JDK 8
Eclipse Version: 2021-03 (4.19.0)
---
都位于java.lang包下,java.lang.System、java.langRuntime(位于 rt.jar)
public final class System {...}
public class Runtime {...}目录
System下有下面的公开对象和方法:
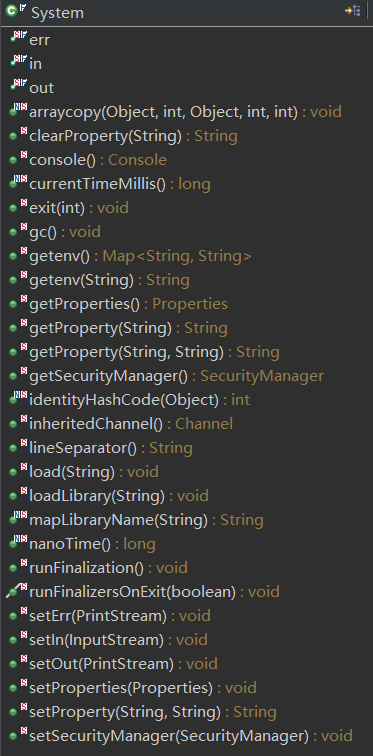
常用:
out
public final static PrintStream out = null;使用out的 print、println、printf 输出内容到 控制台,其中,print 不自动换行,printf自定义格式。
当然,除了上面的print函数,还有 append、write、flush、close等。
注意,执行 close 函数后,out对象就不会输出内容到 控制台了,因为 被关闭了。
测试out
System.out.print("1.a");
System.out.println("2.ab");
PrintStream ps = System.out.printf("3.%s", "abc");
ps.append("4.-append");
System.out.println();
ps.write(12);
ps.write(65);
ps.write(66);
ps.write(67);
ps.write(123);
ps.flush();
System.out.println();
System.out.println("关闭前:");
ps.close();
// 没有输出
System.out.println("关闭后.");
/*
// 测试结果:
1.a2.ab
3.abc4.-append
ABC{
关闭前:
*/arraycopy(Object, int, Object, int, int)
public static native void arraycopy(Object src, int srcPos,
Object dest, int destPos,
int length);数组拷贝,但src、dest都是Object(WHY?)。
测试arraycopy
// arraycopy 测试
final int size = 5;
byte[] src = new byte[] {1,2,4,8,16};
byte[] dest = new byte[size];
System.out.println("拷贝前dest:");
for (int i=0; i<size; i++) {
System.out.println("dest[" + i + "]=" + dest[i]);
}
System.arraycopy(src, 0, dest, 0, dest.length);
System.out.println("拷贝后dest:");
for (int i=0; i<size; i++) {
System.out.println("dest[" + i + "]=" + dest[i]);
}
// 发生异常
System.arraycopy(src, 0, dest, 0, dest.length + 1);
/*
// 执行结果
拷贝前dest:
dest[0]=0
dest[1]=0
dest[2]=0
dest[3]=0
dest[4]=0
拷贝后dest:
dest[0]=1
dest[1]=2
dest[2]=4
dest[3]=8
dest[4]=16
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException
at java.lang.System.arraycopy(Native Method)
at aug.Test081001.testSystem(Test081001.java:52)
at aug.Test081001.main(Test081001.java:11)
*/疑问:对象数组拷贝 如何,是 浅拷贝还是 深拷贝?
测试arraycopy-对象数组
class Abc {
public Abc(String name) {
super();
this.name = name;
}
/**
* 属性name
*/
private String name;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
// 主函数
// 拷贝对象数组:浅拷贝、深拷贝?
Abc[] arr1 = new Abc[] {new Abc("name1"), new Abc("name2")};
Abc[] arr2 = new Abc[2];
System.out.println("拷贝前:");
for (int i=0; i<2; i++) {
System.out.println("arr1[" + i + "]=" + arr1[i]);
System.out.println("arr2[" + i + "]=" + arr2[i]);
}
System.out.println("拷贝后:");
System.arraycopy(arr1, 0, arr2, 0, arr2.length);
for (int i=0; i<2; i++) {
System.out.println("arr1[" + i + "]=" + arr1[i]);
System.out.println("arr2[" + i + "]=" + arr2[i]);
}
/*
// 测试结果:浅拷贝!执行拷贝后,src、dest数组存了相同的对象
拷贝前:
arr1[0]=aug.Abc@816f27d
arr2[0]=null
arr1[1]=aug.Abc@87aac27
arr2[1]=null
拷贝后:
arr1[0]=aug.Abc@816f27d
arr2[0]=aug.Abc@816f27d
arr1[1]=aug.Abc@87aac27
arr2[1]=aug.Abc@87aac27
*/
currentTimeMillis() & nanoTime()
测试Time
System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis());
System.out.println(System.nanoTime());
/*
// 测试结果
1628585409683
721089123470600
*/currentTimeMillis 可以转换为 当前时间——年月日时分秒,
nanoTime 和 时钟时间无关,但可以用来计算 系统流逝的时间,比如,一个程序执行花了多少 纳秒。
注:
ns(nanosecond):纳秒,时间单位。一秒的十亿分之一,等于10的负9次方秒(1 ns = 10 s)。
getenv() & getenv(String)
获取环境变量。
在Windows系统中,可以获取到 配置的 所有环境变量。
测试期间发现一个小问题,打开IDE(Eclipse)后,修改、添加环境变量,此时获取不到,但重启IDE后就可以获取到了。
public static java.util.Map<String,String> getenv() {
//...
}
public static String getenv(String name) {
//...
}
注:底层使用 ProcessEnvironment类-非public 实现。
注:对于同一个程序,可能环境变量不同,其执行的行为也不一定相同,实现一定的控制作用。
测试环境变量
Consumer<Object> cs = System.out::println;
cs.accept(">>>>>System->env:");
Map<String, String> env = System.getenv();
env.forEach((k,v)->{
cs.accept("key=" + k + ", val=" + v);
});getProperties() & getProperty(String) & getProperty(String, String)
getProperties源码
// System properties.
public static Properties getProperties() {
SecurityManager sm = getSecurityManager();
if (sm != null) {
sm.checkPropertiesAccess();
}
return props;
}
// System properties.
private static Properties props;
// 本地方法
private static native Properties initProperties(Properties props);系统属性,使用本地方法进行初始化。
包括但不限于下面的属性:
部分系统属性
key=java.runtime.name, val=Java(TM) SE Runtime Environment
key=sun.boot.library.path, val=D:Program FilesJavajdk1.8.0_202jrein
key=java.vm.version, val=25.202-b08
key=abcd, val=99999
key=java.vm.vendor, val=Oracle Corporation
key=java.vendor.url, val=http://java.oracle.com/
key=path.separator, val=;
key=java.vm.name, val=Java HotSpot(TM) 64-Bit Server VM
key=file.encoding.pkg, val=sun.io
key=java.runtime.version, val=1.8.0_202-b08
key=java.class.path, val=D:WSews21apr argetclasses;D:workmvnrepoorgprojectlomboklombok1.18.20lombok-1.18.20.jar
key=java.vm.specification.version, val=1.8
...还可以自定义属性。
Eclipse中添加如下 VM参数即可:
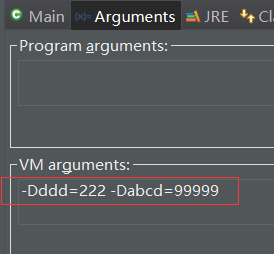
通过系统属性 可以得到 ddd、abcd的值。
疑问:既有环境变量,又有系统属性,在开发程序时,要是两者有相同的变量,应该听谁的呢?需要设定优先级才是。
除了添加,还有 设置系统属性函数 setProperties、setProperty,程序设置后,前面IDE里面配置的 ddd、abcd还有效吗?
测试系统属性获取&设置
cs.accept(">>>>>System->Properties:");
Properties props = System.getProperties();
props.keySet().forEach(key->{
cs.accept("key=" + key + ", val=" + props.getProperty((String) key));
});
System.setProperty("ddd", "in main");
System.setProperty("abcd", "in main");
Properties props2 = System.getProperties();
props2.keySet().forEach(key->{
cs.accept("key=" + key + ", val=" + props2.getProperty((String) key));
});测试结果:
程序中的设置生效了,而Eclipse的VM arguments中配置的无效——被覆盖了。
key=abcd, val=in main
key=ddd, val=in main命令行的先被设置,然后,程序里面执行了设置,所以,变更了,没问题。
identityHashCode(Object)
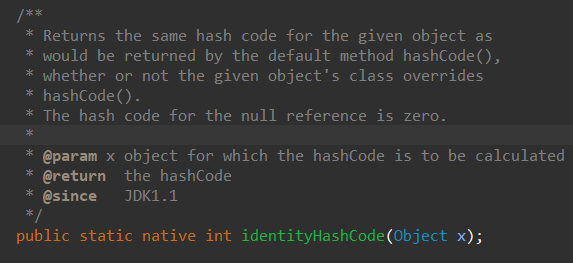
一致hash函数。
对象的hashCode函数可以被修改,重写,返回的hashCode会变化,,但这个 identityHashCode 却不会,可以用来判断 两个对象是否是同一个——调用这个值的返回值相同。
类没有重写 hashCode函数时,两个函数返回的相同:
Abc obj1 = new Abc("n1");
System.out.println(obj1.hashCode());
System.out.println(System.identityHashCode(obj1));
执行结果:
135721597
135721597重写Abc类的hashCode函数:
// Abc类下有一个 String类型的 name属性
@Override
public int hashCode() {
if (this.name == null) {
return 0;
}
return this.name.hashCode();
}
再次执行结果:
3459
135721597可以用 十六进制打印出来:
System.out.printf("0x%08x", System.identityHashCode(obj1));未使用:
getSecurityManager()
inheritedChannel()
load(String)
loadLibrary(String)
mapLibraryName(String)
exit(int)
Runtime下有下面的公开对象和方法:
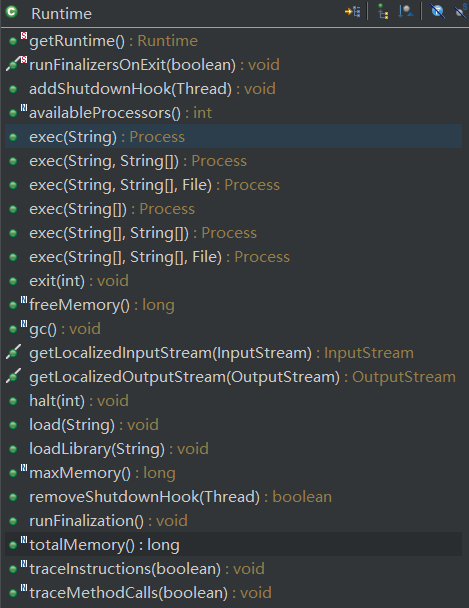
源码中如是说:每个Java应用都有一个唯一的 Runtime实例...
Runtime源码注释
/**
* Every Java application has a single instance of class
* <code>Runtime</code> that allows the application to interface with
* the environment in which the application is running. The current
* runtime can be obtained from the <code>getRuntime</code> method.
* <p>
* An application cannot create its own instance of this class.
