(一)运动基础(匀速运动)
框架:1,在开始运动前,关闭之前的所有定时器。
2,if(运动到达某个位置) {则关闭定时器} else{运动}
3,距离终点足够近即可
例子:当鼠标移入侧边分享时,分享侧边栏展开;当鼠标移出侧边栏时,分享侧边栏回缩。
鼠标移入,移出时发生的行为:



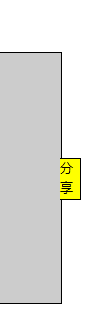
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Document</title> </head> <body> <style type="text/css"> #div1{ width: 100px; height: 250px; top: 30%; left: -100px; background-color: #CCC; position: absolute; /*开定时器必须定义绝对定位*/ border: 1px solid black; } #div1 span{ width: 20px; height: 40px; line-height: 20px; right: -20px; top: 105px; position: absolute; background-color: yellow; font-size: 13px; border-right:solid 1px black; border-top: solid 1px black; border-bottom: solid 1px black; } </style> <script type="text/javascript"> window.onload=function() { var div1=document.getElementById('div1'); var span=div1.getElementsByTagName('span')[0]; div1.onmouseover=function() { change(0); //鼠标进入侧边栏,则侧边栏展开 } div1.onmouseout=function() { change(-100); //鼠标移出侧边栏,则侧边栏回缩 } var timer=null; //定时器必须保证只开一个,每次开始一个定时器时,其他开的定时器必须关闭 function change(finish) { var speed=0; var div1=document.getElementById('div1'); clearInterval(timer); timer=setInterval(function() { if(finish>div1.offsetLeft) { speed=10; } else{ speed=-10; } //alert(div1.offsetLeft+' '+speed+' '+finish); if(div1.offsetLeft==finish) { clearInterval(timer); } else { div1.style.left=div1.offsetLeft+speed+'px'; } },30); } } </script> </body> <div id="div1"> <span>分享</span> </div> </html>
(二)缓冲运动
1,特点:速度越来越慢,最后停止;速度越来越快
2,停止:两点重合
当物体距离目标越远,速度越快;当物体距离目标越近,速度越慢,直到零。(缓冲运动时,速度必须取整,速度必须是整数,因为像素px最小单位是1,不能取小数)
当速度>0;向上取整Math.ceil(speed);当速度<0;向下取整Math.floor(speed);取绝对值Math.abs(speed)
例子:

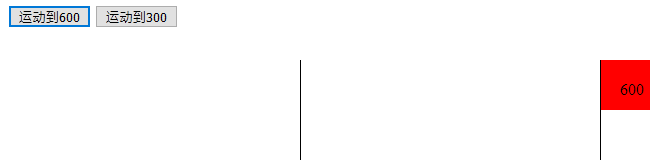
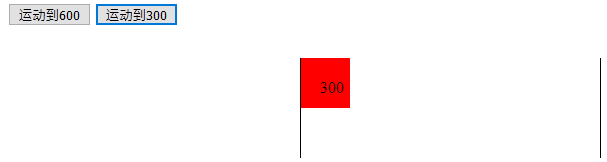
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Document</title> </head> <style type="text/css"> #div1{ width: 50px; height: 50px; position: absolute; left: 0px; top:10%; background-color: red; } #div1 span{ position: absolute; top: 40%; left: 40%; } #div2{ width: 1px; height: 100px; position: absolute; left: 600px; top: 10%; background-color: black; } #div3{ width: 1px; height: 100px; position: absolute; left: 300px; top: 10%; background-color: black; } </style> <script type="text/javascript"> window.onload=function() { var div1=document.getElementById('div1'); var div2=document.getElementById('div2'); var div3=document.getElementById('div3'); var btn1=document.getElementById('btn1'); var btn2=document.getElementById('btn2'); var span=div1.getElementsByTagName('span')[0]; btn1.onclick=function() { change(600); } btn2.onclick=function() { change(300); } var timer=null; function change(finish) { clearInterval(timer); timer=setInterval(function() { var speed=0; if(div1.offsetLeft>finish) { speed=(finish-div1.offsetLeft)/10; speed=speed>0?Math.ceil(speed):Math.floor(speed); div1.style.left=div1.offsetLeft+speed+'px'; } else{ speed=(finish-div1.offsetLeft)/10; speed=speed>0?Math.ceil(speed):Math.floor(speed); div1.style.left=div1.offsetLeft+speed+'px'; } span.innerHTML=div1.offsetLeft; },30); } } </script> <body> <input type="button" value="运动到600" id="btn1"> <input type="button" value="运动到300" id="btn2"> <div id="div1"> <span >0</span> </div> <div id="div2"></div> <div id="div3"></div> </body> </html>
(三)多物体运动
1,运动的物体不能共用一个属性和定时器,应该用object[i].属性(定时器)。
2,offsetWidth和offsetHeight获取的宽和高是(width/height+margin+padding)后的结果,当设置了margin,padding等属性后。要想改变width/height可以使用
parseInt(getStyle(object,"width/height"))获取非行间样式的weight/height。
例子:
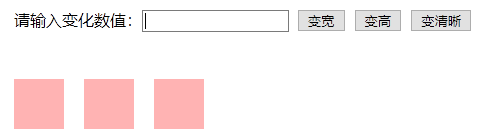



