.StringRedisSerializer; 19 20 import java.lang.reflect.Method; 21 import java.time.Duration; 22 import java.util.HashMap; 23 import java.util.HashSet; 24 import java.util.Map; 25 import java.util.Set; 26 27 28 /** 29 * redis配置类 30 **/ 31 @Configuration 32 @EnableCaching//开启注解式缓存 33 //继承CachingConfigurerSupport,为了自定义生成KEY的策略。可以不继承。 34 public class RedisConfig extends CachingConfigurerSupport { 35 36 /** 37 * 生成key的策略 根据类名+方法名+所有参数的值生成唯一的一个key 38 * 39 * @return 40 */ 41 @Bean 42 @Override 43 public KeyGenerator keyGenerator() { 44 return new KeyGenerator() { 45 @Override 46 public Object generate(Object target, Method method, Object... params) { 47 StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); 48 sb.append(target.getClass().getName()); 49 sb.append(method.getName()); 50 for (Object obj : params) { 51 sb.append(obj.toString()); 52 } 53 return sb.toString(); 54 } 55 }; 56 } 57 58 /** 59 * 管理缓存 60 * 61 * @param redisConnectionFactory 62 * @return 63 */ 64 @Bean 65 public CacheManager cacheManager(RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory) { 66 //通过Spring提供的RedisCacheConfiguration类,构造一个自己的redis配置类,从该配置类中可以设置一些初始化的缓存命名空间 67 // 及对应的默认过期时间等属性,再利用RedisCacheManager中的builder.build()的方式生成cacheManager: 68 RedisCacheConfiguration config = RedisCacheConfiguration.defaultCacheConfig(); // 生成一个默认配置,通过config对象即可对缓存进行自定义配置 69 config = config.entryTtl(Duration.ofMinutes(1)) // 设置缓存的默认过期时间,也是使用Duration设置 70 .disableCachingNullValues(); // 不缓存空值 71 72 // 设置一个初始化的缓存空间set集合 73 Set<String> cacheNames = new HashSet<>(); 74 cacheNames.add("my-redis-cache1"); 75 cacheNames.add("my-redis-cache2"); 76 77 // 对每个缓存空间应用不同的配置 78 Map<String, RedisCacheConfiguration> configMap = new HashMap<>(); 79 configMap.put("my-redis-cache1", config); 80 configMap.put("my-redis-cache2", config.entryTtl(Duration.ofSeconds(120))); 81 82 RedisCacheManager cacheManager = RedisCacheManager.builder(redisConnectionFactory) // 使用自定义的缓存配置初始化一个cacheManager 83 .initialCacheNames(cacheNames) // 注意这两句的调用顺序,一定要先调用该方法设置初始化的缓存名,再初始化相关的配置 84 .withInitialCacheConfigurations(configMap) 85 .build(); 86 return cacheManager; 87 } 88 89 @Bean 90 public RedisTemplate<Object, Object> redisTemplate(RedisConnectionFactory connectionFactory) { 91 RedisTemplate<Object, Object> template = new RedisTemplate<>(); 92 template.setConnectionFactory(connectionFactory); 93 94 //使用Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer来序列化和反序列化redis的value值(默认使用JDK的序列化方式) 95 Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer serializer = new Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer(Object.class); 96 97 ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper(); 98 mapper.setVisibility(PropertyAccessor.ALL, JsonAutoDetect.Visibility.ANY); 99 mapper.enableDefaultTyping(ObjectMapper.DefaultTyping.NON_FINAL); 100 serializer.setObjectMapper(mapper); 101 102 template.setValueSerializer(serializer); 103 //使用StringRedisSerializer来序列化和反序列化redis的key值 104 template.setKeySerializer(new StringRedisSerializer()); 105 template.afterPropertiesSet(); 106 return template; 107 } 108 109 @Bean 110 public StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate(RedisConnectionFactory factory) { 111 StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate = new StringRedisTemplate(); 112 stringRedisTemplate.setConnectionFactory(factory); 113 return stringRedisTemplate; 114 } 115 116 }
详细针对下面这段代码进行讲解

在整合ehcache的时候,会有一个配置文件spring-ehcache.xml如下
1 <!-- 使用ehcache缓存 --> 2 <bean id="cacheManagerFactory" class="org.springframework.cache.ehcache.EhCacheManagerFactoryBean"> 3 <property name="configLocation" value="classpath:ehcache.xml"/> 4 <property name="shared" value="true"></property> 5 </bean> 6 <!-- 默认是cacheManager --> 7 <bean id="cacheManager" class="org.springframework.cache.ehcache.EhCacheCacheManager"> 8 <property name="cacheManager" ref="cacheManagerFactory"/> 9 </bean>
ehcache.xml
<!--defaultCache:默认的管理策略-->
<!--eternal:设定缓存的elements是否永远不过期。如果为true,则缓存的数据始终有效,如果为false那么还要根据timeToIdleSeconds,timeToLiveSeconds判断-->
<!--maxElementsInMemory:在内存中缓存的element的最大数目-->
<!--overflowToDisk:如果内存中数据超过内存限制,是否要缓存到磁盘上-->
<!--diskPersistent:是否在磁盘上持久化。指重启jvm后,数据是否有效。默认为false-->
<!--timeToIdleSeconds:对象空闲时间(单位:秒),指对象在多长时间没有被访问就会失效。只对eternal为false的有效。默认值0,表示一直可以访问-->
<!--timeToLiveSeconds:对象存活时间(单位:秒),指对象从创建到失效所需要的时间。只对eternal为false的有效。默认值0,表示一直可以访问-->
<!--memoryStoreEvictionPolicy:缓存的3 种清空策略-->
<!--FIFO:first in first out (先进先出)-->
<!--LFU:Less Frequently Used (最少使用).意思是一直以来最少被使用的。缓存的元素有一个hit 属性,hit 值最小的将会被清出缓存-->
<!--LRU:Least Recently Used(最近最少使用). (ehcache 默认值).缓存的元素有一个时间戳,当缓存容量满了,而又需要腾出地方来缓存新的元素的时候,那么现有缓存元素中时间戳离当前时间最远的元素将被清出缓存-->
<defaultCache eternal="false" maxElementsInMemory="1000" overflowToDisk="false" diskPersistent="false"
timeToIdleSeconds="0" timeToLiveSeconds="600" memoryStoreEvictionPolicy="LRU"/>
截图中代码的意思是:从RedisCacheConfiguration获取一个默认的缓存策略,针对这一策略做对应的调整,生成一个全新的策略。
然后,初始化两个缓存槽,赋予名字my-redis-cache1和my-redis-cache2,,赋予再基于之前的缓存策略,初始化两个缓存策略,
存储与configMap,然后策略与缓存槽对应上,生成缓存管理器交个spring进行管理,替代掉SSM时代的配置文件。
ssm框架中如果整合redis,那么会有个spring-redis.xml配置文件,里面的配置内容如下
1 <!-- 1. 引入properties配置文件 --> 2 <!--<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:redis.properties" />--> 3 4 <!-- 2. redis连接池配置--> 5 <bean id="poolConfig" class="redis.clients.jedis.JedisPoolConfig"> 6 <!--最大空闲数--> 7 <property name="maxIdle" value="${redis.maxIdle}"/> 8 <!--连接池的最大数据库连接数 --> 9 <property name="maxTotal" value="${redis.maxTotal}"/> 10 <!--最大建立连接等待时间--> 11 <property name="maxWaitMillis" value="${redis.maxWaitMillis}"/> 12 <!--逐出连接的最小空闲时间 默认1800000毫秒(30分钟)--> 13 <property name="minEvictableIdleTimeMillis" value="${redis.minEvictableIdleTimeMillis}"/> 14 <!--每次逐出检查时 逐出的最大数目 如果为负数就是 : 1/abs(n), 默认3--> 15 <property name="numTestsPerEvictionRun" value="${redis.numTestsPerEvictionRun}"/> 16 <!--逐出扫描的时间间隔(毫秒) 如果为负数,则不运行逐出线程, 默认-1--> 17 <property name="timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis" value="${redis.timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis}"/> 18 <!--是否在从池中取出连接前进行检验,如果检验失败,则从池中去除连接并尝试取出另一个--> 19 <property name="testOnBorrow" value="${redis.testOnBorrow}"/> 20 <!--在空闲时检查有效性, 默认false --> 21 <property name="testWhileIdle" value="${redis.testWhileIdle}"/> 22 </bean> 23 24 <!-- 3. redis连接工厂 --> 25 <bean id="connectionFactory" class="org.springframework.data.redis.connection.jedis.JedisConnectionFactory" 26 destroy-method="destroy"> 27 <property name="poolConfig" ref="poolConfig"/> 28 <!--IP地址 --> 29 <property name="hostName" value="${redis.hostName}"/> 30 <!--端口号 --> 31 <property name="port" value="${redis.port}"/> 32 <!--如果Redis设置有密码 --> 33 <property name="password" value="${redis.password}"/> 34 <!--客户端超时时间单位是毫秒 --> 35 <property name="timeout" value="${redis.timeout}"/> 36 </bean> 37 38 <!-- 4. redis操作模板,使用该对象可以操作redis --> 39 <bean id="redisTemplate" class="org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate"> 40 <property name="connectionFactory" ref="connectionFactory"/> 41 <!--如果不配置Serializer,那么存储的时候缺省使用String,如果用User类型存储,那么会提示错误User can't cast to String!! --> 42 <property name="keySerializer"> 43 <bean class="org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.StringRedisSerializer"/> 44 </property> 45 <property name="valueSerializer"> 46 <bean class="org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer"/> 47 </property> 48 <property name="hashKeySerializer"> 49 <bean class="org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.StringRedisSerializer"/> 50 </property> 51 <property name="hashValueSerializer"> 52 <bean class="org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer"/> 53 </property> 54 <!--开启事务 --> 55 <property name="enableTransactionSupport" value="true"/> 56 </bean> 57 58 <!-- 5.使用中间类解决RedisCache.RedisTemplate的静态注入,从而使MyBatis实现第三方缓存 --> 59 <bean id="redisCacheTransfer" class="com.yuan.ssm2.util.RedisCacheTransfer"> 60 <property name="redisTemplate" ref="redisTemplate"/> 61 </bean>
