title: woj1018(HDU4384)KING KONG 循环群
date: 2020-03-19 09:43:00
categories: [acm]
tags: [acm,woj,数学]
一道数学题?感觉像贪心。
1 描述
Have you seen the movie King Kong? If you have seen it, you must be impressed by the scene of the exciting fight between dinosaurs and
King Kong,right? Though the dinosaurs have been fight off, King Kong has been injured very heavily. Considering that dinosaurs will come back
very quickly, King Kong brings a lot of stones for fear that the dinosaurs attack again.
Now King Kong has arranged the stones at random in one line. But Different alignments of these stones would be different to King Kong. If the
alignment is not the target in his mind, he will move the stones to their proper positions. Taking the physical consumption into consideration,
King Kong could swap only two stones (whose weight is a and b weight units) at one time and for each time he will consume a+b thermal units.
In order to minimize the physical consumption, King Kong should set a plan to move these stones. But this is too complex for king Kong and
he needs your help.
2 输入输出
输入格式
There are several test cases. For each test case, it contains:
Line 1: One integer N (1<=N<=5000) which specifies the total number of stones.
Line 2: N integers (you are ensured that the absolute value of each integer is less than) which the weight of each stone initially. These numbers
specify the initial stone alignment. There is a blank between two consecutive integers.
Line 3: N integers (you are ensured that the absolute value of each integer is less than ) which the weight of each stone finally. These numbers
specify the target alignment in King Kong?s mind. There is a blank between two consecutive integers.The input will be ended by zero.
输出格式
Output the answer of the minimum total thermal units consumed by King Kong in the stone moving process.
3 样例
样例输入
3
3 2 1
1 2 3
3
1 2 3
1 2 3
4
8 1 2 4
1 2 4 8
0
样例输出
4
0
17
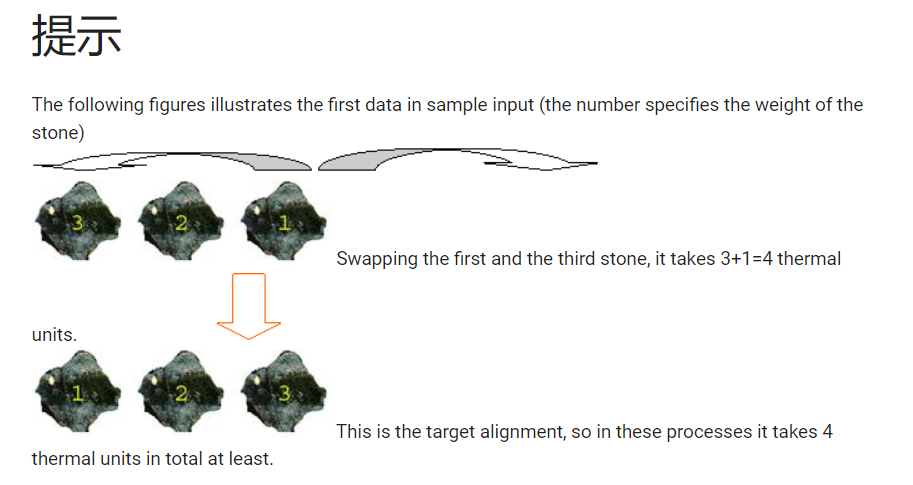
4 分析
给出两串数字,交换两个数字的代价是两数之和,问从源串到目的串的最小代价
例子 8 1 2 4-> 1 2 4 8 =17 顺序 12 14 18
思路:
不在正确位置的数至少要交换一次,贪心策略是每次交换当前不在位置的最小的数和它占据的位置的数
证明:证不出来,错了
查题解,发现用循环群?(不明白)
//直接根据目的序列找。目的序列中的数target[q]如果一开始的位置h1[target[q]]就在q,那么交换次数就是1;
否则target[q]现在不在q,找到它现在的位置h1[target[q]],target[h1[target[q]]]必然也不在位置(因为target[q]占据了这个位置)
,找到这个数的位置,如果刚好在位置q,就构成循环,交换
否则继续找,一直找到一个数刚好在q,那么刚刚找到的所有数构成一个交换的循环,
将这些数的目的位置标记为true。设这个循环有num个数,有两种交换方式使得符合要求:
1:就在num个数中交换,那么每次用循环中最小的数tpmin交换它所占据的位置的target数,交换次数为num-1,交换代价为tpmin(num-1)+循环中其他数1。
因为预处理cost += origin[i] (每个数都认为交换了一次),所以计算时cost+=(num-2)tpmin即可
2:用所有数(n个数,包括循环外的数)中的最小数minn交换,策略是先把tpmin和minn交换出来,然后把minn当成tpmin采用策略1,然后最后minn就在tpmin的目标位置,
再交换tpmin,minn。代价tpmin+min(第一次交换)+minn(num-1)+minn+tpmin+其他数*1
对于每个置换两种方案取min值相加就可以了。
从目的序列的第一个数开始寻找循环,标记sign=true,所有的sign都为true说明都到了目的位置,结束
这题也是HDU4384,2012 Multi-University Training Contest 9,(14/124)11.29% 看到一些大佬都做不出来我有一点安慰
5 code
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cstring>
#include <cmath>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int h1[65537];//存储数所在的位置
int origin[5001];//初始序列。比如origin[2]=3,说明一开始第二个位置是3
int target[5001]; // target[i] 目标序列,第i个数
bool sign[5001];//标记这个数是否移动到所想位置 目的序列第i个数是否已经到位。比如 目的12345 sign[1]=true,说明当前1已经到了第一个位置
int n, i, num, tpmin, cost, q; //cost答案 num一次交换的数量 tpmin一次交换中最小的数
int minn; //最小的数
int main()
{
//freopen("in.txt", "r", stdin);
while (scanf("%d", &n) != EOF && n != 0)
{
minn = 65538;
memset(sign, 0, sizeof(sign));
for(int i=0;i<=n;i++)
sign[i]=false;
cost = 0;
for (i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
scanf("%d", &origin[i]);
if (origin[i] < minn) minn = origin[i];
cost += origin[i];//每个数都至少要交换一次
h1[origin[i]] = i;
}
for (i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
scanf("%d", &target[i]);
}
for (i = 1; i <= n; i++)
if (!sign[i])
{
tpmin = 65538;//记录循环中最小的数 输入绝对值不大于 2^16= 65536
q = i;
num = 0;
do//直接根据目的序列找。目的序列中的数target[q]如果一开始的位置h1[target[q]]就在q,那么交换次数就是1;
//否则target[q]现在不在q,找到它现在的位置h1[target[q]],target[h1[target[q]]]必然也不在位置(因为target[q]占据了这个位置)
//,找到这个数的位置,如果刚好在位置q,就构成循环,交换
//否则继续找,一直找到一个数刚好在q,那么刚刚找到的所有数构成一个交换的循环,
//将这些数的目的位置标记为true。设这个循环有num个数,有两种交换方式使得符合要求:
//1:就在num个数中交换,那么每次用循环中最小的数tpmin交换它所占据的位置的target数,交换次数为num-1,交换代价为tpmin*(num-1)+循环中其他数*1。
//因为预处理cost += origin[i](每个数都认为交换了一次),所以计算时cost+=(num-2)*tpmin即可
//2:用所有数(n个数,包括循环外的数)中的最小数minn交换,策略是先把tpmin和minn交换出来,然后把minn当成tpmin采用策略1,然后最后minn就在tpmin的目标位置,
//再交换tpmin,minn。代价tpmin+min(第一次交换)+minn*(num-1)+minn+tpmin+其他数*1
{
sign[q] = true;
if (target[q] < tpmin)
tpmin = target[q];
q = h1[target[q]];
num++;
}while (q != i);
cost += (num - 2) * tpmin < tpmin + (num + 1) * minn ? (num - 2) * tpmin : tpmin + (num + 1) * minn;//两种方式中选择小的
}
printf("%d
", cost);
}
return 0;
}