样例输入:
file1 file2
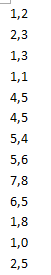

实验思路:我们设置一个新类myNewKey,这个类继承WritableComparable接口。然后我们把myNewKey写入map中,然后在map阶段中,实现自动排序,我们只需在reduce阶段输出就可以了。
代码:
MyNewKey.java:
import java.io.DataInput;
import java.io.DataOutput;
import java.io.IOException;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.WritableComparable;
public class MyNewKey implements WritableComparable<MyNewKey> {
long firstNum;
long secondNum;
public MyNewKey() {
}
public MyNewKey(long first, long second) {
firstNum = first;
secondNum = second;
}
@Override
public void write(DataOutput out) throws IOException {
out.writeLong(firstNum);
out.writeLong(secondNum);
}
@Override
public void readFields(DataInput in) throws IOException {
firstNum = in.readLong();
secondNum = in.readLong();
}
/*
* 当key进行排序时会调用以下这个compreTo方法
*/
@Override
public int compareTo(MyNewKey anotherKey) {
long min = firstNum - anotherKey.firstNum;
if (min != 0) {
// 说明第一列不相等,则返回两数之间小的数
return (int) min;
} else {
return (int) (secondNum - anotherKey.secondNum);
}
}
public long getFirstNum() {
return firstNum;
}
public long getSecondNum() {
return secondNum;
}
}
现在是我们的mapreduce代码:
import java.io.IOException;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.FileSystem;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.NullWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat;
public class doublesort {
static String INPUT_PATH = "hdfs://master:9000/ls";
static String OUTPUT_PATH="hdfs://master:9000/output";
static class MyMapper extends Mapper<Object,Object,MyNewKey,NullWritable>{
MyNewKey output_key = new MyNewKey();
NullWritable output_value = NullWritable.get();
protected void map(Object key,Object value,Context context) throws IOException,InterruptedException{
String[] tokens = value.toString().split(",",2);
MyNewKey output_key=new MyNewKey(Long.parseLong(tokens[0]),Long.parseLong(tokens[1]));
context.write(output_key, output_value);
}
}
static class MyReduce extends Reducer<MyNewKey,NullWritable,LongWritable,LongWritable> {
LongWritable output_key = new LongWritable();
LongWritable output_value = new LongWritable();
protected void reduce(MyNewKey key, Iterable<NullWritable> values,Context context) throws IOException,InterruptedException{
output_key.set(key.getFirstNum());
output_value.set(key.getSecondNum());
context.write(output_key, output_value);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
Path outputpath = new Path(OUTPUT_PATH);
Configuration conf = new Configuration();
FileSystem fs = outputpath.getFileSystem(conf);
if(fs.exists(outputpath)){
fs.delete(outputpath,true);
}
Job job=Job.getInstance(conf);
FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job,INPUT_PATH);
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, outputpath);
job.setMapperClass(MyMapper.class);
//job.setPartitionerClass(MyPartitioner.class);
//job.setNumReduceTasks(2);
job.setReducerClass(MyReduce.class);
job.setMapOutputKeyClass(MyNewKey.class);
job.setMapOutputValueClass(NullWritable.class);
job.setOutputKeyClass(LongWritable.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(LongWritable.class);
job.waitForCompletion(true);
}
}
输出结果:
