一、绪论
一个进程在终止时会关闭所有文件描述符,释放在用户空间分配的内存,但它的PCB还保留着,内核在其中保存了一些信息:如果
是正常终止则保存着退出状态,如果是异常终止则保存着导致该进程终止的信号是哪个。这个进程的父进程可以调用wait或waitpi
d获取这些信息,然后彻底清除掉这个进程。
二、wait()
1. 功能:父进程调用wait函数可以回收子进程终止信息。该函数有三个功能:
① 阻塞等待子进程退出
② 回收子进程残留资源
③ 获取子进程结束状态(退出原因)。
wait一旦被调用,就会一直阻塞在这里,直到有一个子进程退出出现为止。
2. 函数原型:
pid_t wait(int *status);
成功:清理掉的子进程ID;失败:-1 (没有子进程)
使用wait函数传出参数status来保存进程的退出状态 (正常终止→退出值;异常终止→终止信号)。借助宏函数来进一步判断进程终止的具体原因。
宏函数可分为如下三组:
1). WIFEXITED(status) 为非0 → 进程正常结束
WEXITSTATUS(status) 如上宏为真,使用此宏 → 获取进程退出状态 (exit的参数)
2). WIFSIGNALED(status) 为非0 → 进程异常终止
WTERMSIG(status) 如上宏为真,使用此宏 → 取得使进程终止的那个信号的编号。
*3). WIFSTOPPED(status) 为非0 → 进程处于暂停状态
WSTOPSIG(status) 如上宏为真,使用此宏 → 取得使进程暂停的那个信号的编号。
WIFCONTINUED(status) 为真 → 进程暂停后已经继续运行
3. 例程
1 #include <unistd.h> 2 #include <stdlib.h> 3 #include <stdio.h> 4 #include <sys/wait.h> 5 6 int main(void) 7 { 8 pid_t pid, wpid; 9 int status; //定义传出参数 10 11 pid = fork(); 12 if(pid == -1){ 13 perror("fork error"); 14 exit(1); 15 } else if(pid == 0){ //子进程 16 printf("I'm process child, pid = %d ", getpid()); 17 #if 0 18 execl("./abnor", "abnor", NULL); 19 perror("execl error"); 20 exit(1); 21 #endif 22 sleep(1); 23 exit(20); 24 } else { 25 //wpid = wait(NULL); //无传出参数,无需判断 26 wpid = wait(&status); //status为传出参数,wpid返回的进程ID 27 if(WIFEXITED(status)){ //正常退出 非0 28 printf("I'm parent, The child process%d exit normally ", wpid); 30 printf("return value:%d ", WEXITSTATUS(status));//获取退出值31 32 } else if (WIFSIGNALED(status)) { //异常退出 33 printf("The child process exit abnormally, killed by signal %d ", WTERMSIG(status));//获取终止信号编号 36 } else { 37 printf("other... "); 38 } 39 } 40 return 0; 41 }
编译与执行结果:

异常退出:

二、waitpid()
1. 功能与wait相同,但可指定pid进程清理,可以不阻塞。
pid_t waitpid(pid_t pid, int *status, in options);
成功:返回清理掉的子进程ID;失败:-1(无子进程)
特殊参数和返回情况,参数pid:
> 0 回收指定ID的子进程
-1 回收任意子进程(相当于wait)
0 回收和当前调用waitpid一个组的所有子进程
< -1 回收指定进程组内的任意子进程
注意:
1)参3为WNOHANG(非阻塞),且子进程正在运行,则返回0。
2)一次wait或waitpid调用只能清理一个子进程,清理多个子进程应使用循环。
2. 例程一
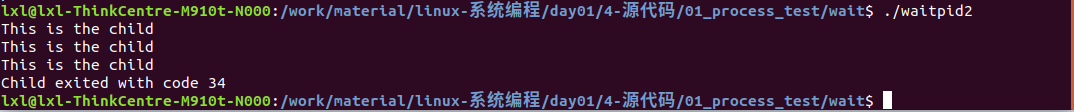
1 #include <sys/types.h> 2 #include <sys/wait.h> 3 #include <unistd.h> 4 #include <stdio.h> 5 #include <stdlib.h> 6 int main(void) 7 { 8 pid_t pid; 9 int i; 10 int stat_val; 11 12 pid = fork(); 13 14 if (pid < 0) { 15 perror("fork failed"); 16 exit(1); 17 } 18 if (pid == 0) { 19 for (i = 3; i > 0; i--) { 20 printf("This is the child "); 21 sleep(1); 22 } 23 exit(34); 24 } else { 25 waitpid(pid, &stat_val, 0); //0阻塞 26 if (WIFEXITED(stat_val)) ////stat_val为传出参数 27 printf("Child exited with code %d ", WEXITSTATUS(stat_val)); 28 else if (WIFSIGNALED(stat_val)) 29 printf("Child terminated abnormally, signal %d ", WTERMSIG(stat_val)); 30 } 31 return 0; 32 }
编译与执行结果:
例程二(循环清理多个子进程)
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <unistd.h> 3 #include <stdlib.h> 4 #include <sys/wait.h> 5 6 int main(int argc, char *argv[]) 7 { 8 int n = 5, i; 9 pid_t p; 10 11 for(i = 0; i < n; i++) { 12 p = fork(); 13 if(p == 0) break; 14 } 15 if(n == i){ // parent 16 sleep(n); 17 printf("I am parent, pid = %d ", getpid()); 18 for (i = 0; i < n; i++) { 19 p = waitpid(0, NULL, WNOHANG); 20 printf("wait pid = %d ", p); 21 } 22 } else { 23 sleep(i); 24 printf("I'm %dth child, pid = %d ", i+1, getpid()); 25 } 26 return 0; 27 }
编译与执行结果:
