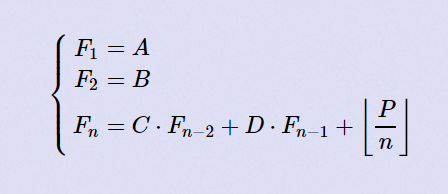
Your job is simple, for each task, you should output Fn module 109+7.
Input
The first line has only one integer T, indicates the number of tasks.
Then, for the next T lines, each line consists of 6 integers, A , B, C, D, P, n.
1≤T≤200≤A,B,C,D≤1091≤P,n≤109
Output
36
24
Sample Input
2
3 3 2 1 3 5
3 2 2 2 1 4
Sample Output
36
24
首先处理递推式这里,因为直接递推会超时,我们考虑矩阵快速幂,然后看题,有三个未知量,我们构造3*3的矩阵,然后因为还有一个数论分块,不能直接使用矩阵快速幂,应该相等的位置使用矩阵快速幂,然后完事了
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int mod = 1e9+7;
int a, b, c, d, p, n, t;
struct mat{
int m[3][3];
mat(){
memset(m, 0, sizeof(mat));
}
friend mat operator*(mat a, mat b){
mat c;
for(int i=0; i<3; i++){
for(int j=0; j<3; j++){
ll t = 0;
for(int k=0; k<3; k++){
t += (ll)a.m[i][k]*b.m[k][j];
}
c.m[i][j] = t%mod;
}
}
return c;
}
}I;
mat pow_mat(mat a, int b){
mat c = I;
while(b){
if(b&1){
c = c*a;
}
a = a*a;
b >>= 1;
}
return c;
}
int main(){
I.m[0][0] = I.m[1][1] = I.m[2][2] = 1;
scanf("%d", &t);
while(t--){
scanf("%d%d%d%d%d%d", &a, &b, &c, &d, &p, &n);
if(n == 1){
printf("%d
", a);
continue;
}
mat f;
f.m[0][0] = d;
f.m[0][1] = c;
f.m[1][0] = 1;
f.m[2][2] = 1;
int flag = 0;
for(int i=3; i<=n;){
if(p/i == 0){
mat w = f;
w = pow_mat(w, n-i+1);
ll ans = w.m[0][0]*(ll)b%mod + w.m[0][1]*(ll)a + w.m[0][2]%mod;
ans %= mod;
printf("%lld
", ans);
flag = 1;
break;
}
int j = min(n, p/(p/i));
mat w = f;
w.m[0][2] = p/i;
w = pow_mat(w, j-i+1);
ll tmp1 = (w.m[1][0]*(ll)b + w.m[1][1]*(ll)a + w.m[1][2]) % mod;
ll tmp2 = (w.m[0][0]*(ll)b + w.m[0][1]*(ll)a + w.m[0][2]) % mod;
a = tmp1; b = tmp2;
i = j+1;
}
if(!flag)
printf("%d
", b);
}
}