树
树形结构常用来表示层次化或序列化的结构。
树是含有n个结点的有限集合。结点数n=0的树称为空树。任意一棵非空树中有且仅有一个根结点。
为方便描述结点间的层次关系,有以下定义:
子结点:位于当前结点之下,且与当前结点直接相连的结点。一个结点可以有任意个子结点。没有子结点的结点又被称为叶子结点。
父结点:位于当前结点之上,且与当前结点直接相连的结点。除了根结点之外,每一个结点都有一个父结点。
兄弟结点:与当前结点处于同一层次,且有相同父结点的结点。除了根结点之外,每一个结点都可以有兄弟结点。
结点的层次是指从根结点开始计,根结点为第1层,根结点的子结点为第2层......依次往下。一棵树的深度指的是从根结点出发所能到达的最大层次。
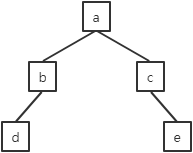
例如,非空树:

1.结点a是根结点。根结点没有父结点,也没有兄弟结点。结点a处于第1层。结点a有3个子结点b、c、d。
2.结点b、c、d有共同的父结点a。它们互为兄弟结点。结点b、c、d处于第2层。结点b、c、d都各有1个子结点,分别是e、f、g。
3.结点e、f、g的父结点分别是b、c、d。虽然它们处于同一层次,但是父结点不同,所以它们不是兄弟结点。结点e、f、g处于第3层。
4.因为从根结点a出发所能到达的最大层次是第3层,所以该树的深度为3。
链式结构
树的存储结构有多种,较常用的是链式结构,即使用结点来存储信息,包括数据、父结点指针、兄弟结点指针、子结点指针等。定义如下:

1 class TNode { 2 3 E data; 4 TNode parent; 5 TNode priorSibling; 6 TNode nextSibling; 7 TNode firstChild; 8 TNode lastChild; 9 10 }
a.若parent == null,表示没有父结点,即当前结点为根结点,没有兄弟结点,故有priorSibling == null,nextSibling == null。
b.若priorSibling == null,表示没有左兄弟结点,即当前结点为其父结点的首子结点,故有parent.firstChild == this。同理,若nextSibling == null,表示没有右兄弟结点,即当前结点为其父结点的尾子结点,故有parent.lastChild == this。
c.若为叶子结点,其firstChild == null,lastChild == null。
d.若一个结点只有一个子结点,其firstChild == lastChild。
遍历
遍历一棵树指的是访问该树所有的结点,使得每个结点都只被访问一次。由于树是一种层次结构,结点与其子结点是一对多的关系,对子结点的访问次序不同就会得到不同的遍历次序。
树的遍历次序区别在于根结点和子结点访问的先后,以及子结点的访问方向,所以树的遍历策略分为4种:
VLR:先访问根结点,后访问子结点,子结点从左往右访问。
VRL:先访问根结点,后访问子结点,子结点从右往左访问。
LRV:先访问子结点,子结点从左往右访问,后访问根结点。
RLV:先访问子结点,子结点从右往左访问,后访问根结点。
递归遍历:

1 public void VLR(TNode node) { 2 System.out.print(node.data + " "); 3 if (node.firstChild != null) VLR(node.firstChild); 4 if (node.nextSibling != null) VLR(node.nextSibling); 5 }

1 public void VRL(TNode node) { 2 System.out.print(node.data + " "); 3 if (node.lastChild != null) LRV(node.lastChild); 4 if (node.priorSibling != null) LRV(node.priorSibling); 5 }

1 public void LRV(TNode node) { 2 if (node.firstChild != null) LRV(node.firstChild); 3 System.out.print(node.data + " "); 4 if (node.nextSibling != null) LRV(node.nextSibling); 5 }

1 public void RLV(TNode node) { 2 if (node.lastChild != null) LRV(node.lastChild); 3 System.out.print(node.data + " "); 4 if (node.priorSibling != null) LRV(node.priorSibling); 5 }
非递归遍历:

1 public void VLR(TNode node) { 2 TNode n = node; 3 System.out.print(n.data + " "); 4 while (n.firstChild != null) { 5 n = n.firstChild; 6 System.out.print(n.data + " "); 7 } 8 while (n != node.parent) { 9 while (n.nextSibling != null) { 10 n = n.nextSibling; 11 System.out.print(n.data + " "); 12 while (n.firstChild != null) { 13 n = n.firstChild; 14 System.out.print(n.data + " "); 15 } 16 } 17 n = n.parent; 18 } 19 }

1 public void VRL(TNode node) { 2 TNode n = node; 3 System.out.print(n.data + " "); 4 while (n.lastChild != null) { 5 n = n.lastChild; 6 System.out.print(n.data + " "); 7 } 8 while (n != node.parent) { 9 while (n.priorSibling != null) { 10 n = n.priorSibling; 11 System.out.print(n.data + " "); 12 while (n.lastChild != null) { 13 n = n.lastChild; 14 System.out.print(n.data + " "); 15 } 16 } 17 n = n.parent; 18 } 19 }

1 public void LRV(TNode node) { 2 TNode n = node; 3 while (n.firstChild != null) n = n.firstChild; 4 while (n != node.parent) { 5 System.out.print(n.data + " "); 6 while (n.nextSibling != null) { 7 n = n.nextSibling; 8 while (n.firstChild != null) n = n.firstChild; 9 System.out.print(n.data + " "); 10 } 11 n = n.parent; 12 } 13 }

1 public void RLV(TNode node) { 2 TNode n = node; 3 while (n.lastChild != null) n = n.lastChild; 4 while (n != node.parent) { 5 System.out.print(n.data + " "); 6 while (n.priorSibling != null) { 7 n = n.priorSibling; 8 while (n.lastChild != null) n = n.lastChild; 9 System.out.print(n.data + " "); 10 } 11 n = n.parent; 12 } 13 }
在定义结点时若没有parent指针,则在遍历时需要使用栈存储经过的结点,这样就可以通过出栈获取父结点。
除了上述遍历之外,还有一种层次遍历。层次遍历是按二叉树层次从小到大且每层从左到右的顺序依次遍历访问结点。
递归层次遍历:

1 public void levelOrderTraverse(TNode node) { 2 for (int level = 1; level <= getDepth(node); level++) levelOrderTraverse(node, level); 3 } 4 5 public void levelOrderTraverse(TNode node, int level) { 6 for (TNode n = node; n != null; n = n.nextSibling) { 7 if (level == 1) System.out.print(n.data + " "); 8 else levelOrderTraverse(n.firstChild, level - 1); 9 } 10 }
非递归层次遍历:

1 public void levelOrderTraverse(TNode node) { 2 Queue<TNode> q = new LQueue<TNode>(false); 3 System.out.print(node.data + " "); 4 q.enQueue(node); 5 while (! q.queueEmpty()) { 6 for (TNode n = q.deQueue().firstChild; n != null; n = n.nextSibling) { 7 System.out.print(n.data + " "); 8 q.enQueue(n); 9 } 10 } 11 }
对该树进行遍历:

VLR:a --> b --> e --> c --> f --> d --> g
VRL:a --> d --> g --> c --> f --> b --> e
LRV:e --> b --> f --> c --> g --> d --> a
RLV:g --> d --> f --> c --> e --> b --> a
层次遍历:a --> b --> c --> d --> e --> f --> g
插入
树的插入操作分为4种(设指定结点为node,插入结点为n):
a.插入根结点:若原根结点不存在,即root == null,则插入一个根结点,即root = n。定义如下:

1 public void addRoot(E data) throws TreeException { 2 if (root != null) throw new TreeException("结点已存在!"); 3 root = new TNode(data); 4 num++; 5 }
b.插入子结点:若指定结点的子结点不存在,即node.firstChild == null,node.lastChild == null,则插入一个子结点,node.firstChild = n,node.lastChild = n。定义如下:

1 public void addChild(TNode node, E data) throws TreeException { 2 if (node.firstChild != null) throw new TreeException("孩子结点已存在!"); 3 node.firstChild = node.lastChild = new TNode(data, node); 4 num++; 5 }
c.插入左兄弟结点:插入一个左兄弟结点,若指定结点为其父结点的首子结点,即node.priorSibling == null,则node.parent.firstChild = n;否则node.priorSibling.nextSibling = n。定义如下:

1 public void addPriorSibling(TNode node, E data) throws TreeException { 2 if (node == root) throw new TreeException("根结点没有兄弟结点!"); 3 TNode n = new TNode(data, node.parent, null, node); 4 if (node.priorSibling == null) { 5 node.parent.firstChild = n; 6 } else { 7 n.priorSibling = node.priorSibling; 8 node.priorSibling.nextSibling = n; 9 } 10 node.priorSibling = n; 11 num++; 12 }
d.插入右兄弟结点:插入一个右兄弟结点,若指定结点为其父结点的尾子结点,即node.nextSibling == null,则node.parent.lastChild = n;否则node.nextSibling.priorSibling = n。

1 public void addNextSibling(TNode node, E data) throws TreeException { 2 if (node == root) throw new TreeException("根结点没有兄弟结点!"); 3 TNode n = new TNode(data, node.parent, node, null); 4 if (node.nextSibling == null) { 5 node.parent.lastChild = n; 6 } else { 7 n.nextSibling = node.nextSibling; 8 node.nextSibling.priorSibling = n; 9 } 10 node.nextSibling = n; 11 num++; 12 }
删除
树的删除操作分为5种情况(设删除结点为node):
a.若指定结点为根结点,则删除整棵树,即root = null。
b.若指定结点为其父结点的唯一子结点,即node.parent.firstChild == node,node.parent.lastChild == node,则node.parent.firstChild = null,node.parent.lastChild = null。
c.若指定结点为其父结点的首子结点,即node.parent.firstChild == node,则node.parent.firstChild = node.nextSibling,node.nextSibling.priorSibling = null。
d.若指定结点为其父结点的尾子结点,即node.parent.lastChild == node,则node.parent.lastChild = node.priorSibling,node.priorSibling.nextSibling = null。
e.非上述4种特殊结点,则node.priorSibling.nextSibling = node.nextSibling,node.nextSibling.priorSibling = node.priorSibling。
删除操作的定义如下:

1 public void remove(TNode node) { 2 if (node == root) root = null; 3 else { 4 if (node.priorSibling == null) { 5 if (node.nextSibling == null) node.parent.firstChild = node.parent.lastChild = null; 6 else node.parent.firstChild = node.nextSibling; 7 } 8 else node.priorSibling.nextSibling = node.nextSibling; 9 if (node.nextSibling == null) node.parent.lastChild = node.priorSibling; 10 else node.nextSibling.priorSibling = node.priorSibling; 11 } 12 num--; 13 }
二叉树
二叉树是每个结点最多只有两个子结点的树。由于限制了子结点数,相比于一般的树,二叉树具有以下性质:
a.深度为k(k≥0)的二叉树最多有2k-1个结点。
b.非空二叉树的第l(1≤l≤k)层最多有2l-1个结点。
c.非空二叉树叶子结点总比子结点数为2的结点多1个。
链式结构
因为二叉树每个结点最多只有两个子结点,所以相较于树的结点,二叉树的结点少了指向兄弟结点的指针。二叉树结点的定义如下:

1 class BTNode { 2 3 E data; 4 BTNode parent; 5 BTNode lchild; 6 BTNode rchild; 7 char tag; 8 9 }
a.若结点为根结点,则parent = null,tag = 0。
b.若结点为其父结点的左子结点,则tag = 'l'。
c.若结点为其父结点的右子结点,则tag = 'r'。
d.若为叶子结点,则lchild = null,rchild = null。
遍历
二叉树的遍历策略有:
VLR:先访问根结点,再访问左子结点,最后访问右子结点。
VRL:先访问根结点,再访问右子结点,最后访问左子结点。
LRV:先访问左子结点,再访问右子结点,最后访问根结点。
RLV:先访问右子结点,再访问左子结点,最后访问根结点。
LVR:先访问左子结点,再访问根结点,最后访问右子结点。
RVL:先访问右子结点,再访问根结点,最后访问左子结点。
通常情况下,遍历二叉树时左子结点先于右子结点被访问。若加上该限定,则只剩下3种策略:VLR(前序遍历)、LVR(中序遍历)、LRV(后序遍历)。
除此之外,二叉树也有层次遍历。
递归遍历:

1 public void VLR(BTNode node) { 2 System.out.print(node.data + " "); 3 if (node.lchild != null) VLR(node.lchild); 4 if (node.rchild != null) VLR(node.rchild); 5 }

1 public void VRL(BTNode node) { 2 System.out.print(node.data + " "); 3 if (node.rchild != null) VRL(node.rchild); 4 if (node.lchild != null) VRL(node.lchild); 5 }

1 public void LRV(BTNode node) { 2 if (node.lchild != null) LRV(node.lchild); 3 if (node.rchild != null) LRV(node.rchild); 4 System.out.print(node.data + " "); 5 }

1 public void RLV(BTNode node) { 2 if (node.rchild != null) RLV(node.rchild); 3 if (node.lchild != null) RLV(node.lchild); 4 System.out.print(node.data + " "); 5 }

1 public void LVR(BTNode node) { 2 if (node.lchild != null) LVR(node.lchild); 3 System.out.print(node.data + " "); 4 if (node.rchild != null) LVR(node.rchild); 5 }

1 public void RVL(BTNode node) { 2 if (node.rchild != null) RVL(node.rchild); 3 System.out.print(node.data + " "); 4 if (node.lchild != null) RVL(node.lchild); 5 }

1 public void levelOrderTraverse(BTNode node) { 2 for (int level = 1; level <= getDepth(node); level++) levelOrderTraverse(node, level); 3 } 4 5 public void levelOrderTraverse(BTNode node, int level) { 6 if (level == 1) System.out.print(data + " "); 7 else { 8 if (node.lchild != null) levelOrderTraverse(node.lchild, level - 1); 9 if (node.rchild != null) levelOrderTraverse(node.rchild, level - 1); 10 } 11 }
非递归遍历:

1 public void VLR(BTNode node) { 2 BTNode n = node; 3 while (n != null) { 4 System.out.print(n.data + " "); 5 if (n.lchild != null) n = n.lchild; 6 else if (n.rchild != null) n = n.rchild; 7 else { 8 BTNode nr; 9 do { 10 nr = n; 11 n = n.parent; 12 } while (n != null && (nr.tag == 'r' || n.rchild == null)); 13 if (n != null) n = n.rchild; 14 } 15 } 16 }

1 public void VRL(BTNode node) { 2 BTNode n = node; 3 while (n != null) { 4 System.out.print(n.data + " "); 5 if (n.rchild != null) n = n.rchild; 6 else if (n.lchild != null) n = n.lchild; 7 else { 8 BTNode nr; 9 do { 10 nr = n; 11 n = n.parent; 12 } while (n != null && (nr.tag == 'l' || n.lchild == null)); 13 if (n != null) n = n.lchild; 14 } 15 } 16 }

1 public void LRV(BTNode node) { 2 BTNode n = node; 3 while (n != null) { 4 if (n.lchild != null) n = n.lchild; 5 else if (n.rchild != null) n = n.rchild; 6 else { 7 BTNode nr; 8 do { 9 System.out.print(n.data + " "); 10 nr = n; 11 n = n.parent; 12 } while (n != null && (nr.tag == 'r' || n.rchild == null)); 13 if (n != null) n = n.rchild; 14 } 15 } 16 }

1 public void RLV(BTNode node) { 2 BTNode n = node; 3 while (n != null) { 4 if (n.rchild != null) n = n.rchild; 5 else if (n.lchild != null) n = n.lchild; 6 else { 7 BTNode nr; 8 do { 9 System.out.print(n.data + " "); 10 nr = n; 11 n = n.parent; 12 } while (n != null && (nr.tag == 'l' || n.lchild == null)); 13 if (n != null) n = n.lchild; 14 } 15 } 16 }

1 public void LVR(BTNode node) { 2 BTNode n = node; 3 while (n != null) { 4 if (n.lchild != null) n = n.lchild; 5 else { 6 System.out.print(n.data + " "); 7 if (n.rchild != null) n = n.rchild; 8 else { 9 BTNode nr; 10 do { 11 nr = n; 12 n = n.parent; 13 } while (n != null && (nr.tag == 'r' || n.rchild == null)); 14 if (n != null) { 15 System.out.print(n.data + " "); 16 n = n.rchild; 17 } 18 } 19 } 20 } 21 }

1 public void RVL(BTNode node) { 2 BTNode n = node; 3 while (n != null) { 4 if (n.rchild != null) n = n.rchild; 5 else { 6 System.out.print(n.data + " "); 7 if (n.lchild != null) n = n.lchild; 8 else { 9 BTNode nr; 10 do { 11 nr = n; 12 n = n.parent; 13 } while (n != null && (nr.tag == 'l' || n.lchild == null)); 14 if (n != null) { 15 System.out.print(n.data + " "); 16 n = n.lchild; 17 } 18 } 19 } 20 } 21 }

1 public void levelOrderTraverse(BTNode node) { 2 Queue<BTNode> q = new LQueue<BTNode>(false); 3 System.out.print(node.data + " "); 4 q.enQueue(node); 5 while (! q.queueEmpty()) { 6 BTNode n = q.deQueue(); 7 if (n.lchild != null) { 8 System.out.print(n.lchild.data + " "); 9 q.enQueue(n.lchild); 10 } 11 if (n.rchild != null) { 12 System.out.print(n.rchild.data + " "); 13 q.enQueue(n.rchild); 14 } 15 } 16 }
对该树进行遍历:
VLR:a --> b --> d --> c --> e
VRL:a --> c --> e --> b --> d
LRV:d --> b --> e --> c --> a
RLV:e --> c --> d --> b --> a
LVR:d --> b --> a --> c --> e
RVL:e --> c --> a --> b --> d
层次遍历:a --> b --> c --> d --> e
插入
二叉树的插入操作需要注意插入位置没有结点存在。插入操作的定义如下:

1 public void addRoot(E data) throws TreeException { 2 if (data == null) return; 3 if (root != null) throw new TreeException("结点已存在!"); 4 root = new BTNode(data); 5 num++; 6 }

1 public void addLchild(BTNode node, E data) throws TreeException { 2 if (data == null) return; 3 if (node.lchild != null) throw new TreeException("结点已存在!"); 4 node.lchild = new BTNode(data, node, 'l'); 5 num++; 6 }

1 public void addRchild(BTNode node, E data) throws TreeException { 2 if (data == null) return; 3 if (node.rchild != null) throw new TreeException("结点已存在!"); 4 node.rchild = new BTNode(data, node, 'r'); 5 num++; 6 }
删除
二叉树的删除操作分3种情况(设删除结点为node):
a.若删除结点为根结点,即node == root,则root = null。
b.若删除结点为其父结点的左结点,即node.tag == 'l',则node.parent.lchild = null。
c.若删除结点为其父结点的右结点,即node.tag == 'r',则node.parent.rchild = null。
删除操作的定义如下:

1 public void remove(BTNode node) { 2 if (node == root) { 3 root = null; 4 num = 0; 5 } else { 6 if (node.tag == 'l') node.parent.lchild = null; 7 else node.parent.rchild = null; 8 num -= getNum(node); 9 } 10 }
完全二叉树
满二叉树是每一层的结点数都达到最多的非空二叉树。满二叉树的性质有:
a.深度为k(k≥0)的二叉树有2k-1个结点。
b.第l(1≤l≤k)层有2l-1个结点。
c.前k-1层的结点的子结点数都为2。
结点编号:从根结点起,自上而下,自左而右给满二叉树每个结点从1开始编号。
若n(n>0)个结点的二叉树的每个结点都与同深度的满二叉树中编号1~n的结点一一对应,则称为完全二叉树。完全二叉树的性质有:
a.根结点编号为1,左结点编号为正偶数,右结点编号为大于1的正奇数。
b.结点i(i≥1)的左子结点编号为2i,右子结点编号为2i+1。
c.结点i(i>1)的父结点编号为⌊i/2⌋。
d.第i(1≤i<k,k为深度)层有2i-1个结点。第一个结点编号为2i-1,最后一个结点编号为2i-1。
e.第k层的结点数在[1,2k-1]范围内。结点编号在[2k-1,n]范围内。第k层的结点数达到最大,则为满二叉树。
f.最大结点编号为结点数,在[2k-1,2k-1]范围内。最大结点编号达到2k-1,则为满二叉树。
g.设叶子结点的个数为n0,子结点数为1的结点的个数为n1,子结点数为2的结点的个数为n2,则:n0=[n+(n%2)]/2,n1=1-(n%2),n2=[n+(n%2)-2]/2。

顺序结构
因为完全二叉树结点间的关系可以通过结点编号计算得到,所以无需再定义指针来表示结点间的关系。于是可以使用数组来存储元素,有2种方式:
a.数组容量比结点数大1,数组第一个位置不使用。这样的话,数组下标就是结点编号,结点数比数组长度少1。
b.数组容量与结点数相同。这样的话,数组下标比结点编号少1,结点数就是数组长度。
遍历
遍历顺序结构的完全二叉树通常是直接按数组下标顺序遍历,此时遍历的结果为层次遍历。
插入
为了保证插入结点之后的二叉树仍为完全二叉树,一般只允许在末尾插入结点。
删除
为了保证删除某个结点之后的二叉树仍为完全二叉树,一般是将当前结点中的元素与最后一个结点中的元素交换,然后删除最后一个结点。
判定
顺序存储的完全二叉树(结点数为n(n>1))可以通过结点编号的计算来得到结点的某些信息。例如:
a.若结点编号为1,则该结点为根结点。
b.结点i(1≤i<⌊n/2⌋)的子结点数为2。
c.结点i(⌊n/2⌋<i≤n)为叶子结点。
d.若n为奇数,则结点⌊n/2⌋的子结点数为2;否则结点⌊n/2⌋的子结点数为1。
二叉查找树
二叉查找树是一种专为查找而设计的二叉树,可提高查找效率。二叉查找树的元素必须是可比较的,即元素类型对应的类必须实现Comparable接口并重写其compareTo()方法。
二叉查找树的结点有以下特点:
a. 对任意一个结点,若其左子结点存在,则左子结点的元素值小于该结点的元素值。
b. 对任意一个结点,若其右子结点存在,则右子结点的元素值大于该结点的元素值。
c. 对任意一个结点,若其父结点存在,则父结点的元素值要大于该结点及其所有子结点的元素值。
d. 二叉查找树不存在元素值相同的结点。
e. 最小元素值的结点是根结点的最左子结点。
f. 最大元素值的结点是根结点的最右子结点。
链式结构
二叉查找树的结点与二叉树的结点一样,都是存储元素、父结点指针和左右子结点指针。
遍历
二叉查找树的遍历与二叉树相同。特殊的是:
a.采用LVR遍历策略遍历,则结果呈升序排列。
b.采用RVL遍历策略遍历,则结果呈降序排列。
查找
根据二叉查找树结点的特点,可以知道:若待查元素值比当前结点的元素值小,则其结点是当前结点左子;比当前结点的元素值大,则其结点是当前结点的右子。据此可以递归查找当前二叉查找树是否存在指定元素值的结点。
二叉查找树的查找过程是一个逐步缩小查找范围的过程。查找过程中关键字的比较次数不超过其深度。所以,二叉查找树的查找性能与其深度相关,深度越小的二叉查找树的查找性能越好。最好的情况是二叉查找树的深度最小,时间复杂度为O(log n);最坏的情况是单支树,时间复杂度为O(n)。
插入
在二叉查找树上插入结点时,应该找到合适的位置,即通过比较寻找位置,同时判断元素值是否重复。
删除
二叉查找树删除结点时,必须维持二叉查找树的特性,分为3种情况:
a.被删结点为叶子结点:直接删除。
b.被删结点只有一个子结点:将该子结点移至该结点的位置,然后删除该结点。
c.被删结点有两个子结点:将该子结点的元素值改为其左子结点的最右子结点的元素值(待删除结点左子最大元素值的结点),然后删除其左子结点的最右子结点。由于是最右子结点,其右子结点必定不存在,删除时就变成了a或b的情况。
获取结点
无论是查找、插入还是删除操作都涉及到根据元素值获取结点的操作。于是将该操作提取为一个函数。若指定元素值的元素存在,则返回该结点;否则返回最接近的结点。定义如下:

1 public BTNode getNode(BTNode node, E data) { 2 if (data.equals(node.data)) return node; 3 BTNode n; 4 if (data.compareTo(node.data) < 0) { 5 if (node.lchild != null) { 6 n = getNode(node.lchild, data); 7 if (n != null) return n; 8 } 9 } else { 10 if (node.rchild != null) { 11 n = getNode(node.rchild, data); 12 if (n != null) return n; 13 } 14 } 15 return node; 16 }
查找操作变为:若获取结点的结点值为指定结点值,则返回true;否则返回false。定义如下:

1 public boolean isExist(E data) { 2 return root != null && data.equals(getNode(root, data).data); 3 }
插入操作变为:若获取结点的结点值为指定结点值,表示存在待插入元素值的结点,则不能进行插入操作;否则获取到的结点即为待插入结点的父结点,若待插入结点的元素值较大,则为右子结点,否则为左子结点。定义如下:

1 public void add(E data) throws TreeException { 2 if (isEmpty()) { 3 addRoot(data); 4 } else { 5 BTNode node = getNode(root, data); 6 if (data.equals(node.data)) { 7 throw new TreeException("该元素已存在!"); 8 } 9 if (data.compareTo(node.data) < 0) { 10 node.lchild = new BTNode(data, node, 'l'); 11 node = node.lchild; 12 } else { 13 node.rchild = new BTNode(data, node, 'r'); 14 node = node.rchild; 15 } 16 } 17 num++; 18 }
删除操作变为:若获取结点的结点值为指定结点值,表示结点存在,对该结点进行删除操作;否则表示结点不存在,直接返回。定义如下:

1 public void remove(E data) { 2 BTNode node = getNode(root, data); 3 if (data.equals(node.data)) remove(node); 4 } 5 6 @SuppressWarnings("preview") 7 public void remove(BTNode node) { 8 if (node.lchild == null && node.rchild == null) { 9 if (node == root) root = null; 10 else { 11 switch (node.tag) { 12 case 'l' -> { 13 node.parent.lchild = null; 14 } 15 case 'r' -> { 16 node.parent.rchild = null; 17 } 18 } 19 } 20 } else if (node.lchild == null) { 21 if (node.tag == 'l') { 22 node.rchild.tag = 'l'; 23 node.parent.lchild = node.rchild; 24 } 25 else if (node.tag == 'r') node.parent.rchild = node.rchild; 26 node.rchild.parent = node.parent; 27 } else if (node.rchild == null) { 28 if (node.tag == 'l') node.parent.lchild = node.lchild; 29 else if (node.tag == 'r') { 30 node.lchild.tag = 'r'; 31 node.parent.rchild = node.lchild; 32 } 33 node.lchild.parent = node; 34 } else { 35 BTNode rNode = node.lchild; 36 while (rNode.rchild != null) rNode = rNode.rchild; 37 node.data = rNode.data; 38 rNode.parent.rchild = rNode.lchild; 39 remove(rNode); 40 } 41 num--; 42 }
平衡二叉树
欲使二叉查找树性能达到最优,其深度应该最小。结点数相同的二叉树中,完全二叉树的深度最小,但是如果采用完全二叉树来作为二叉查找树,在插入操作和删除操作后维护的代价较大。平衡二叉树是一种兼顾查找和插入删除后的维护性能的折中方案。
平衡二叉树是特殊的二叉查找树,其左子和右子的深度差不超过1。使用平衡因子来表示一个结点左子和右子的深度差,其定义为左子深度减去右子深度。平衡二叉树的平衡因子取值必须保持在-1、0、1这三个值中。若平衡因子大于1或小于-1,则表示该结点失衡,需要进行调整。
链式结构
在二叉查找树结点结构的基础上新增一个数据域来存储平衡因子。定义如下:

1 class BBSTNode { 2 3 E data; 4 BBSTNode parent; 5 BBSTNode lchild; 6 BBSTNode rchild; 7 char tag; 8 int bf; 9 10 }
查找、插入、删除
平衡二叉树的查找过程和二叉查找树的查找过程相同。由于平衡二叉树是经过平衡调整的二叉查找树,比较次数和log n是同数量级的。
相比二叉查找树,在平衡二叉树上插入或删除结点时可能导致平衡二叉树失衡,所以在每次插入和删除操作后都必须判断是否失衡,若失衡则需要进行调整。
失衡判断以及平衡调整
结点的平衡因子大于1或小于-1时表示该结点失衡。其中若平衡因子大于1,表示左子过深,需要进行左平衡调整;若平衡因子小于1,表示右子过深,需要进行右平衡调整。
在一个结点上新插入子结点,则从该结点开始,需要变更平衡因子。具体步骤如下:
a.若插入的是左子结点,则该结点的平衡因子+1;若插入的是右子结点,则该结点的平衡因子-1。
b.若该结点的平衡因子变化后不为0,则需要修改其父结点的平衡因子。该结点若为其父结点的左子结点,则其父结点的平衡因子+1;若为其父结点的右子结点,则其父结点的平衡因子-1。若其父结点的平衡因子变化后大于1,则需要进行左平衡调整;小于-1,则需要进行右平衡调整。
c.循环步骤b,直到结点的平衡因子为0或结点为根结点时结束。
插入平衡调整的定义如下:

1 public void addBalance(BBSTNode node, int bf) { 2 node.bf += bf; 3 while (node != root && node.bf != 0) { 4 if (node.tag == 'l') { 5 node.parent.bf++; 6 if (node.parent.bf > 1) lBalance(node); 7 } else { 8 node.parent.bf--; 9 if (node.parent.bf < -1) rBalance(node); 10 } 11 node = node.parent; 12 } 13 }
删除一个结点子结点,则从该结点开始,需要变更平衡因子。具体步骤如下:
a.若删除的是左子结点,则该结点的平衡因子-1;若删除的是右子结点,则该结点的平衡因子+1。若该结点的平衡因子变化后大于1,则需要进行左平衡调整;小于-1,则需要进行右平衡调整。
b.若该结点不是根结点(存在父结点),且经过变化后其平衡因子为0,则需要递归修改其父结点的平衡因子。该结点若为左结点,则其父结点的平衡因子-1;若为右结点,则其父结点的平衡因子+1。
删除平衡调整的定义如下:

1 public void removeBalance(BBSTNode node, int bf) { 2 node.bf += bf; 3 if (node.bf > 1) lBalance(node.lchild); 4 else if (node.bf < -1) rBalance(node.rchild); 5 if (node != root && node.bf == 0) { 6 if (node.tag == 'l') removeBalance(node.parent, -1); 7 else removeBalance(node.parent, 1); 8 } 9 }
左平衡调整分为3种情况:
a.当前结点的平衡因子为1(插入、删除操作可能出现该情况):将当前结点的平衡因子和其父结点的平衡因子置为0,并对其父结点的平衡因子进行右旋处理。

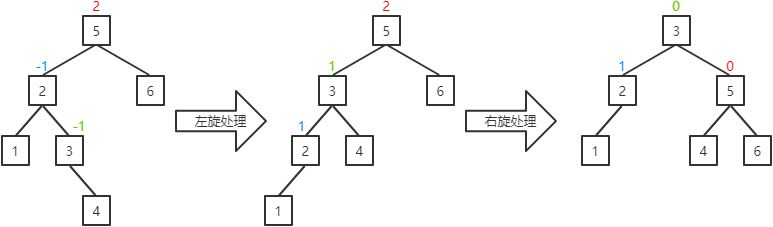
b.当前结点的平衡因子为-1(插入、删除操作可能出现该情况):分为3种情况:
I. 当前结点的右子结点的平衡因子为-1:将当前结点的平衡因子置为1,其父结点的平衡因子置为0,其右子结点的平衡因子置为0,并对当前结点进行左旋处理,然后对其父结点进行右旋处理。
II. 当前结点的右子结点的平衡因子为0:将当前结点的平衡因子和其父结点的平衡因子置为0,其右子结点的平衡因子置为0,并对当前结点进行左旋处理,然后对其父结点进行右旋处理。
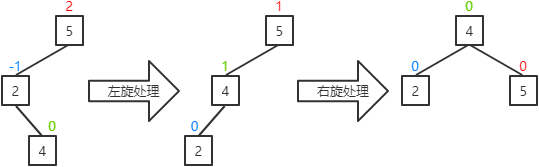
III.当前结点的右子结点的平衡因子为1:将当前结点的平衡因子置为0,其父结点的平衡因子置为-1,其右子结点的平衡因子置为0,并对当前结点进行左旋处理,然后对其父结点进行右旋处理。
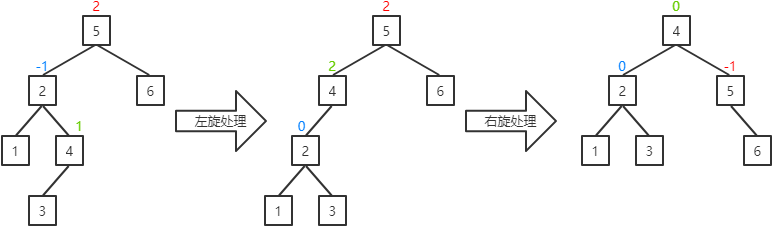
c.当前结点的平衡因子为0(删除操作可能出现该情况):将当前结点的平衡因子置为-1,其父结点的平衡因子置为1,并对其父结点进行右旋处理。
左平衡处理的定义如下:

1 @SuppressWarnings("preview") 2 public void lBalance(BBSTNode node) { 3 BBSTNode parent = node.parent; 4 switch (node.bf) { 5 case 1 -> { 6 node.bf = parent.bf = 0; 7 rRotate(parent); 8 } 9 case -1 -> { 10 BBSTNode rchild = node.rchild; 11 switch (rchild.bf) { 12 case -1 -> { 13 node.bf = 1; 14 parent.bf = 0; 15 } 16 case 0 -> { 17 node.bf = parent.bf = 0; 18 } 19 case 1 -> { 20 node.bf = 0; 21 parent.bf = -1; 22 } 23 } 24 rchild.bf = 0; 25 lRotate(node); 26 rRotate(parent); 27 } 28 case 0 -> { 29 node.bf = -1; 30 parent.bf = 1; 31 rRotate(parent); 32 } 33 } 34 }
右平衡调整分为3种情况:
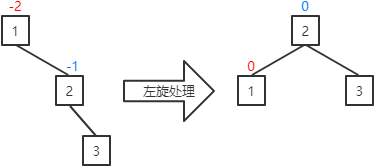
a.当前结点的平衡因子为-1(插入、删除操作可能出现该情况):将当前结点的平衡因子和其父结点的平衡因子置为0,并对其父结点进行左旋处理。
b.当前结点的平衡因子为1(插入、删除操作可能出现该情况):
I. 当前结点的左子结点的平衡因子为-1:将当前结点的平衡因子置为0,其父结点的平衡因子置为1,其左子结点的平衡因子置为0,并对当前结点进行右旋处理,然后对其父结点进行左旋处理。
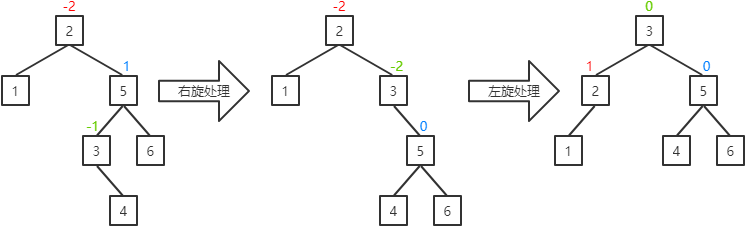
II. 当前结点的左子结点的平衡因子为0:将当前结点和其父结点的平衡因子置为0,其左子结点的平衡因子置为0,并对当前结点进行右旋处理,然后对其父结点进行左旋处理。