<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Document</title> </head> <style type="text/css"> div{ width: 50px; height: 50px; background-color: red; margin: 10px; float: left; filter:alpha(opacity:30); /*IE9以下低版本浏览器设置透明度为30%*/ opacity: 0.3; /*设置透明度为30%*/ } #div1{ width: 550px; height: 50px margin:10px; opacity: 1; float: none; background-color: white; } </style> <script type="text/javascript"> window.onload=function() { var oDiv=document.getElementsByTagName('div'); var aInput=document.getElementsByTagName('input'); aInput[1].onclick=function() //点击变宽 { change("width",parseInt(aInput[0].value)); } aInput[2].onclick=function() //点击变高 { change("height",parseInt(aInput[0].value)); } aInput[3].onclick=function() //点击变清晰 { change("opacity",parseFloat(aInput[0].value)); } function change(style,num) { for(var i=1;i<oDiv.length;i++) { oDiv[i].timer=null; //当多个物体共同运动时,定时器不能共用 changeDiv(oDiv[i],style,num); } } //多物体,单物体缓冲运动框架 function changeDiv(oDivn,style,finish) //对象名,变化样式,变化后的数据 { clearInterval(oDivn.timer); oDivn.timer=setInterval(function() { var speed=0; //变化速度 var oldStyle=0; //老样式数据 if(style=="opacity") //Math.round(小数)将小数四舍五入取整 { oldStyle= Math.round(parseFloat(getStyle(oDivn,style))*100); //如果是清晰度,则将获取的数据转为浮点数,可能会出现不确定的小数, if(finish>=100){finish=100;} else{finish=finish;} } else { oldStyle= parseInt(getStyle(oDivn,style)); } speed=(finish-oldStyle)/10; speed=speed>0?Math.ceil(speed):Math.floor(speed); if(finish==oldStyle){ clearInterval(oDivn.timer); } else{ if(style=="opacity") { oDivn.style.filter='alp ha(opacity:'+(oldStyle+speed)+')'; oDivn.style[style]=(oldStyle+speed)*0.01; } else{ oDivn['style'][style]=oldStyle+speed+'px'; } } },30); } //获取对象样式框架 function getStyle (obj, name) //获取对象的样式 { if (obj [ 'currentStyle']) // If we can use currentStyle get style (low version of Firefox, Google Chrome can not get, is not compatible) { return obj [ 'currentStyle'] [name]; } else { return getComputedStyle (obj, null) [name]; // get style by the function (low version IE browser can not acquire incompatible) } } } </script> <body> <div id="div1"> 请输入变化数值:<input type="text" id="text1"> <input type="button" value="变宽"> <input type="button" value="变高"> <input type="button" value="变清晰"> </div> <div></div> <div></div> <div></div> </body> </html>
(四)