其中前面redis链接工厂的创建,已经交于springboot中的application.yml文件来完成。
所以,springboot整合redis我们只需要关注下面这部分配置。
2、SpringBoot整合redis及其注解式开发
常用缓存注解
@Cacheable:作用是主要针对方法配置,能够根据方法的请求参数对其结果进行缓存
主要参数说明:
1) value :
缓存的名称,在 spring 配置文件中定义,必须指定至少一个,
例如:@Cacheable(value=”mycache”) 或者 @Cacheable(value={”cache1”,”cache2”}。
2) key :缓存的 key,可以为空,
如果指定要按照 SpEL 表达式编写,如果不指定,则缺省按照方法的所有参数进行组合,
例如:@Cacheable(value=”testcache”,key=”#userName”)。
3) condition :缓存的条件,可以为空,
案例代码:
service层
1 package com.yuan.springboot02.Service; 2 3 import com.yuan.springboot02.entity.Book; 4 import com.yuan.springboot02.util.PageBean; 5 import org.springframework.cache.annotation.CacheEvict; 6 import org.springframework.cache.annotation.CachePut; 7 import org.springframework.cache.annotation.Cacheable; 8 9 import java.util.List; 10 11 public interface BookService { 12 13 14 15 @CachePut(value = "my-redis-cache2", condition = "#bid>30", key = "'bookid'+#bid")//只存不取 16 // @Cacheable(value = "my-redis-cache1", condition = "#bid>30", key = "'bookid'+#bid")//存取 17 Book selectByPrimaryKey(Integer bid); 18 19 @CachePut(value = "my-redis-cache1") 20 List<Book> listPager(Book book, PageBean pageBean); 21 }
测试代码
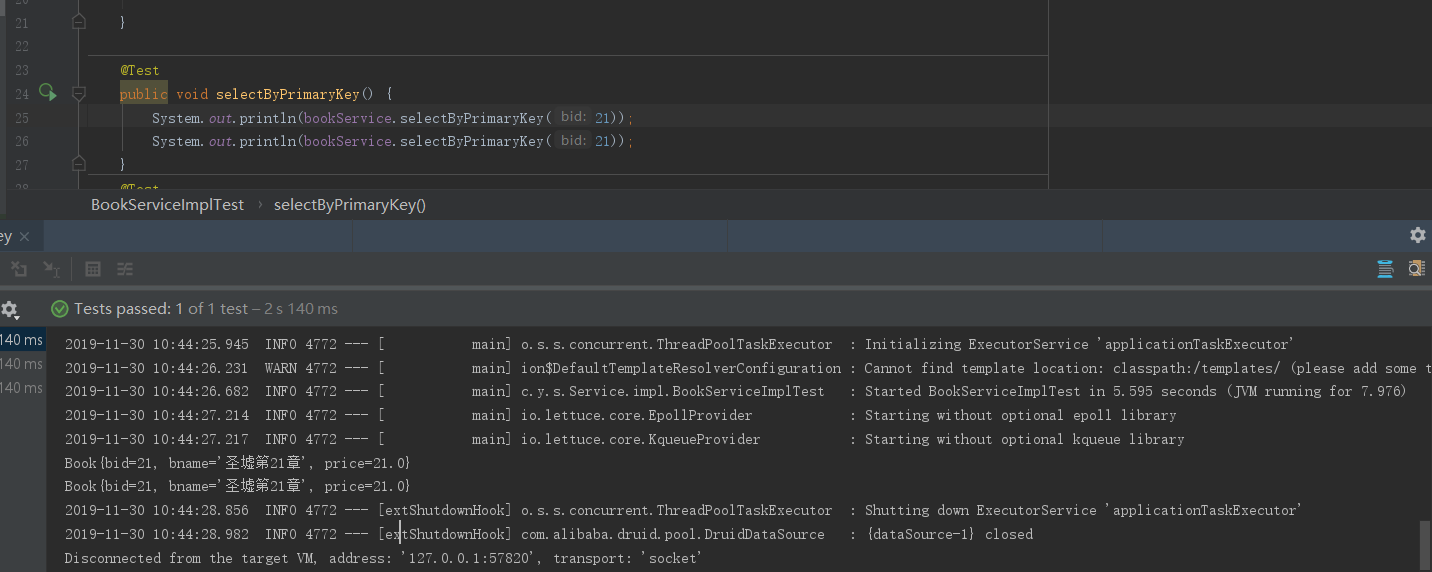
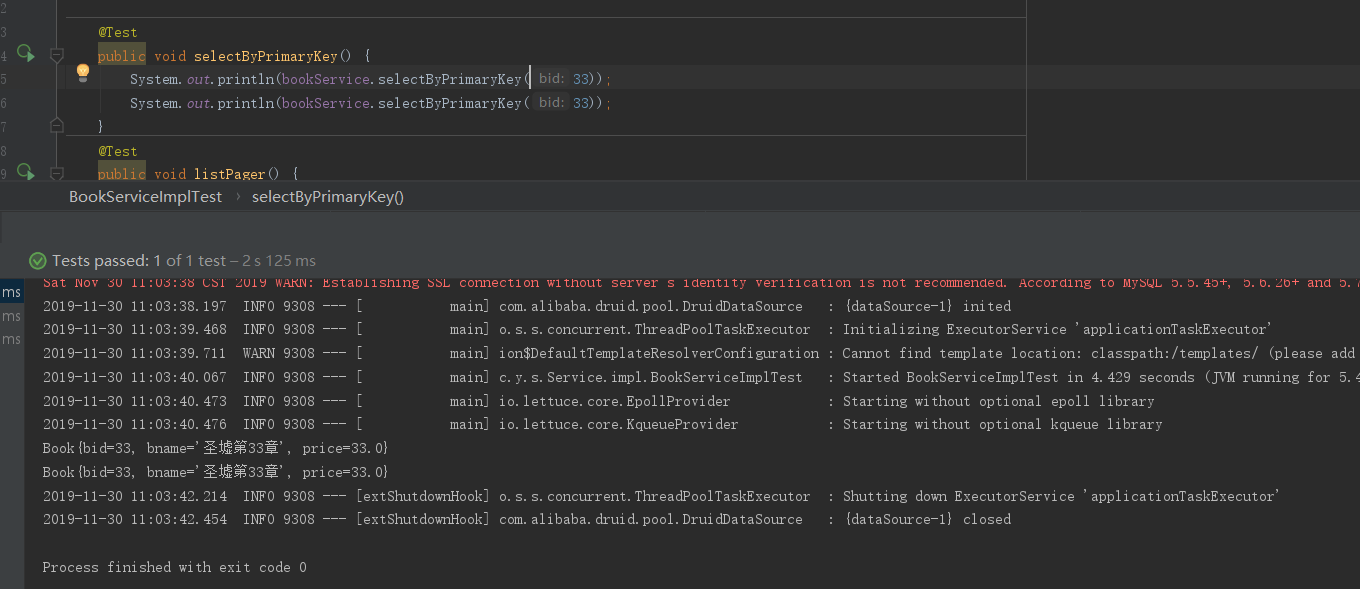
1 @Test 2 public void selectByPrimaryKey() { 3 System.out.println(bookService.selectByPrimaryKey(31)); 4 System.out.println(bookService.selectByPrimaryKey(31)); 5 } 6 @Test 7 public void listPager() { 8 Book book = new Book(); 9 book.setBname("%圣墟%"); 10 PageBean pageBean = new PageBean(); 11 pageBean.setPage(2); 12 for (Book book1 : bookService.listPager(book, pageBean)) { 13 System.out.println(book1); 14 } 15 }
当bid分别为21和31的时候,bid=21是不触发缓存的,bid=31的时候才会缓存查询结果
@CachePut:作用是主要针对方法配置,能够根据方法的请求参数对其结果进行缓存,和 @Cacheable 不同的是,它每次都会触发真实查询方法的调用
主要参数说明:
参数配置和@Cacheable一样。
@CacheEvict:作用是主要针对方法配置,能够根据一定的条件对缓存进行清空
主要参数说明:
1)value , key 和 condition 参数配置和@Cacheable一样。
2) allEntries :
是否清空所有缓存内容,缺省为 false,
如果指定为 true,则方法调用后将立即清空所有缓存,
例如:@CachEvict(value=”testcache”,allEntries=true)
service层代码
@CacheEvict(value = "my-redis-cache2",allEntries = true) void clear();
测试
@Test public void clear() { bookService.clear(); }
是否在方法执行前就清空,缺省为 false,
如果指定为 true,则在方法还没有执行的时候就清空缓存,
缺省情况下,如果方法执行抛出异常,则不会清空缓存,
例如@CachEvict(value=”testcache”,beforeInvocation=true)