III.当前结点的左子结点的平衡因子为1:将当前结点的平衡因子置为-1,其父结点的平衡因子置为0,其左子结点的平衡因子置为0,并对当前结点进行右旋处理,然后对其父结点进行左旋处理。

c.当前结点的平衡因子为0(删除操作可能出现该情况):将当前结点的平衡因子置为1,其父结点的平衡因子置为-1,并对其父结点进行左旋处理。

右平衡调整的定义如下:

1 @SuppressWarnings("preview") 2 public void rBalance(BBSTNode node) { 3 BBSTNode parent = node.parent; 4 switch (node.bf) { 5 case -1 -> { 6 node.bf = parent.bf = 0; 7 lRotate(parent); 8 } 9 case 1 -> { 10 BBSTNode lchild = node.lchild; 11 switch (lchild.bf) { 12 case -1 -> { 13 node.bf = 0; 14 parent.bf = 1; 15 } 16 case 0 -> { 17 node.bf = parent.bf = 0; 18 } 19 case 1 -> { 20 node.bf = -1; 21 parent.bf = 0; 22 } 23 } 24 lchild.bf = 0; 25 rRotate(node); 26 lRotate(parent); 27 } 28 case 0 -> { 29 node.bf = 1; 30 parent.bf = -1; 31 lRotate(parent); 32 } 33 } 34 }
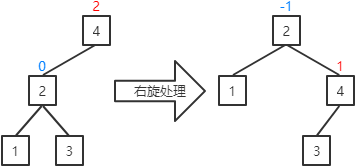
左旋处理过程为:
a.若当前结点的右子结点存在左子,则成为当前结点的右子。(结点5存在左子结点3,所以结点3成为结点2的右子)
b.当前结点成为其右子结点的左子。(结点2成为结点5的左子)
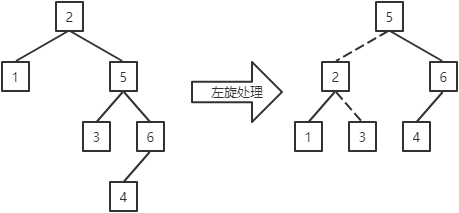
左旋处理的定义如下:

1 @SuppressWarnings("preview") 2 public void lRotate(BBSTNode node) { 3 BBSTNode rchild = node.rchild; 4 if (rchild.lchild != null) { 5 rchild.lchild.tag = 'r'; 6 rchild.lchild.parent = node; 7 } 8 node.rchild = rchild.lchild; 9 if (node == root) { 10 rchild.tag = 0; 11 node.tag = 'l'; 12 root = rchild; 13 } else { 14 switch (node.tag) { 15 case 'l' -> { 16 node.parent.lchild = rchild; 17 } 18 case 'r' -> { 19 node.tag = 'l'; 20 node.parent.rchild = rchild; 21 } 22 } 23 } 24 rchild.parent = node.parent; 25 node.parent = rchild; 26 rchild.lchild = node; 27 node = rchild; 28 }
右旋处理过程为:
a.若当前结点的左子结点存在右子,则成为当前结点的左子。(结点3存在右子结点4,所以结点4成为结点5的左子)
b.当前结点成为其左子结点的左子。(结点5成为结点3的右子)

右旋处理的定义如下:

1 @SuppressWarnings("preview") 2 public void rRotate(BBSTNode node) { 3 BBSTNode lchild = node.lchild; 4 if (lchild.rchild != null) { 5 lchild.rchild.tag = 'l'; 6 lchild.rchild.parent = node; 7 } 8 node.lchild = lchild.rchild; 9 if (node == root) { 10 lchild.tag = 0; 11 node.tag = 'r'; 12 root = lchild; 13 } else { 14 switch (node.tag) { 15 case 'l' -> { 16 node.tag = 'r'; 17 node.parent.lchild = lchild; 18 } 19 case 'r' -> { 20 node.parent.rchild = lchild; 21 } 22 } 23 } 24 lchild.parent = node.parent; 25 node.parent = lchild; 26 lchild.rchild = node; 27 node = lchild; 28 }
赫夫曼树
带权二叉树是每个结点都有一个权值的二叉树,其非叶子结点的权值为其子结点的权值之和。带权路径长度(Weighted Path Length,WPL)是指带权二叉树所有叶子结点的权值与所在层次的乘积之和。
例如,带有3个叶子结点(权值分别为:1,2,3)的带权二叉树:
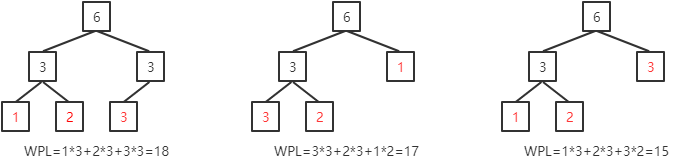
赫夫曼树是带权路径长度WPL最小的带权二叉树,也称为最优二叉树。欲使WPL最小,明显地,权值越高的结点离根结点越近,即层次越低。所以,创建赫夫曼树的思路是:把所有结点按权值排序,取出权值最小的两个结点,创建这两个结点的父结点,并将父结点放入结点集中继续排序......重复该步骤,直到结点集中只剩下一个结点,这个结点即为赫夫曼树的根结点。
赫夫曼树的结点定义如下:

1 public class Node<E> implements Comparable<Node<E>> { 2 3 int weight; 4 E value; 5 Node<E> left; 6 Node<E> right; 7 8 Node (int weight, E value) { 9 this (weight, value, null, null); 10 } 11 Node (int weight, Node<E> left, Node<E> right) { 12 this (weight, null, left, right); 13 } 14 Node (int weight, E value, Node<E> left, Node<E> right) { 15 this.weight = weight; 16 this.value = value; 17 this.left = left; 18 this.right = right; 19 } 20 21 @Override 22 public int compareTo(Node<E> o) { 23 return Integer.compare(weight, o.weight); 24 } 25 26 @Override 27 public String toString() { 28 String str = "(" + (value == null ? "" : "value: " + value + ", ") + "weight: " + weight + ")"; 29 if (left != null || right != null) { 30 str += "["; 31 if (left != null) str += left.toString(); 32 if (right != null) str += ", " + right.toString(); 33 str += "]"; 34 } 35 return str; 36 } 37 38 }
创建赫夫曼树的代码如下:

1 public static <E> Node<E> makeHuffmanTree(List<Node<E>> nodes) { 2 nodes.sort(null); 3 while (nodes.size() > 1) { 4 Node<E> n1 = nodes.remove(0); 5 Node<E> n2 = nodes.remove(0); 6 Node<E> n = new Node<E>(n1.weight + n2.weight, n1, n2); 7 int index = 0; 8 while (index < nodes.size() && nodes.get(index).compareTo(n) == -1) index++; 9 nodes.add(index, n); 10 } 11 return nodes.remove(0); 12 }
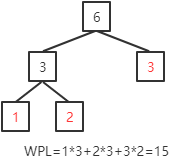
创建带有3个叶子结点(权值分别为:1,2,3)的赫夫曼树,输出结果为:

即赫夫曼树形状为:
赫夫曼编码
数据以字节(8位二进制)为单位保存。例如,字符串“abcdedcba”转换为二进制是“01100001 01100010 01100011 01100100 01100101 01100100 01100011 01100010 01100001”,长度为72。
赫夫曼编码是一种压缩存储,先统计每个字符出现的次数,然后以次数作为权值,创建结点集,从而创建赫夫曼树,再根据赫夫曼树,重新定义编码表,最后根据该编码表对原数据进行压缩存储,或解压压缩数据成原来的数据。
例如,对于字符串“abcdedcba”:
a. 统计每个字符出现的个数:
| a | b | c | d | e |
| 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 |
b. 创建赫夫曼树:
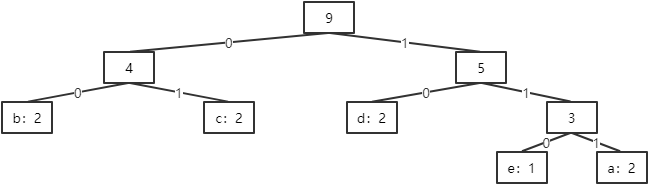
c. 定义左分支为0,右分支为1,则编码表为:
| a | b | c | d | e |
| 111 | 00 | 01 | 10 | 110 |
d. 对“abcdedcba”按照编码表压缩,结果为“111 00 01 10 110 10 01 00 111”,长度为21。
可以看到,对于“abcdedcba”,原来数据长度为72位,压缩后只需要21位。压缩率为:(72 - 21) / 72 * 100% = 70.83%。
赫夫曼编码的代码如下:
创建编码表:

1 public static Map<Byte, String> makeHuffmanCodes(byte[] datas) { 2 // 统计次数 3 int[] count = new int[256]; 4 for (byte data : datas) count[data + 128]++; 5 List<Node<Byte>> nodes = new ArrayList<Node<Byte>>(); 6 // 创建结点集 7 for (int i = 0; i < 256; i++) { 8 if (count[i] > 0) nodes.add(new Node<Byte>(count[i], (byte) (i - 128))); 9 } 10 // 创建赫夫曼树 11 Node<Byte> root = makeHuffmanTree(nodes); 12 // 定义编码表 13 Map<Byte, String> map = new HashMap<Byte, String>(); 14 map(root, "", map); 15 return map; 16 }

1 public static void map(Node<Byte> node, String s, Map<Byte, String> map) { 2 if (node == null) return; 3 if (node.value != null) { 4 map.put(node.value, s); 5 } else { 6 map(node.left, s + "0", map); 7 map(node.right, s + "1", map); 8 } 9 }
压缩:

1 public static byte[] encode(byte[] plain, Map<Byte, String> map) { 2 String s = ""; 3 for (byte data : plain) { 4 s += map.get(data); 5 } 6 byte[] cypher = new byte[(s.length() + 7) / 8]; 7 for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i += 8) { 8 cypher[i / 8] = (byte) Integer.parseInt(s.substring(i, Integer.min(i + 8, s.length())), 2); 9 } 10 return cypher; 11 }
解压:

1 public static byte[] decode(byte[] cypher, Map<Byte, String> map) { 2 String s = "", str; 3 for (int i = 0; i < cypher.length; i++) { 4 str = Integer.toString(Byte.toUnsignedInt(cypher[i]), 2); 5 if (i < cypher.length - 1) 6 for (int j = str.length(); j < 8; j++) str = "0" + str; 7 s += str; 8 } 9 str = ""; 10 List<Byte> datas = new ArrayList<Byte>(); 11 for (char c : s.toCharArray()) { 12 str += c; 13 for (byte b : map.keySet()) { 14 if (str.equals(map.get(b))) { 15 datas.add(b); 16 str = ""; 17 } 18 } 19 } 20 byte[] plain = new byte[datas.size()]; 21 for (int i = 0; i < datas.size(); i++) plain[i] = datas.get(i); 22 return plain; 23 }
赫夫曼编码除了可以对文本进行压缩解压,也可以对图片、视频、音频等文件进行压缩解压。