*
* @author unascribed
* @see java.lang.Runtime#getRuntime()
* @since JDK1.0
*/常用(用过):
getRuntime()
获取这个Java应用的Runtime实例,第一步。
获取后,就可以调用 下面的实例方法了。
和System不同,这个类下面 还有 getRuntime() 是 类方法,其它公开的都是 实例方法。
addShutdownHook(Thread) & removeShutdownHook(Thread)
最近接触到这个 addShutdownHook 方法,用来在 Java应用 关闭的时候 执行一个线程里面的内容。
至于removeShutdownHook 方法,暂未使用过。
测试程序1:removeShutdownHook 无效!其remove的Thread和 addShutdownHook的不是同一个。
public static void main(String[] args) {
Runtime rt = Runtime.getRuntime();
System.out.println(rt.availableProcessors());
System.out.println(rt.maxMemory());
System.out.println(rt.totalMemory());
System.out.println(rt.freeMemory());
System.out.println(rt.totalMemory() - rt.freeMemory());
rt.addShutdownHook(new Thread(()->{
try {
Thread.sleep(5000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("int addShutdownHook. now=" + new Date());
}));
rt.removeShutdownHook(new Thread(()->{
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("in removeShutdownHook. now=" + new Date());
}));
System.out.println("main end. now=" + new Date());
}执行结果:
8
119537664
64487424
63144640
1342784
main end. now=Tue Aug 10 18:09:48 CST 2021
int addShutdownHook. now=Tue Aug 10 18:09:53 CST 2021改造后的程序:removeShutdownHook 生效了
使用removeShutdownHook
public static void main(String[] args) {
Runtime rt = Runtime.getRuntime();
System.out.println(rt.availableProcessors());
System.out.println(rt.maxMemory());
System.out.println(rt.totalMemory());
System.out.println(rt.freeMemory());
System.out.println(rt.totalMemory() - rt.freeMemory());
Thread td = new Thread(()->{
try {
Thread.sleep(5000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("int addShutdownHook. now=" + new Date());
});
rt.addShutdownHook(td);
new Thread(()->{
try {
// 3秒
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
Runtime.getRuntime().removeShutdownHook(td);
System.out.println("int removeShutdownHook. now=" + new Date());
}).start();
System.out.println("main end. now=" + new Date());
}执行结果:
8
119537664
64487424
63144640
1342784
main end. now=Tue Aug 10 18:13:53 CST 2021
int removeShutdownHook. now=Tue Aug 10 18:13:56 CST 2021availableProcessors()
Java应用可用的 处理器核心 数量。
注:在虚拟机、Docker中运行时,可以更改 程序使用的核心数量。
freeMemory() & maxMemory() & totalMemory()
返回内存信息,单位字节,堆内存信息,可以通过 Xms、Xmx 来设置。
测试memory
System.out.println(rt.maxMemory());
System.out.println(rt.totalMemory());
System.out.println(rt.freeMemory());
System.out.println(rt.totalMemory() - rt.freeMemory());
// 执行结果
1883242496
128974848
126929816
2045032
// 设置 -Xms64m -Xmx128m 后
// 执行结果
119537664
64487424
63144640
1342784
exec(...)
执行系统命令,比如,Linux系统的ls命令(Windows的dir),或者,执行某个其它语言编写的程序,比如,Python、GO开发的。
执行后,返回结果,再对结果进行分析。
Linux 使用 sh -c,Windows 使用 cmd /c。
在Windows上的测试:
// 测试exec
try {
// Windows 10
Process ps = rt.exec("cmd /c dir c:");
try (InputStream is = ps.getInputStream()) {
InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(is);
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(isr);
String ret = null;
while ((ret = br.readLine()) != null) {
System.out.println(ret);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}执行结果:存在一些乱码,是一些中文没有做转换
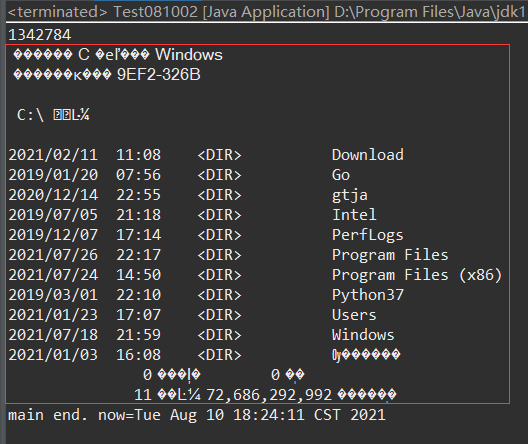
未使用:
runFinalizersOnExit(boolean)
halt(int)
exit(int)
load(String)
loadLibrary(String)
traceInstructions(boolean)
traceMethodCalls(boolean)
3、IOException: 系统找不到指定的文件,java调用可执行程序
4、