(1)
如何解释这样的输出结果?从中你能总结出什么?请运行以下示例代码StringPool.java,查看其输出结果
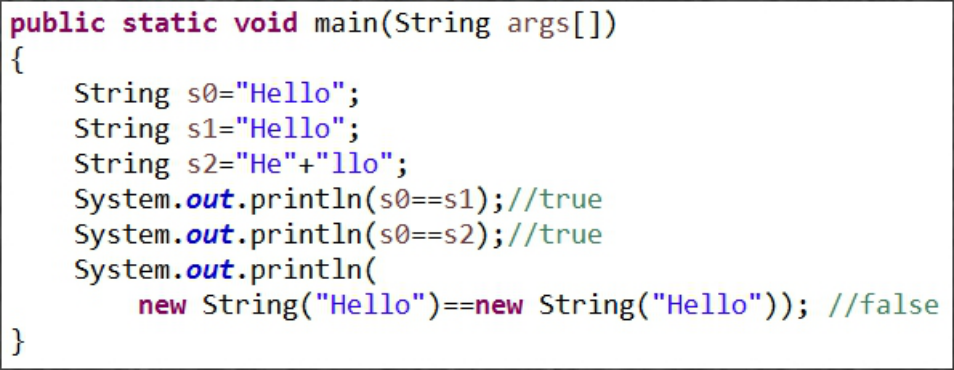
解释:因为s0,s1,s2内容相同,所以java实际上把它们把存在一个地方,地址相同,指向的对象相同,所以s0==s1,s0==s2位true。而new则新开辟了一个空间,
所以最后输出结果为false。
(2)为什么会有下面的输出结果?从中你又能总结出什么?

解释:一开始将s1赋给s2,后来s1进行运算为ab,所以s1==s2为false,而‘ab’为常量,并不与内容为ab的s1相等,所以为false,最后调用了判断字符串内容是否相等的
equals函数,所以结果为true。
(3)String.equals()方法
实现代码:
1 public boolean equals(Object anObject) { 2 if (this == anObject) { 3 return true; 4 } 5 if (anObject instanceof String) { 6 String anotherString = (String)anObject; 7 int n = count; 8 if (n == anotherString.count) { 9 char v1[] = value; 10 char v2[] = anotherString.value; 11 int i = offset; 12 int j = anotherString.offset; 13 while (n-- != 0) { 14 if (v1[i++] != v2[j++]) 15 return false; 16 } 17 return true; 18 } 19 } 20 return false; 21 }
感悟:
首先上边的语句,先判断anObject是不是String类的一个实例,如果是运行下边的语句
String anotherString = (String)anObject;
字符串是一个引用数据类型,本身是String个对象,
在这里把传进来的anObject这个对象,赋给anotherString (需要类型转换)
然后调用String类里的成员,count、value、offset是String的成员
int n = count;//这个count是原始字符串的长度
if (n == anotherString.count) { //把字符串长度和要比较的字符串长度对比,长度都不同的话就不用比字符串内容了
char v1[] = value;//把原始字符串义字符形式存入数组
char v2[] = anotherString.value; //把要比较字符串义字符形式存入数组
int i = offset;//数组下标
int j = anotherString.offset;
while (n-- != 0) { //遍历数组,比较 数组元素是否相同
if (v1[i++] != v2[j++])
return false;//在遍历的过程中如果有不同的就返回false;
}
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
(4)String类的方法使用说明
length():public int length()//求字符串长的方法
String s=”abcdefghigk”;
System.out.println(s.length());
charAt():public charAt(int index)//index 是字符下标,返回字符串中指定位置的字符
String s=”HelloWorld”;
System.out.println(s.charAt(5));
getChars():public int getChars()//将字符从此字符串复制到目标字符数组
String str = "hahaxixixi";
Char[] ch = new char[8];
str.getChars(2,5,ch,0);
replace():public int replace()//替换字符串
String s=”abc”;
System.out.println(s.replace(“abc”,”def”));
toUpperase():public String toUpperCase()//将字符串全部转换成大写
System.out.println(new String(“whoareyou”).toUpperCase());
toLowerCse():public String toLowerCase()//将字符串全部转换成小写
System.out.println(new String(“WHOAREYOU”).toLowerCase());
trim():public String trim()
String s=”wh o”;
System.out.println(s.trim());//是去两边空格的方法
toCharArray(): String x=new String(“abcd”);// 将字符串对象中的字符转换为一个字符数组
char c[]=s.toCharArray();
System.out.println(“c[1]”+c[3])